HW Set 12: Chap 4
advertisement
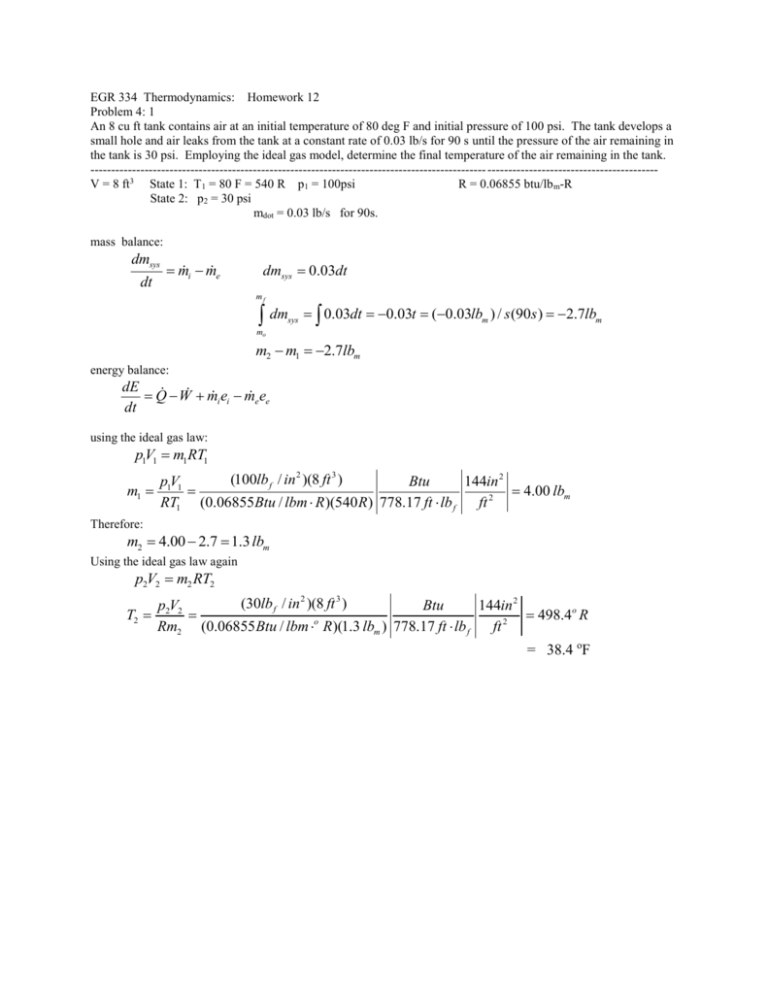
EGR 334 Thermodynamics: Homework 12 Problem 4: 1 An 8 cu ft tank contains air at an initial temperature of 80 deg F and initial pressure of 100 psi. The tank develops a small hole and air leaks from the tank at a constant rate of 0.03 lb/s for 90 s until the pressure of the air remaining in the tank is 30 psi. Employing the ideal gas model, determine the final temperature of the air remaining in the tank. ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ----------------------------------------V = 8 ft3 State 1: T1 = 80 F = 540 R p1 = 100psi R = 0.06855 btu/lb m-R State 2: p2 = 30 psi mdot = 0.03 lb/s for 90s. mass balance: dmsys dt mi me dmsys 0.03dt mf dm sys 0.03dt 0.03t (0.03lbm ) / s (90s ) 2.7lbm mo m2 m1 2.7lbm energy balance: dE Q W mi ei me ee dt using the ideal gas law: p1V1 m1RT1 m1 (100lb f / in 2 )(8 ft 3 ) p1V1 Btu 144in 2 4.00 lbm RT1 (0.06855Btu / lbm R )(540 R ) 778.17 ft lb f ft 2 Therefore: m2 4.00 2.7 1.3 lbm Using the ideal gas law again p2V2 m2 RT2 (30lb f / in 2 )(8 ft 3 ) p2V2 Btu 144in 2 T2 498.4o R Rm2 (0.06855Btu / lbm o R)(1.3 lbm ) 778.17 ft lb f ft 2 = 38.4 oF EGR 334 Thermodynamics: Homework 12 Problem 4:6 The figure shows a mixing tank initially containing 3000 lb of liquid water. The tank is fitted with two inlet pipes, one delivering hot water at a mass flow rate of 0.8 lb/s and the other delivering cold water at a mass flow rate of 1.3 lb/s. Water exits through a single exit pipe at a mass flow rate of 2.6 lb/s. Determine the amount of water in the tank after1 hr. -----------------------------------------------------------------------------mi = 3000 lbm of H2O m1 = 0.8 lbm/s m2 = 1.3 lbm/s m3 = 2.6 lb/s Mass balance: dm mi me dt dmsys m1 m2 m3 dt dmsys (m1 m2 m3 )dt t 1hr mf dm sys mi (m1 m2 m3 )dt t 0 m f mi (m1 m2 m3 )t m f (m1 m2 m3 )t mi m f (0.8lb f / s 1.3lb f / s 2.6lb f / s)(1hr ) 3600 s 3000lb f 1200lb f hr EGR 334 Thermodynamics: Homework 12 Problem 4:11 As shown in the figure, air with volumetric flow rate of 15000 cu ft/min enters an air handling unit at 35 deg F, 1 atm. The air handling unit delivers air at 80 deg F, atm to a duct system with three branches consisting of two 26 in diameter ducts and one 50 in duct. The velocity in each 26 in duct is 10 ft/s. Assuming ideal gas behavior for the air, determine at steady state a) the mass flow rate of air entering the air handling unit in lb/s. b) the volumetric flow rate in each 26 in duct in cu. ft/min. c) the velocity in the 50 in duct in ft/s. ---------------------------------------------------------------------Air: R = 0.06855 btu/lbm-R State 1: p1 = 1 atm T1 = 35 deg F= 495 R V1dot = (AV)1= 15000 ft3/min State 2, 3, and 4: p2=p3=p4 = 1 atm T2 = T3=T4 = 80 deg F.