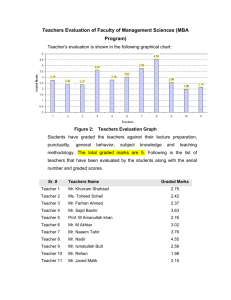
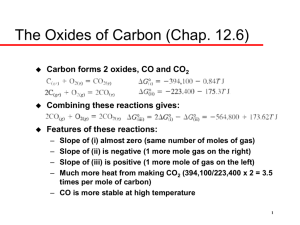
Only the answer sheet will be graded
advertisement

Version A: Instructions Midterm is worth 50 points, not including extra credit, which gives you up to 10 extra points. Put your notes away: any notes seen out during the exam will result in a failing course grade. RIGHT NOW- fill in your ID number, the bubbles and your version letter on the You’ll lose 5 points if you don’t do this on the front page of the answer sheet. answer sheet, do this now so you don’t forget. There are multiple versions of the exam. Where I changed words such as “increase” to “decrease” or numbers. If you copy, you are most likely copying the wrong answer, and makes cheating even more pointless than normal, please don’t do it. If you think someone nearby may be copying, or something is simply disturbing you, please let me know and we can adjust people’s seats appropriately. Tell me as early as possible. Be sure to sign the sign in sheet. This sheet is the record you attended the exam. If you are not sitting in your assigned seat for a reason approved by me, you’ll need to write next to your name, the seat where you are actually sitting next to your name. I know this exercise is mildly distracting during a stressful exam, but it makes sure that if your exam is lost (which I have heard horror stories of from other professors) that you have proof that you attended class. It is for your benefit!!!! You will also need to show your ID to the TA when you turn in your exam. Only the answer sheet will be graded. You may (and should) keep the exam sheet. Go home, retake it, see how you did . If you write any work on scrap paper, the question sheet or anywhere other than the space given, it will not be graded and you will not get any credit for it. Do not write on the back of the sheets, do not write anything you want graded anywhere other than the space given. I’d suggest writing in pencil or doing scratch work elsewhere and then copying over. Pace yourself, pay attention to point distribution and do your best to complete it all. Exams will be sent through eee dropbox. They will be graded the same day as you take it but the scanning department (who have nothing to do with me or the TAs) take a week to get them back to you. It will be returned to you via the dropbox (note: not the gradebook, the dropbox) the moment that I get the email allowing me to do so. Finally, relax. Take a deep breath, pick up your writing utensil and show me how amazing you are at chemistry! Long Answer Problems Problem 1: The pH of an 0.800 M aqueous monoprotic weak acid is 0.61. What is the Ka value for the acid? 0.11 Problem 2: (sig figs graded for a and b) Calculate the volume required of 0.255 M HCl to neutralize (a) one half and (b) all the hydroxide ions in 25.0 mL of 0.305M KOH. C) what is the pH at equivalence point? a) 15.0 mL, b) 29.9 mL c) 7 Problem 3: (sig figs graded for a and b) Suppose that 5.25g of an unknown monoprotic weak acid, HA, is dissolved in water (1.00L). To reach the equivalence point, 52.0mL of 0.350 M NaOH was used. After the addition of 26.0 mL, the pH of the solution was found to be 3.02. a) State how many moles of acid were added initially b) what is the molar mass of the acid? c) what is the value of pKa for the acid? d) What is the pH at the equivalence point(assume that auto ionization of water assumption is valid)? a) 0.0182 mol b) 288 g/mol c)3.02 d) 7.64 Problem 4: A 100 mL buffer solution is 0.100M Acetic Acid (CH3COOH) and 0.100M Sodium Acetate. Calculate the pH if a) 0.05 moles of NaOH is added to the solution b) calculate the pH of 0.04 moles of HCl is added to the solution. c) calculate the pH of 0.150 mols of NaOH is added to the solution. Assume no change in volume. 5.22, 4.37, 14.15 Problem 5: CHOOSE ONLY ONE: IF YOU ANSWER BOTH YOU WILL RECEIVE A ZERO Explain how our body regulates pH through respiration. Be specific! Not everything here was needed to get all three points, but a majority of it was: CO2 is a lewis acid and becomes HCO3 when dissolved in water. Because carbonic acid is a weak acid it creates an equilibrium with HCO3-. This creates a buffer system that the body can control by taking in or expelling CO2. We are able to regulate the CO2 levels thanks to hemoglobin in the blood. This bonds to either O2 or H+. Note: It is NOT that CO2 is and acid and O2 is a base. This was a super common answer that was not correct. While the balance of CO2 and O2 is important, its because this is one of the ways the body regulates the amount of CO2, not that the O2 balances the pH directly. OR Explain how acid rain occurs, and one way to reverse the effect. Acid rain occurs when nitrogen and sulfur oxides are released into the environment due to industrial applications, cars ect….These are formed under the high heats and pressures in the pollution creating system. These nitrogen and sulfur oxides are lewis acids, and turn into nitric and sulfuric acid when they come in contact with water, such as in