Vocabulary List - Mr. Muench @ CMS
advertisement

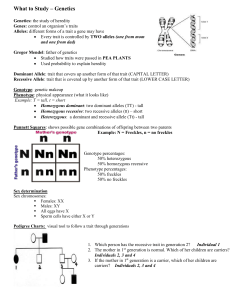
The language of heredity Mastered? Term Definition An alternative form of a gene (one member of a pair) or code at a specific position allele on a specific chromosome; can be dominant or recessive. Offspring inherit one code from each parent. The basic unit of heredity, segments of DNA with codes for production of specific gene proteins, which in turn are responsible for traits passed from parent to offspring. Found at specific locations on chromosomes. Found in nucleus of each cell; contains the DNA molecule. In humans, this long chromosome molecule is divided into 23 pairs, for a total of 46. dominant A trait that appears in offspring if one parent contributes it; masks a recessive trait. trait Usually represented by an upper-case letter. recessive A trait that appears in offspring only if both parents contribute it; represented as a trait lower case of the corresponding dominant trait (aa). Characteristics or attributes of an organism that are expressed by genes and/or trait influenced by the environment. The genetic makeup of an individual; can refer to an organism's entire genetic genotype makeup or the specific alleles at a particular locus responsible for a trait. The observable or detectable characteristics (traits) of an individual organism. The phenotype detectable expression of a genotype. A genotype consisting of two identical alleles of a gene for a particular trait, homozygous whether dominant (AA) or recessive (aa). heterozygous A genotype consisting of two different alleles of a gene for a particular trait (Aa). The passing of genetic factors from parent to offspring (or from one generation to heredity the next). sexual A form of reproduction in which TWO individuals produce a unique offspring having reproduction genetic characteristics from both parents. asexual Reproduction in which offspring are genetically identical to a SINGLE parent. reproduction Cells that come together during fertilization or conception in organisms that reproduce sexually. Each consists of a single set of unpaired chromosomes – 23 in gamete humans – half from mother and half from father. (Also known as sex cells or germ cells.) the molecule that holds the code for heredity; shaped like a twisted ladder (doubleDNA helix); comes apart like a zipper and can make copies of itself Punnett a chart that shows the possible combinations of alleles in a genetic cross; Square calculates probability of genotypes genome the complete genetic material of an individual genetic code the ordering of "rungs on the ladder" of DNA that carries genetic information a change in the structure of DNA that creates a different trait that may be passed mutation along to offspring long molecule consisting of chains of organic compounds; essential for structure, protein function and regulation of cells