Name:Chapter 11 Study GuideMods: Word Definition Heredity
advertisement

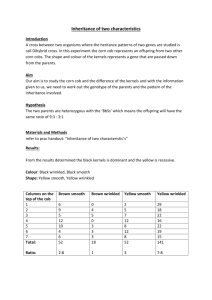
Name: Chapter 11 Study Guide Word Mods: Definition Heredity Monohybrid Cross A cross for two traits. Form of the trait that is observed in AA or Aa genotypes Recessive . F1 Generation An alternative form of a single gene 2 of the same alleles (AA or aa) for a trait Heterozygous (hybrid) An organisms pair of alleles Phenotype The offspring from a second cross Recessive Genetic Disorders Dominant Genetic Disorders Codominance Incomplete Dominance Carrier Sex-linked Disorder Name: Chapter 11 Study Guide Mods: 1. Individual II-1 is a __________________. 2. If individual III-2 marries a person with the same genotype as individual I-1, what is the chance that one of their children will be afflicted with hemophilia? ______________ (Hint: draw a punnett square with the genotypes of the parents) 3. What is the relationship between individual I-2 and III-1? ______________________ 4. If a female rabbit heterozygous for yellow eyes (XRXr ) is crossed with a red-eyed male (XrY), what percent of their offspring would have red eyes? ____________________ 5) A cross between a white flower and a red flower results in 100% pink flowers. When two of these pink offspring are mated, the probable phenotypic ration seen in their offspring would be __________. 6. A phenotype that results from a dominant allele must have at least ______ (number) dominant allele. 7.) A woman heterozygous for blood type B marries a man who is heterozygous for blood type A. The chance of their first child having type O blood is ______________. Name: Chapter 11 Study Guide Mods: 8.) When the offspring from a first cross (F1 generation) self-fertilize, the resulting offspring is called the ___________ generation. 9.) A man who has Cystic Fibrosis marries a woman whose father also had the same disease. The probability that their children will have Cystic Fibrosis is ______________ percent. 10.) Fill in the Roman numerals and number each individual in the pedigree. Write the genotype for each individual using the letter “A” as the allele for the trait shown. Identify the following pedigree as simple recessive, or simple dominant. 12. Background Information: Trait Dominant Recessive Plant Height Tall (T) Short (t) Pod Shape Smooth (S) Wrinkled (s) Pod Color Yellow (Y) Green (y) Seed Coat Gray (G) White (g) Write down the phenotypes for each of the following genotypes. a. SS ________________________________________________ b. Yy ________________________________________________ Name: Chapter 11 Study Guide Mods: c. Gg ________________________________________________ d. Tt ________________________________________________ e. TtGg ________________________________________________ f. SSyy ________________________________________________ g. yyTT ________________________________________________ 2. Write down the possible genotypes for each of the possible phenotypes. a. Smooth pods ________________________________________________ b. Green pods ________________________________________________ c. Tall plants ________________________________________________ d. Tall plant and Green pods ________________________________________________ e. Wrinkled and short ________________________________________________ f. Gray seeds and smooth pods ________________________________________________ 3. Use a punnett square to complete the following cross. YyTt and yyTt . What are the genotype and phenotype ratios? Name: Chapter 11 Study Guide Mods: Monohybrid cross: Cross a heterozygous round seeded plant with a homozygous round seeded plant. Wrinkled is the recessive trait. What are the phenotypes and genotypes of the possible offspring? Incomplete Dominance: When a red flower and a white flower are crossed, the resulting offspring are pink. Cross a red flower with a pink flower. What are the genotypic and phenotypic ratios? Name: Chapter 11 Study Guide Mods: Codominance: When a white cow and a brown cow are crossed, the resulting offspring is a roan (white and brown) cow. Create a punnett square that demonstrates this fact. Multiple Alleles: A man with A blood type (heterozygous) has a child with a woman with B blood type (heterozygous). Their child has O blood. Create a punnett square proving this is possible.