Biology Notes: Cell Theory & Microscopes
advertisement

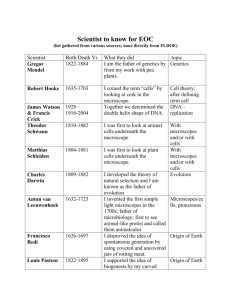
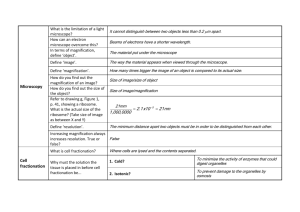
Biology Chapter 7.1 Notes-Microscope Chapter 7.1 Voc word List (include people): People: Robert Hooke, Anton van Leeuwenhoek, Mathias Schleiden, Theodor Schwann Voc. Words: Compound Light Microscope, Scanning Electron Microscope, Transmission Electron Microscope, Scanning Tunneling Microscope, Cell theory, Prokaryotes, and Eukaryotes Section 7.1: The Discovery of Cells Cell Theory History/Microscopes Before microscopes people believed that diseases came from curses and supernatural spirits. When microscopes were invented scientists found cells and microorganisms Simple Light Microscope-one lens microscope Robert Hooke developed a gold-embossed leather case in 1665 for a simple compound microscope o English scientist o He looked at cork cells (dead oak tree bark) and observed and drew the structures he saw o He called the structures- cells Anton van Leeuwenhoek designed and used simple light microscope in the late 1600’s –early 1700’s o Dutch scientist o By 1700 he developed 240 single-lens versions o He was the first to discover and describe red blood cells and bacteria and is often credited as the invention of a microscope-invented many years before his birth Mathias Schleiden was a German scientist that studied a variety of plants under the microscope in the 1830’s and determined that all plants are made of cells Theodor Schwann was another German scientist that studied a variety of animal cells and determined all animals are made of cells Microscopes were developed over the next 200 years with series of lenses to magnify objects 1 Compound Light Microscope- Uses light and more than one lens to look at living cells (Can magnify up to 1500 times) 2 Scanning Electron Microscope- (SEM) sweeps a beam of electrons over the surface of the specimen causing electrons to be emitted from the specimen (3-D realistic pictures with magnification up to 20,000 times) 1 3 Transmission Electron Microscope-(TEM) aims a beam of electrons through a specimen Invented and developed in the 1930’s-1940’s Makes 2-D images Denser portions are darker Used to study details of cells Magnification up to hundreds of thousands times 4 Scanning Tunneling Microscope-(STM) invented in the 1980’s and revolutionized microscopy because scientists were able to see atoms on the surface of an object A very fine metal probe is place near the object. Electrons flow between the tip of the probe and the atoms on the surface of the specimen Can see objects such as DNA molecules A computer makes the 3-D image Magnification can reach 100 million times Cell Theory 1 All organisms are composed of one or more cells 2 The cell is the basic unit of structure and organization of organisms 3 All cells come from preexisting cells Two basic types of cells o All cells contain specialized parts known as organelles Many organelles are protected with membranes Each organelle as a specific function in the cell 1 Prokaryotes a. These cells do not contain membrane bound organelles b. Their nucleus is incomplete c. Parts include: cell wall, one strand of DNA, plasma membrane, cytoplasm, ribosomes d. These cells are 0.001 mm to 0.1 mm in size e. Usually unicellular bacteria 2 Eukaryotes a. These cells do contain membrane bound organelles 2 b. Most organisms with this type of cell are multicellular but a few like the amoeba and some algae are unicellular c. Parts include: Plasma membrane, cytoplasm, complete nucleus with chromosomes, nucleolus, and organelles d. These cells are 0.01 mm to 0.1 mm in size 3