Properties
advertisement

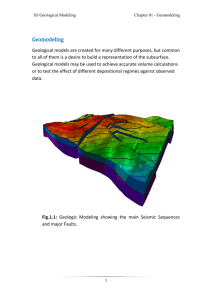
Chapter 17 – Petrophysical Modeling 3D Geological Modeling Deterministic Modeling When the well logs have been scaled up to the resolution of the cells in the 3D grid, the values for each cell along the well trajectory can be interpolated between the wells in the 3D grid. The result is a grid with Property values for each cell. To deterministic modeling, follow the steps: 1. Activate the depth converted grid under the HAH project. 2. Open the Petrophysical Modeling process. 3. Select Use Existing Property and select the Porosity property as the property to be modeled from the drop down menu. 4. Select the Tarbert 1 from the Pull down menu and de-select the Leave Zone Unchanged icon for that zone to create a realization. 5. Select the Moving average as the Method; leave all other settings as default, as shown by Fig. 17.1. 1 Chapter 17 – Petrophysical Modeling 3D Geological Modeling Fig. 17.1: Petrophysical Modeling with Top Tarbert Model Final 3D Grid (DC) dialog box 2 Chapter 17 – Petrophysical Modeling 3D Geological Modeling 6. Click OK to create the property model and display the model in the 3D Window. 7. Use the Zone Filter to display the appropriate zone. 8. Bring up a Histogram window from the Window menu. Display the Porosity property and use the Zone Filter to look at the modeled zone. Compare the histogram distribution for the well logs, the upscaled cells and the whole property. See Fig. 17.2. Fig. 17.2: Petrophysical Modeling displayed in a 3D window Fig. 17.3: Setting for Porosity [U] 3 Chapter 17 – Petrophysical Modeling 3D Geological Modeling 9. Double-click on the porosity property in the Properties folder and check the statistics in the statistics tab. See Fig. 17.4. Fig. 17.4: Settings for 'Porosity [U]' dialog box – Statistics tab page 4 Chapter 17 – Petrophysical Modeling 3D Geological Modeling Stochastic Modeling Petrel can generate stochastic petrophysical property models based on the Sequential Gaussian Simulation method. This is the most straightforward algorithm for generating realizations of a multivariable Gaussian field. Creating first model: To create stochastic modeling, follow the steps: 1. Activate the Top Tarbert Model Final 3D grid (DC) . 2. Open the Petrophysical Modeling process. GO to the Use Existing property and select Porosity from the drop-down list. 3. Activate the lock icon for the Tarbert 1 zone and de-select the lock for Ness2. 4. Select Sequential Gaussian Simulation as the method to use. 5. In the Variogram tab, select Exponential Variogram type, 3500 as Major Range, 1500 as Minoer Range, 10 as Vertical Range and 25 degrees as Azimuth. 6. Click OK create the property model. See Fig. 17.5. 5 Chapter 17 – Petrophysical Modeling 3D Geological Modeling Fig. 17.5: Petrophysical Modeling with Top Tarbert Model Final 3D Grid (DC) dialog box Viewing the result: 1. Bring up a Histogram window from the Windows menu and select Tile Vertical. 2. Use the Zone Filter to display the 3D property model and the Histogram distribution for the well logs, the up-scaled cells and the whole property for zone Ness 2. Changing the model: 1. Click on the 3D window to make it active and click on the Open Process Dialog icon on the Function bar. 2. Go to the Distribution tab in the Petrophysical Modeling processes window. Under Output data range click on Estimate (this will estimate the porosity range from the up-scaled cells within the zone). Specify an output data range (e.g. 0.1-0.25), as shown bellow. 6 Chapter 17 – Petrophysical Modeling 3D Geological Modeling 3. Click OK and observe the changes in the model. Fig. 17.6: Petrophysical Modeling with Top Tarbert Model Final 3D Grid (DC) dialog box 7 Chapter 17 – Petrophysical Modeling 3D Geological Modeling Property Calculator As for the well logs there is a similar calculator associated with the properties. This calculator can be used to create new 3D properties and to do operations between properties. There is a whole range of predefined functions associated with the calculator, such as logical and mathematical functions. It is possible to write nested statements and there is no limit for the length and the complexity of such statements. If a calculation is getting complex then it is possible (and useful) to create macros containing the calculation. The macro can be read from file to do several operations in one go. Creating a new property model: To property calculator, follow the steps: 1. Click Right Click on the Properties folder in the 3D Grid (DC) and select Calculator from the pull down menu. 2. Change the Properties Type to Porosity and type in the white formula field. 3. test = Porosity [Press Enter], as shown in Fig. 17.7. 8 Chapter 17 – Petrophysical Modeling 3D Geological Modeling Fig. 17.7: Calculator for Properties folder dialog box 3. test = testO.8 [Press Enter], as shown in Fig. 17.8. Fig. 17.8: Calculator for Properties folder dialog box 9 Chapter 17 – Petrophysical Modeling 3D Geological Modeling 4. See the statistical result by selecting Result in the upper right-hand corner. See Fig. 17.9. Fig. 17.9: Result for Porosity after calculated 10 Chapter 17 – Petrophysical Modeling 3D Geological Modeling Display the new test property model in a 3D Window. See Fig. 17.10. