Lab Assignment 5

Name ________________
Animal Science 320
Spring 2012
Problem Set 5
Due February 27
1.
When balancing rations in practice, usually more than two nutrients need to be considered. In this case, ingredients that aren’t being considered to balance the primary nutrient should considered to be fixed ingredients. One good example of this involves leaving space in the ration for the necessary mineral and vitamin supplements. Given the requirements below,
A.
Balance the diets for the crude protein requirements of growing pigs in the following weight ranges using corn grain and soybean meal on an as-fed basis assuming 2% fixed ingredients.
B.
Then calculate how much dicalcium phosphate is needed to meet the pigs’ phosphorus requirements
C.
Then calculate how much limestone is needed to meet the pig’s requirements for calcium
D.
Then add 0.25% salt and 0.1% trace mineral/vitamin premix on an as-fed basis.
E.
Then check the diets of adequacy of Crude protein, Lysine, Calcium, and Phosphorus.
Do all work on the following pages.
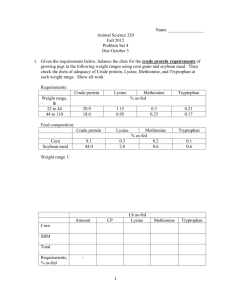
Requirements:
Lysine
% as-fed
Calcium Phosphorus
Weight range, lb
22 to 44
44 to 110
Feed composition:
Crude protein
20.9
18.0
1.15
0.95
0.7
.6
0.6
0.5
Corn
Soybean meal
Limestone
Dicalcium phosphate
Crude protein
9.1
44.0
0
0
Lysine
% as-fed
Calcium
0.03 0.3
2.8
0
0
0.3
37
22
Phosphorus
0.3
0.7
0
18
1
Weight range 1: a.
Calculate adjusted CP concentration b.
Balance Corn and SBM for adjusted CP c.
Calculate amounts of dicalcium phosphate and limestone needed and add salt and trace mineral/vitamin premix
Requirement
Total fed
100
CP
Lb, as-fed basis
Lysine Calcium Phosphorus
Corn
Soybean meal
Dicalcium phosphate
Phosphorus needed from Dicalcium phosphate
Calcium needed from Limestone
Limestone
Salt
Premix
Total
*Do not include values from shaded squares in diet totals.
2
Weight range 2: a.
Calculate adjusted CP concentration b.
Balance Corn and SBM for adjusted CP c.
Calculate amounts of dicalcium phosphate and limestone needed and add salt and trace mineral/vitamin premix
Requirement
Total fed CP
Lb, as-fed basis
Lysine Calcium Phosphorus
100
Corn
Soybean meal
Phosphorus needed from Dicalcium phosphate
Dicalcium phosphate
Calcium needed from Limestone
Limestone
Salt
Premix
Total*
*Do not include values from shaded squares in diet totals.
-
3
2.
Often some of the fixed ingredients will contribute to the primary nutrient. Therefore, their contribution must be subtracted from the requirement before balancing the primary nutrient. Although this could occur when balancing the ration for any species, a good example is considering the contribution of animal protein concentrates to the diet of growing pigs before balancing the corn and soybean meal. Given the requirements below, a.
Balance the diets for the lysine requirements of growing pigs in the following weight ranges using corn grain and soybean meal on an as-fed basis, assuming that each diet will contain 4% fish meal, 3% spray-dried animal plasma, and 1.5% other fixed ingredients. b.
Then calculate how much dicalcium phosphate is needed to meet the pigs’ phosphorus requirements c.
Then calculate how much limestone is needed to meet the pig’s requirements for calcium d.
Then add 0.25% salt and 0.1% trace mineral/vitamin premix on an as-fed basis. e.
Then check the diets of adequacy of Crude protein, Lysine, Methionine, Calcium, and
Phosphorus. Do all work on the following pages.
Requirements:
Crude protein
Lysine Methionine Calcium Phosphorus
Weight range, lb
% as-fed
22 to 44
44 to 110
20.9
18.0
1.15
0.95
.3
.25
0.7
.6
0.6
0.5
Feed composition:
Crude protein
Fish meal
Spray-dried blood plasma
62
78
Corn
Soybean meal
Limestone
Dicalcium phosphate
9.1
44.0
0
0
Lysine
4.8
6.8
0.3
2.8
0
0
Methionine
1.8
.7
.2
.6
0
0
Calcium
% as-fed
5.2
.15
0.03
0.3
37
22
Phosphorus
3.0
1.5
0.3
0.7
0
18
4
Weight range 1. a.
