Thermodynamics Homework: Water, Steam, and Ideal Gases
advertisement

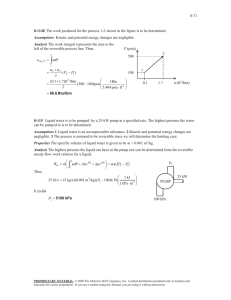
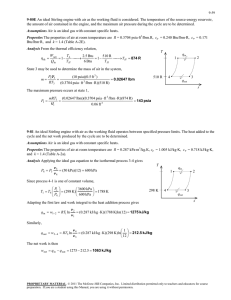
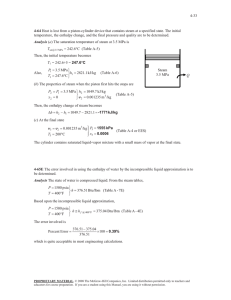
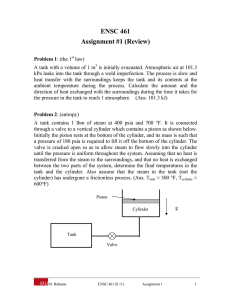
Homework of thermodynamic(I) Dr Alizadeh 1. A cylinder which has a volume of 0.4 m3 holds 2.0 kg of a mixture of liquid water and water vapor. The mixture is in equilibrium at a pressure of 6 bar (0.6 MPa). Calculate: 1) The volume and mass of liquid, 2) The volume and mass of vapor. 2. A cylinder which contains 3 pounds of saturated liquid water at a constant pressure of 30 Psia is heated until the quality of the mixture is 70 percent. Calculate: 1) The initial temperature, 2) The final pressure and temperature, and 3) The volume change of the mixture. 3. A container with a plunger compresses one lb-mol of an ideal gas from 1 atmosphere pressure to 10 atmospheres. Calculate the amount of work done if the process is considered to be polytropic. Assume the temperature to be 273K and k for the process to be 1.4. All losses are neglected. 4. The figure shows a container having 4Kg of saturated water at 35˚C. It also has a frictionless piston with a cross sectional area of 0.06m2 initially resting on the stops enclosing a volume of 0.03m3. To raise this piston against atmospheric pressure, a pressure of 300KPa has to be applied. On moving the piston upwards, it will encounter a linear spring when the contained volume is 0.075m3. To the final pressure is 7MPa, determine: a) The final state of water. b) The work done during the process. 5. What can you say about the following statements if one has an adiabatic process in which there is no heat transfer between the system and the surroundings, either because the system is well insulated or because the process occurs very rapidly? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. q = +w q=0 ∆E = q ∆E = w p∆V = 0 A medical ampoule containing dextrose (liquid water) at 1000 Psia, 100° F and having a volume of 0.3 in3 is placed in a cylinder having a volume of 1 ft3. A vacuum is created in the cylinder and the capsule is broken. Dextrose now evaporates and fills the cylinder. a) Calculate the final quality of the water vapor mixture in the cylinder if it reaches a final equilibrium temperature of 100° F. b) Also calculate the heat transfer with the surroundings. 7. Heat is transferred to steam at 50 lbf in a cylinder having a volume of 2 ft3. The temperature of steam rises from 300°F to 500°F while the pressure remains constant. Calculate i. The heat transfer , ii. The work done , iii. The change in initial energy for the above process. (Assume the system to be a close one) 8. A partition separates the two compartment of an insulated vessel as shown in the figure. Compartment A, contains 2 Kg of water at 200°C, 5 MPa and compartment B, contains 0.983 Kg of water at 200°C and 0.1 MPa. The partition is removed and the water in both the compartments fills up the entire vessel. Determine the final pressure, and the heat transfer involved in the mixing process, if the final temperature is 200°C. 9. A container with an air tight piston is at a pressure of 100 Psia and a temperature of 70°F. The piston moves up when 100 Btu of heat is transferred and the volume changes from 0.5 ft3 to 2.0 ft3. Assuming perfect gas behavior, calculate: i. The change in initial energy, ii. The final temperature, and iii. The heat capacity of the process. 10. Calculate the total work transfer that takes place for a process as shown in the figure. T1= -50°F T2= +70°F P1= 650 Psia p2= 25 Psia H1= 300 Btu/lbm H2= 410 Btu/lbm S1= 1.0 Btu/lbm°R s2= 1.65 Btu/lbm°R Z1= 100 ft z2= 100 ft v1= 450 ft/sec v2= 150 ft/sec 11. 10,000 lbm/min of air expands polytropically from 60 Psia and 2000°F to 15 Psia in a turbine. Calculate the work and heat in S.I. units if the value of the exponent n is taken as 1.75. 12. A reversible cyclic device does work, while exchanging heat with three constant temperature reservoirs as illustrated in the figure. The three reservoirs 1, 2 and 3are at temperature of 1000K, 300K and 500K respectively. It is known that 400KJ of heat are transferred from reservoir 1 to the device, and the total work done by the cyclic device is 100KJ. Determine both the magnitude and direction of the heat transfer with the other two reservoirs. 13. 34Kg steel casting at a temperature of 427˚C is quenched in 136Kg of oil initially at 21˚C. Assuming no heat losses and the steel casting and oil to have constant specific heats of 0.5024 and 2.5121KJ/Kg.K respectively, determine the change in entropy for a system consisting of the oil and casting. 14. One lbm/min of steam initially at 14.7Psia, 284.5˚F is compressed in a water cooled compressor to a final state of 150Psia, 1200˚F. The cooling water enters at 284.5˚F and a mass flow rate of 0.465 lbm/min, and leaves at 500˚F. For a combined system of the steam and water, calculate the change in entropy of the universe for the process. (Show this process on a T-S diagram.) 15. The heat engine of a thermal power station can be approximated by a Carnot cycle operating between 650˚F and 150˚F. If the maximum rise in the cooling water is restricted to 50˚F, and the power output is 10 6KW, at what rate must the cooling water be supplied? 16. Calculate the quality and work for a steady flow and no flow process, when three pounds per second of steam expand isentropically from 300 lbf/in2, 700˚F to a final temperature of 200˚F. Good Luck