lab for relative time
advertisement
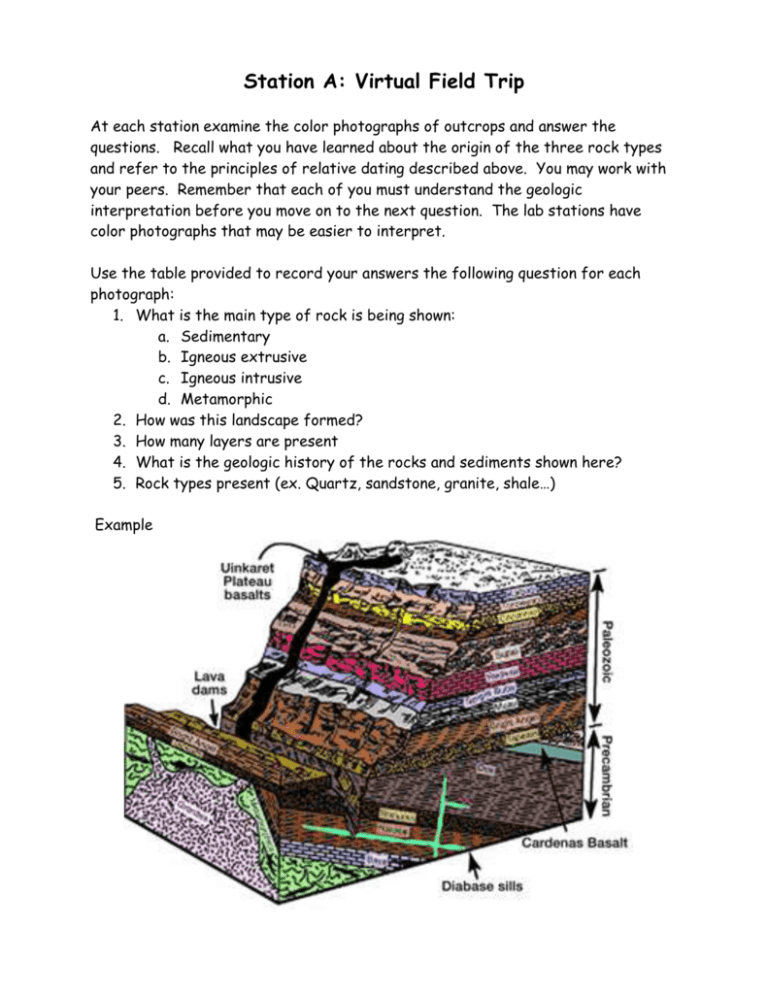
Station A: Virtual Field Trip At each station examine the color photographs of outcrops and answer the questions. Recall what you have learned about the origin of the three rock types and refer to the principles of relative dating described above. You may work with your peers. Remember that each of you must understand the geologic interpretation before you move on to the next question. The lab stations have color photographs that may be easier to interpret. Use the table provided to record your answers the following question for each photograph: 1. What is the main type of rock is being shown: a. Sedimentary b. Igneous extrusive c. Igneous intrusive d. Metamorphic 2. How was this landscape formed? 3. How many layers are present 4. What is the geologic history of the rocks and sediments shown here? 5. Rock types present (ex. Quartz, sandstone, granite, shale…) Example A Black Tusk, Garibaldi Park BC A B Giant’s Causeway, Ireland 2 C Gravel Pit D Limestone Quarry 3 E Guilin Twin Peak F Banff, Rocky Mountains 4 G Grand Canyon Notice the two series of sedimentary rocks: the Grand Canyon Series occurs in the lower right of the photograph and is dipping towards the right. The Paleozoic series is flat-lying and lies above the Grand Canyon series H Cardinal Mountains 5 H Mountain Beltway, Difficult Run Mtn I Tepui Table Top Mountains, Venezuela 6 J Hoodoos, Alberta K Petite Saleve, Geneva 7 8 Station B: Key of Standard Lithological Symbols Geologic maps and illustration use standard symbols to represent specific rock types. Understanding these lithology or rock symbols is essential to interpreting geologic maps and graphics. 9 Lithology Lab Worksheet Copy the symbols from the guide onto your lab worksheet. Rock type Symbol Rock type Sedimentary rock Limestone Metamorphic rock Erosional contact Igneous rock Fault Sandstone Alluvium Conglomerate 10 Symbol Station C: Relative Dating Comic Strip In the following diagrams, number the formation of the units or features in their correct chronological order. Write a comic strip that describes the formation of the different layers. Example Cartoon A “E was lying on the river side, quiet peacefully when a landslide came along and completely covered him. At first he really didn’t like G, but then a river flooded, bring along L who was really loud and annoying, so G really didn’t seem that bad after all. For hundreds of years the three of them lay there wondering if they would ever be dug up when a huge earthquake caused liquefaction and all the animals nearby died. As they decayed, the layers of their bones formed layer C…” Be sure to use the letter of the oldest unit on the bottom of the list and letter of the youngest unit on the top and fill in the rest appropriately. You can write the cartoon strip as a story (text only), or you may use the comic strip outline (with text and pictures) provided at the station. Example E was lying on the river side, quiet peacefully when a landslide came along and completely covered him. At first he really didn’t like G, but then a river flooded, bring along L who was really loud and annoying, so G really didn’t seem that bad after all. For hundreds of years the three of them lay there wondering if they would ever be dug up when a huge earthquake caused liquefaction and all the animals nearby died. 11 As they decayed, the layers of their bones formed layer C 12 Cartoon B. Cartoon C. 13 Cartoon D. ____ Hints: N refers to the time the house was built. Fault T cuts Formation A. 14 Station D: Reconstruction of Geologic History Looking at the structures and rock relationships in the following diagrams, reconstruct a plausible geologic history or sequence of events. Describe the geologic events that must have occurred in the correct chronological order to create the picture in the diagram. Use a list format. Geologic History Diagram A Sequence of events for diagram A: (List oldest event first.) 1) Metamorphism of rock Formation A 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) Geologic History Diagram B Sequence of events for diagram B: (List oldest event first.) 1) Deposition of rock Formation A 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) 8) 9) Geology 2/Labs/Time/Lab #8 time.doc/LTS 10/06/06 15