clouds. When the clouds release the rain, the acid is trapped in the system and falls along with the rain. One way we discussed in class that this can be reversed, is in lakes, we can add CaCO3 (which is also called lime, no relation to the fruit!!!!) into lakes. The CO3 acts as a base, helping to fix the pH of the lake. This is only temporary and wouldn’t work in a system like the ocean which is far too large. There are other acceptable answers for the reversal as well, but this is the discussed one. Note: Many people mentioned something along the lines of high heats and pressures in the atmosphere creating the nitrogen and sulfur oxides. This is not at all true. The atmosphere is actually quite cold and low pressure (this is why hikers on tall mountains like Everest are always in cold weather gear and oxygen masks). The high heats and pressures are in the industrial applications/cars. This creates the oxides which then are released into the environment. The atmospheric part is that that nitrogen oxide forms nitrogen dioxide which is a lewis acid. Then the nitrogen and sulfur oxides are both lewis acids and can form HNO3 and H2SO4, which are strong acids. Second note: CO2 does not significantly contribute to acid rain. While there is CO2 in the air, and this does become detrimental to the environment for other reasons (global warming due to it having an induced dipole and absorbing cosmic rays and turning it into heat), it doesn’t change the pH of the rain to a dangerous level. Typical rain water that has no pollution in it will have a pH of 5.7, while this is a little acidic, it is natural and the plants and animals have evolved for this. HCO3 is a weak acid, so it doesn’t affect the water’s pH to detrimental levels. Because the nitric and sulfuric oxides form strong acids, they affect the pH to a much greater extent, causing the “acid rain” that actually is harmful to the environment, statues, buildings ect….. Problem 6 MUST SHOW ALL WORK SHOWING THAT YOU STARTED WITH THE SLOW REACTION RATE LAW TO GET CREDIT. Short Answer (SEE ATTACHED PICTURE) 1. Give the molecular formula for the conjugate acid of HSO3- 2. Give the molecular formula for the conjugate base of HSO3- ********************************************************* 5) Assume equal concentrations for these aqueous solutions and rank from LOW to HIGH pH value. Also assume the concentration is below the solubility point for each substance given. NH3, HNO3, LiOH, HCN, Sr(OH)2 ******************************************************** Use the following reaction to answer questions 3-4. 3) Which species is the conjugate acid? 4) Which species is the acid? 6) Find the concentration of [OH-], in a 0.40M solution of HCl.(sig figs graded) 7) Determine the percent ionization of a 1.00 M solution of acetic acid. 8) Find the pH if you combine 0.03 mols of Ca(OH)2, 0.04 mols HCl in 2.5 L water. Assume all Ca(OH)2 is soluable. Report to 1 decimal point. 14) HCOONH2(CH3)2: 15) KClO: 16) NaHSO4: 17) NH4Cl: 9) If the auto dissociation of water is endothermic, what will happen to Kw if the temperature is raised (increase, decrease or not change)? (Hint autodissociation means H2O ⇋ H++OH-) 18) NaHSO3: ------------------------------------------------------------------If water is heated to 200oC and placed under 750 atm of pressure it has a Kw of 1.5x10-11, 19) find [H3O+] of water under these conditions. 10) What is the pKa of the conjugate acid of (CH3)2NH, given that the pKb is 3.97 at a given temperature? 20) is it acidic, basic or neutral? -------------------------------------------------------------------- 11) What is the reaction that is described by Ka2 of phosphorous acid? 21) What is the Ksp for the compound MA3, if the molar solubility is 7.0 x 10-6 M? 12) What is the pH of an aqueous solution that is 0.4M HF and 0.015 M NaF? 22) The Ksp of Ca(OH)2 is 5.02x10-6, what is the solubility of Ca(OH)2 in 0.3M CaCl2? 13) Given the following acids and their pka rank in DECREASING order of acidity. (aka from strong acid to weak acid): H3PO3 = 1.3 H2PO3- = 6.7 H2SeO3 = 2.62 HSeO4- = 8.32 If you mix equal volumes of the following solutions, will you form a buffer? ------------------------------------------------------------------ 24) NH3 and NaOH For each of the following, state whether an aqueous solution would be acidic, neutral or basic. 23) NH3 and NH4+ 25) 0.1 M H3PO3 and 0.1M HPO3226) 0.1 M HPO4- and 0.1 M PO42*************************************************** The titration curve for the titration of 0.100 M Na2CO3(aq) with 0.100 M HClO4(aq) is shown below. Use the curve to answer the following questions. What are the main specie(s) present after the following volumes of HClO4 are added: (you do not have to include spectator ions) 27) 10 mL 28)25 mL ******************************************************** 32) Write the rate law for the following reaction given the mechanism shown. 29) 35 mL 30) 50 mL 31) Estimate pka1? Step 1: Slow Step 2: Fast 33) Determine the average reaction rate from 136-272 seconds. Assume first order in A