Document
advertisement

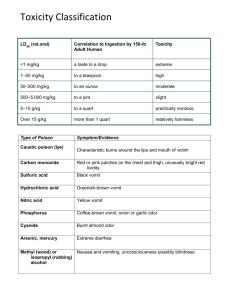
Cerbera Odollam a.k.a Suicide Tree Plant Toxin Reported by: Ruedas, Laurence N. and Teñido, Christene Q. Cerbera Odollam Cerbera Odollam Kingdom: Plantae Phylum/Division:Magnolio phyta Class: Eudicots Order: Gentianales Family: Apocynaceae Genus: Cerbera Species: C. odollam Common Names: Pong Pong Tree Status: Vulnerable Cerbera odollam commonly known as the Suicide tree, Pong-pong, and Othalanga, is a species of tree native to India and other parts of Southern Asia. It grows preferentially in coastal salt swamps and in marshy areas. It grows wild along the coast in many parts of Kerala, India and has been grown as a hedge between home compounds. Cerbera odollam tree is known by a number of vernacular names depending on the region. othalanga maram in the Malayalam language used in Kerala, India kattu arali in the adjacent state of TamilNadu famentana, kisopo, samanta or tangena in Madagascar pong-pong, buta-buta,bintaro or nyan in Southeast Asia. TOXICITY The kernels of C.odollam contain cerberin, a potent alkaloid toxin The poison blocks the calcium ion channels in heart muscle, causing disruption of the heart beat. This is most often fatal. Cerberin is difficult to detect in autopsies and its taste can be masked with strong spices. TOXIN Cerberin- C32H48O9 3β-(2-O-Acetyl-3-O-methyl-6-deoxy-α-Lglucopyranosyloxy)-14β-hydroxy-5β-carda20(22) CERBERIN Cerberin is a cardiac glycoside, a substance that blocks electric impulses in the body (including the beating of the heart). It is found in the leaves and the fruits of plants in the genus Cerbera. Cerbera Manghas Cerbera Tanghin SYMPTOMS Within an hour: retching, nausea, vomiting and abdominal pain occur After few hours: - patient becomes weak and drowsy and may lapse into coma - Bradycardia arrhythmia is the most obvious finding. TREATMENT Management consists of the elimination of unabsorbed poison by stomach wash, purgatives, bowel wash and correction of bradyarrhythmias by intravenous atropine (0.5 mg). TREATMENT In severe cases, the drug has to be repeated even at 15 minutes intervals or it has to be administered as a continuous drip. When bradycardia is not corrected by atropine, the patient may require cardiac pacing. Cerbera Odollam ~Making the History~ In 2004, a team led by Yvan Gaillard of the Laboratory of Analytical Toxicology in La Voulte-surRhône, France documented more than 500 cases of fatal Cerbera poisoning between 1989 and 1999 in the south-west Indian state of Kerala alone. The seeds also have a long history as a poison in Madagascar. The poison was responsible for the death of 2% of the population (3000 people per year, 50,000 per generation) of the central province of Madagascar. References • • • • • • • • • • http://io9.com/5841540/10-of-the-worlds-deadliest-plants-++-and-how-theykill-you http://www.newscientist.com/article/dn6701-suicide-tree-toxin-is-perfectmurder-weapon.html http://www.bukisa.com/articles/180170_cerbera-odollam-a-killer-tree-but-aboon-to-the-human-society http://rmbr.nus.edu.sg/dna/organisms/details/302 http://www.chemicalbook.com/ProductChemicalPropertiesCB51345307_EN .html http://www.drugsandpoisons.com/2008/01/cerberin-to-hell-and-backagain.html http://www.wisegeek.com/what-is-cerbera.html Article Source: http://EzineArticles.com/5875777 http://ezinearticles.com/?The-Negative-Effect-of-Cerbera-Odollam-As-aCommon-Poison&id=5875777 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15507323