= 540 R V2 = V3 = 10 ft/s Assume Ideal Gas Law: p1V1 m1RT1 as a rate equation p1 V1 m1 RT1 m1 m1 p1 V1 RT1 2 (1atm)(15000 ft 3 / min) 14.7lb f / in 1btu 144in2 1202lbm / min (0.06855btu / lbm R)(495R) atm 778.17lb f ft 1 ft 2 = 20 lbm/s For state 2 and 3: A2 A3 d2 4 (26in)2 4 531in2 ft 2 60s 2212.5 ft 3 / min 2 144in 1min 2 3 (1atm)(2212.5 ft / min) 14.7lb f / in 1btu 144in2 m2 m3 162.6 lbm / min (0.06855btu / lbm R)(540 R) atm 778.17lb f ft 1 ft 2 V3 V2 A2V2 (531in 2 )(10 ft / s) using the mass balance at steady state: 0 m1 m2 m3 m4 m4 m1 m2 m3 1202 162.6 126.6 876.8lbm / min V4 m4 RT4 (876.8lbm / min)(0.06855btu / lbm R)(540 R) 1atm 778.17lbf ft 1 ft 2 11932 ft 3 / min 2 p1 (1atm) 14.7lb f / in btu 144in 2 AV4 V4 V4 V4 V4 A4 d 42 4 4(11932 ft 3 / min) 144in 2 875 ft / min 14.6 ft / s (50in) 2 1 ft 2 EGR 334 Thermodynamics: Homework 12 Problem 4:22 The figure shows a cylindrical tank being drained through a duct whose cross sectional area is 3 x 10 -4 m2. The velocity of the water at the exit varies according to (2gz)1/2, where z is the water level in m, and g is the acceleration of gravity, 9.81 m/s2. The tank initially contains 2500 kg of liquid water. Taking the density of the water as 10 3 kg/m3 determine the time in minutes when the tank contains 900 kg of water. --------------------------------------------------------------Ae = 0.0003 m2 Ve = (2gz)1/2 mi = 2500 kg ρ= 1000kg/m3 mf=900 kg Mass flow balance: dmsys dt mi me where mi 0 me ( AeVe ) (1000kg / m3 )(0.0003m2 )(2 9.81m / s 2 z )1/ 2 (1.329kg / m1/ 2 s ) z1/ 2 Volume of Tank: mtan k ( Atan k z ) (1000kg / m3 )(1m 2 ) z (1000kg / m) z for an initial mass of 2500 kg: zi mtank 2500kg 2.5m Atank (1000kg / m3 )(1m 2 ) for a final mass of 900 kg: zf mtank 900kg 0.9m Atank (1000kg / m3 )(1m 2 ) therefore: dmsys me dt d (1000kg / m) z (1.329kg / m1/ 2 s ) z1/ 2 dt dz 1.329(kg / m1/ 2 s) 1/ 2 z (0.001329 m1/ 2 / s ) z1/ 2 dt 1000kg / m z 0.9 t t 1 1/ 2 z1/ 2 dz (0.001329 m / s)t 0 dt z 2.5 2 1/ 2 z 0.9 z (0.001329 m1/ 2 / s )(t 0) z 2.5 1 2 (0.9m)1/ 2 (2.5m)1/ 2 (0.001329 m1/ 2 / s )t t 1.265m1/ 2 951.8s 15.9 min 0.001329 m1/ 2 / s