GEOGRAPHY SKILLS: Understanding the Earth

GEOGRAPHY SKILLS: Understanding the Earth Chapter 1, Section 1
1.
How does the movement of the Earth around the sun affect our environment?
The movement of the Earth around the sun creates seasons.
2.
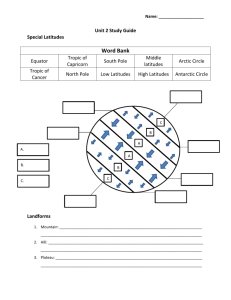
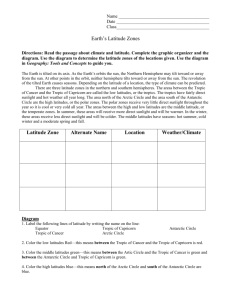
What is the effect of latitude on climate?
The latitudes closest to the Equator have warmer climates, and the latitudes closest to the North or South Poles have colder climates. surroundings environment orbit revolution axis the path the Earth takes around the sun one complete turn of the Earth around the sun (365 ¼ days) middle latitudes imaginary line from North Pole to the South Pole around which the Earth rotates rotation latitude one complete spin of the Earth on its axis; 24 hours imaginary East -> West line around the Earth low latitudes latitudes between the Tropic of Cancer and the Tropic of Capricorn; because they are near the Equator, this is a warm climate zone high latitudes latitudes between the Arctic Circle and the North Pole AND the
Antarctic Circle and the South Pole; these are cold climate zones latitudes between the Tropic of Cancer and the Arctic Circle AND the four seasons
Tropic of Capricorn and the Antarctic Circle; moderate climates with all
Equator
Tropic of
Cancer
Tropic of latitude midway between North and South Pole; largest latitude; 0 latitude at 23 latitude at 23
0
0
North
South
0
Capricorn
GEOGRAPHY SKILLS: Understanding the Earth
Arctic Circle
Antarctic latitude at 66 0 North latitude at 66 0 South
Chapter 1, Section 1
Circle rotates on axis
24 hours rotation low latitudes
Earth’s orbit of sun
Earth latitude middle latitudes affects temperature
365 ¼ days high latitudes
NUGGETS:
maize = corn
galaxy = family of stars
The sun is the largest star in our galaxy.
Our galaxy is called the Milky Way.
The sun makes up 99% of all mass in our solar system; all planets, moons, and billions of stars only make up 1% of the mass in our solar system!
The sun is 93 million miles from Earth
Sun’s effects on Earth: o
Produces light (which is needed to grow plants; photosynthesis) o
Produces warmth (otherwise we would freeze) o
Provides gravitational pull to keep us in the solar system
½ of Earth is in sunlight (facing toward the sun); ½ of Earth is always in darkness (away from sun)
The Earth’s tilt (23 0 ) and its revolution around the sun create seasons.
Earth rotates counter-clockwise around its axis.
Equinox = equal amounts of sunlight and darkness (3/21 and 9/21)
Solstice = unequal mounts of sunlight and darkness; max daylight and min darkness is Summer Solstice (6/21), and min daylight and max darkness is
Winter Solstice (12/21).
Drawings: Earth with latitude lines; seasons drawing.
_______________________________________________________
SUMMARY: The relationship between the Earth and the sun creates our days, seasons, and climate, and influences our environment.