Adjust lysine requirement for lysine from fixed ingredients
Lb, as-fed
CP Lysine Methionine Feed intake
- - Amounts required
Fish meal
Spray-dried plasma
-
-
-
-
Other fixed ingredients
Amounts needed corn/SBM mix
-
-
-
-
Adjusted lysine concentration needed in corn/SBM mix
- -
Balance for adjusted lysine concentration in corn/SBM mix:
-
5
-
-
Ca
-
-
-
-
-
-
P
-
-
-
-
b, c, d, and e. Calculate amounts of dicalcium phosphate, limestone, salt and trace mineral/vitamin Pre-mix required and check for adequacy.
Amounts required
Total fed CP Lysine
Lb, as-fed
Methionine Ca P
Fish meal
Spray-dried plasma
Corn grain
Soybean meal
Amount of supplemental P needed from Dicalcium phosphate
Dicalcium phosphate
Amount of supplemental Ca needed from Limestone
Limestone
Salt
Premix
Total*
Requirements
-
*Do not include values from shaded squares in diet totals.
6
Weight range 2. b.
Adjust lysine requirement for lysine from fixed ingredients
CP
Lb, as-fed
Lysine Methionine
Amounts required
Feed intake
- -
- - Fish meal
Spray-dried plasma
- -
Other fixed ingredients
Amounts needed corn/SBM mix
-
-
-
-
Adjusted lysine concentration needed in corn/SBM mix
- -
Balance for adjusted lysine concentration in corn/SBM mix:
-
-
-
-
-
Ca
-
-
7
-
-
-
-
P
-
-
b, c, d, and e. Calculate amounts of dicalcium phosphate, limestone, salt and trace mineral/vitamin Pre-mix required and check for adequacy.
Amounts required
Total fed CP Lysine
Lb, as-fed
Methionine Ca P
Fish meal
Spray-dried plasma
Corn grain
Soybean meal
Amount of supplemental P needed from Dicalcium phosphate
Dicalcium phosphate
Amount of supplemental Ca needed from Limestone
Limestone
Salt
Premix
Total*
Requirements
-
*Do not include values from shaded squares in diet totals.
8
3.
Another example of fixed ingredients contributing the primary ingredient is the contribution of forage nutrients to the diet of a lactating dairy cow. This contribution must be subtracted from the requirement before balancing the primary nutrient in the grain supplement. Given the requirements below, a.
Balance the diets for the crude protein requirements of lactating dairy cows consuming 30.2 kg dry matter using corn grain and soybean meal on a dry matter basis assuming that corn silage comprises 50% of the diet dry matter and that other fixed ingredients comprise 3% of the dry matter in the grain mixture. b.
Then calculate how much dicalcium phosphate is needed to meet the cows’ phosphorus requirements. c.
Then calculate how much limestone is needed to meet the cows’ requirements for calcium d.
Then add salt and trace mineral/vitamin premix at 0.25 and 0.1% of the ration dry matter. e.
Then check the diets of adequacy of Net energy for lactation, crude protein, calcium, and phosphorus. Show all work and place answer in table on next page.
Requirements:
NE l
Mcal/kg DM Crude protein
% of DM
Calcium Phosphorus
Dairy cow
1500 lb producing 90 lb of milk containing
3.5% fat
1.68 18 0.6 0.38
Feed composition:
Corn silage
Corn grain
Soybean meal
Dicalcium phosphate
Limestone
NE l
Mcal/kg DM Crude protein
1.45
2.01
8.8
9.4
2.13
0
50
0
0 0
% of DM
Calcium
0.3
0.03
0.4
23
33
Phosphorus
0.25
0.3
0.71
18
0
9
a.
Balance grain mix for CP
DM intake
Amounts required
Corn silage kg/d
30.2
Amounts needed in grain
Concentrations needed in grain
Adjusted CP concentration of fixed ingredients
-
-
-
NE l
Mcal/d
Mcal/kg
-
-
Balance for adjusted CP concentration in grain:
CP g/d
% DM
Ca g/d
% DM
-
-
P g/d
% DM
-
-
10
b, c,d, and e. Calculate amounts of dicalcium phosphate, limestone, salt and trace mineral/vitamin Pre-mix required and check for adequacy
DM intake kg/d
NE l
Mcal/d
CP g/d
Ca g/d
P g/d
30.2 Amounts required
Corn silage
Corn grain
Soybean meal
Amount of supplemental P needed from Dicalcium phosphate
Dicalcium phosphate
Limestone
Amount of supplemental Ca needed from Limestone
Salt
Trace mineralvitamin
Premix
Total
Requirements
*Don’t include values from shaded squares in diet totals.
_
11