HEAT TRANSFER

H
EAT
T
RANSFER
Thermal energy is the energy of motion of the particles of a substance.
You recognize thermal energy as heat when it is transferred from one substance to another.
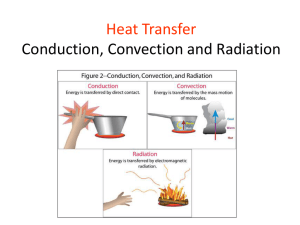
Heat is energy that is transferred between two objects or substances of different temperatures; heat typically flows from a warmer material to a cooler material. Generally, when heat is transferred to a material, the motion of its particles speeds up and its temperature increases. There are three methods of heat transfer: radiation, conduction, and convection .
Radiation transfers energy by electromagnetic waves, a method in which heat can transfer even through empty space (through outer space, for example).
Electromagnetic waves are a form of energy such as visible light, ultraviolet light, infrared light and X-rays.
When electromagnetic radiation strikes an object, the energy carried by the electromagnetic wave is transferred to the object, causing the particle motion within the object to increase, or get hot. The reason that you can feel the warmth of an object at a distance, such as from the Sun, is due to the transfer of heat by radiation. Solar radiation is the energy given off by the sun that travels through space as electromagnetic waves. When solar energy reaches the ground, some of the energy (heat) is absorbed and makes the ground hotter.
Conduction transfers heat through direct contact. If two objects are placed in contact with each other, heat flows from the warmer object (with faster-moving particles) to the cooler object (with slower-moving particles) by the direct interaction of the particles. During the day, the surface of the Earth absorbs energy from sunlight and becomes warmer than the air touching it. When the cooler air touches the warmer ground, some of the heat is transferred to the air. The air becomes warmer and the ground will become cooler as the heat is transferred.
Convection transfers heat through the movement of fluids or gases in a circular motion. A gas is matter that has no definite shape or volume. A gas, like air, will take the shape of its container. A pot of water heated on a stove provides an example of convection. The pot itself, and then water at the bottom, becomes heated by conduction.
When water is heated, it expands, becomes less dense, and rises up through the surrounding cooler water. The cooler, denser water then sinks to the bottom of the pot where it, in turn, is heated. The convection current—the circulating path of hot water rising and cold water sinking—transfers heat by actually moving the warmer water to a new area.
You can see this by looking at the boiling of the water.
H
EAT
T
RANSFER
Thermal energy is the energy of motion of the particles of a substance.
You recognize thermal energy as heat when it is transferred from one substance to another.
Heat is energy that is transferred between two objects or substances of different temperatures; heat typically flows from a warmer material to a cooler material. Generally, when heat is transferred to a material, the motion of its particles speeds up and its temperature increases. There are three methods of heat transfer: radiation, conduction, and convection .
Radiation transfers energy by electromagnetic waves, a method in which heat can transfer even through empty space (through outer space, for example).
Electromagnetic waves are a form of energy such as visible light, ultraviolet light, infrared light and X-rays.
When electromagnetic radiation strikes an object, the energy carried by the electromagnetic wave is transferred to the object, causing the particle motion within the object to increase, or get hot. The reason that you can feel the warmth of an object at a distance, such as from the Sun, is due to the transfer of heat by radiation. Solar radiation is the energy given off by the sun that travels through space as electromagnetic waves. When solar energy reaches the ground, some of the energy (heat) is absorbed and makes the ground hotter.
Conduction transfers heat through direct contact. If two objects are placed in contact with each other, heat flows from the warmer object (with faster-moving particles) to the cooler object (with slower-moving particles) by the direct interaction of the particles. During the day, the surface of the Earth absorbs energy from sunlight and becomes warmer than the air touching it. When the cooler air touches the warmer ground, some of the heat is transferred to the air. The air becomes warmer and the ground will become cooler as the heat is transferred.
Convection transfers heat through the movement of fluids or gases in a circular motion. A gas is matter that has no definite shape or volume. A gas, like air, will take the shape of its container. A pot of water heated on a stove provides an example of convection. The pot itself, and then water at the bottom, becomes heated by conduction.
When water is heated, it expands, becomes less dense, and rises up through the surrounding cooler water. The cooler, denser water then sinks to the bottom of the pot where it, in turn, is heated. The convection current—the circulating path of hot water rising and cold water sinking—transfers heat by actually moving the warmer water to a new area.
You can see this by looking at the boiling of the water.