Calculating Time Travel
advertisement

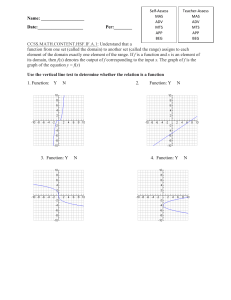
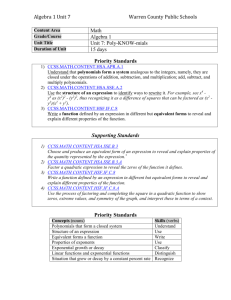
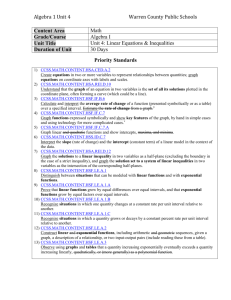
NCGA GeoMath Lesson Plan Name of Lesson Calculating Time Travel Time for Instruction 10-15 minutes Essential Question(s) What equation models time zone change? (Write equations based on GMT) Higher Order Thinking Question(s) Explain how the time zones correlate to base 12 math Common Core Standard(s) CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.HSF.BF.A.1 Write a function that describes a relationship between two quantities.* CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.HSF.BF.A.1.A Determine an explicit expression, a recursive process, or steps for calculation from a context. CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.HSF.BF.A.1.B Common Core Mathematics Combine standard function types using arithmetic operations. For example, build a function that models the temperature of a cooling body by adding a constant function to a decaying exponential, and relate these functions to the model. CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.HSF.BF.A.1.C (+) Compose functions. For example, if T(y) is the temperature in the atmosphere as a function of height, and h(t) is the height of a weather balloon as a function of time, then T(h(t)) is the temperature at the location of the weather balloon as a function of time. National Geography Objective(s) 4. The use of geographic representations to ask and answer geographic questions 8th Grade Standard 1 Therefore, the student is able to: A. Analyze geographic representations to ask and answer questions about spatial distributions and patterns, as exemplified by being able to Analyze printed and digital maps to observe spatial distributions and patterns to generate and answer geographic questions (e.g., use digital census data to determine demographic patterns in a state, or analyze census data and transportation routes to identify and locate services, such as a day-care center or stores needed in a region). Prerequisite skills/knowledge Time zones Greenwich Mean Time (GMT) Anticipatory Activity/Bellringer/Warmup Use the “Calculating Time Travel” PowerPoint to familiarize students with time zones and to illustrate the international date line. Vocabulary Mathematical Terms Geography Terms Modeling equation Function Data GMT (Greenwich Mean Time) Gaining Days Losing Days International Date Line Instructional Strategies/Sequence Using the “Calculating Time Travel” Powerpoint, students will determine the correct time based on the location of the city. Independent Practice Develop a formula based on the GMT time zone. Additional Instructional Resources Use the interactive website to calculate times between locations. http://www.zeitverschiebung.net/en/ Formative Assessment The teacher may assess student understanding by using an electronic voting system (clickers). Students will submit numeric answers for the number of hours gained or lost. Based on the class data, students should explain their mathematical calculations words. Differentiation Students will view options for modeling equations and then choose the best one for the hours between cities. Enrichment Place a copy of the world map on a sheet of cork board for each student. Students will place thumbtacks on two locations and then use a string to show the most direct route. Multiple thumbtacks may be needed if most direct route is not across the Atlantic Ocean. On the string, place markers to aid students to count the hours and/or the days lost or gained between the cities.