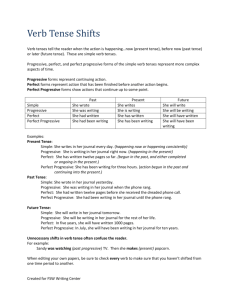
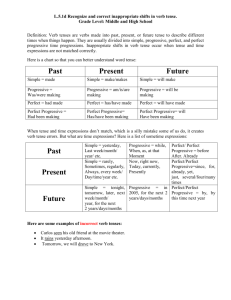
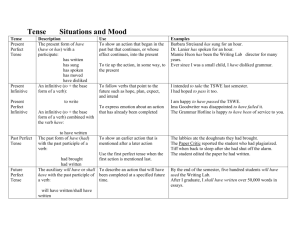
What Does Verb Tense Do?
advertisement
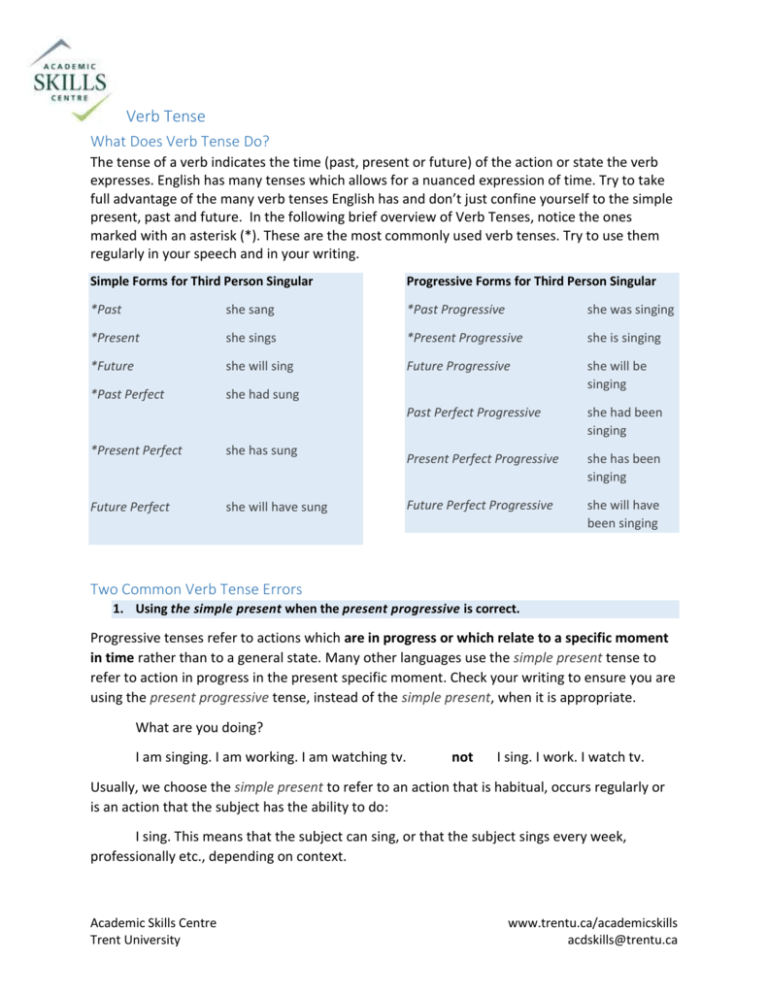
Verb Tense What Does Verb Tense Do? The tense of a verb indicates the time (past, present or future) of the action or state the verb expresses. English has many tenses which allows for a nuanced expression of time. Try to take full advantage of the many verb tenses English has and don’t just confine yourself to the simple present, past and future. In the following brief overview of Verb Tenses, notice the ones marked with an asterisk (*). These are the most commonly used verb tenses. Try to use them regularly in your speech and in your writing. Simple Forms for Third Person Singular Progressive Forms for Third Person Singular *Past she sang *Past Progressive she was singing *Present she sings *Present Progressive she is singing *Future she will sing Future Progressive *Past Perfect she had sung she will be singing Past Perfect Progressive she had been singing Present Perfect Progressive she has been singing Future Perfect Progressive she will have been singing *Present Perfect she has sung Future Perfect she will have sung Two Common Verb Tense Errors 1. Using the simple present when the present progressive is correct. Progressive tenses refer to actions which are in progress or which relate to a specific moment in time rather than to a general state. Many other languages use the simple present tense to refer to action in progress in the present specific moment. Check your writing to ensure you are using the present progressive tense, instead of the simple present, when it is appropriate. What are you doing? I am singing. I am working. I am watching tv. not I sing. I work. I watch tv. Usually, we choose the simple present to refer to an action that is habitual, occurs regularly or is an action that the subject has the ability to do: I sing. This means that the subject can sing, or that the subject sings every week, professionally etc., depending on context. Academic Skills Centre Trent University www.trentu.ca/academicskills acdskills@trentu.ca 2. Using the simple past when the present perfect is correct. Use the simple past to refer to a completed action which occurred in the past: She sang last Saturday at The Pig’s Ear. Use the simple present when referring to action which began in the past, usually the recent past, is not yet over and continues in some way into the present: She has sung at The Pig’s Ear many times this year. The above sentence indicates a period of singing which began in the recent past and which is not yet over – the sentence tells us it is still “this year”, so there is a chance that more singing will take place. If the year were over and she was not going to be singing at The Pig’s Ear anymore, the simple past would be correct: She sang at The Pig’s Ear many times last year. The present perfect tense is translated from English into many languages’ present tense. Try to understand this tense as a combination of past and present. In English, we use the present perfect tense often. When reviewing your writing, check the sentences in which you have used the simple past to see if the present perfect would be correct. Practice: Choose the correct verb tense from the following choices: simple present, simple past, present perfect, present progressive. Choose each tense only once. Put the verb in parentheses into the correct verb tense you chose for the sentence. Name the verb tense at the end of the sentence. 1. 2. 3. 4. This morning, the students (take) an exam in Room 105. Busy students often (study) late at night. The teacher (punish) him for being late yesterday morning. I (love) cats since I was a child. Answer Key 1. 2. 3. 4. The students are taking an exam in Room 105. (present progressive) Busy students often study late at night. (simple present) The teacher punished him for being late yesterday morning. (simple past) I have loved cats since I was a child. (present perfect) Academic Skills Centre Trent University www.trentu.ca/academicskills acdskills@trentu.ca