Introduction to cell notes With answers Which scientist used the term
advertisement

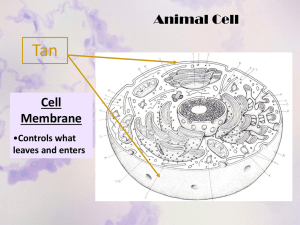
Introduction to cell notes With answers Which scientist used the term “cell” after viewing cork under a microscope? Robert Hook What did Anton van Leeuwenhoek see that nobody had seen before? Living cells and microorganisms What is the cell theory? o All living things are made up of cells o Cells are the basic units of structure and function in an organism o New cells are produced from existing cells What are the levels of organization in a multicellular organism? Cellstissueorganorgan systemorganism What is cell differentiation? Cells become specialized in structure to perform different tasks (jobs) List 3 examples of specialized cells in the human body. o Red blood cells, white blood cells o Muscle (3 types), nerve o Bone Prokaryote Cell Type Nucleus? No nucleus. Organelles? No membrane bound organelles Ribosomes? Small ribosomes Larger ribosomes Size? 1-10 µm 2-1000 µm Evolved when? 3.5 billiion years ago 1.5 billion years ago Kingdoms? Archaebacteria and Eubacteria Protista, fungi, plantae, and animalia Basic structure (draw basic cell) Eukaryote Membrane bound nucleus present Many Shapes of bacteria? (sketch and name each) o Coccus/cocci (spherical) o Bacillus/bacilli (rod shaped) o Spirilla (spiral) What do all cells have in common? o o o o Cell membrane Cytoplasm Ribosomes Genetic material Parts of plant cells (draw arrows) Cytoplasm Endoplasmic reticulum Nucleus Chloroplast Central vacuole Golgi body Ribosomes Mitochondria Cell membrane Cell Wall Parts of animal cells: (draw arrows) Cell membrane Mitochondria Ribosome Golgi body Nucleus Cytoplasm Endoplasmic reticulum Lysosome Functions/description of organelles: Plant? Animal? Both? Organelle Function/description Cytoplasm Semi-liquid material between nucleus and cell membrane Both (all cells) Nucleus Controls cell processes, contains genetic material Both Chloroplast Plants only Central vacuole Photosynthesis takes place here. Captures light energy and converts it into chemical energy in sugar Stores water, salts, ions, and minerals. Ribosomes Manufacture proteins (from DNA’s instructions) Both (all cells) Plants only. (animals have many small vacuoles) Mitochondria Cell membrane Cell wall Golgi body Endoplasmic reticulum Lysosomes Cellular respiration takes place here. Converts chemical energy into useable energy (ATP) for the cell. Creates a barrier around cell that controls what enters and leaves the cell…maintains cellular homeostasis. Cellular support Outer layer that supports and provides protection. Modifies, packages, sorts, and ships proteins from the ER and other materials to be stored in cell or secreted from cell. “post office” Site where lipids for cell membrane are assembled, proteins are modified prior to export from cell. Digestion of biomolecules and breaking down worn out cellular parts Both Both (all cells) Plant Both Both Animals