Genetics 3
advertisement
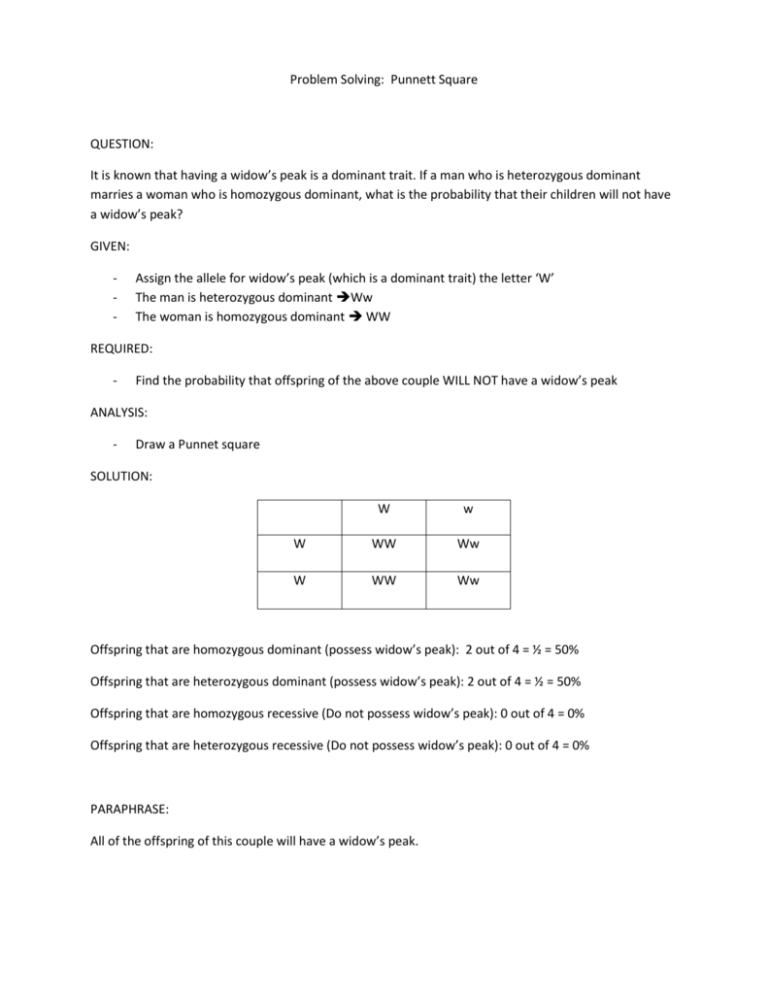
Problem Solving: Punnett Square QUESTION: It is known that having a widow’s peak is a dominant trait. If a man who is heterozygous dominant marries a woman who is homozygous dominant, what is the probability that their children will not have a widow’s peak? GIVEN: - Assign the allele for widow’s peak (which is a dominant trait) the letter ‘W’ The man is heterozygous dominant Ww The woman is homozygous dominant WW REQUIRED: - Find the probability that offspring of the above couple WILL NOT have a widow’s peak ANALYSIS: - Draw a Punnet square SOLUTION: W w W WW Ww W WW Ww Offspring that are homozygous dominant (possess widow’s peak): 2 out of 4 = ½ = 50% Offspring that are heterozygous dominant (possess widow’s peak): 2 out of 4 = ½ = 50% Offspring that are homozygous recessive (Do not possess widow’s peak): 0 out of 4 = 0% Offspring that are heterozygous recessive (Do not possess widow’s peak): 0 out of 4 = 0% PARAPHRASE: All of the offspring of this couple will have a widow’s peak. Problem Solving: Half Life calculation QUESTION: When a certain rock formed, it contained 100.0 g of carbon-14. After 11460 years, the rock now contains 25.0 g of carbon. What is the half life of carbon? GIVEN: - Initial mass of rock = 100.0 grams Final mass of rock = 25.0 grams Total time of decay = 11 460 years REQUIRED: - Number of half-lives = ? half-lives Half-life = ? years ANALYSIS: Total time of decay = number of half-lives Xnumber of years / half life) Number of years / half life = total time of decay / number of half lives SOLUTION: 1. fraction of sample remaining = final mass of rock / initial mass of rock = 25g/100g = ¼ 2. after one half-life = ½ after two half-lives = ½ X ½ = ¼ So two half-lives have passed if only ¼ of the rocks carbon is still available 3. number of years / half life =11 460 y / 2 half – lives = 5730 y / 1 half – life So 1 half life of carbon-14 = 5730 y PARAPHASE: The half life of carbon is 5730 years.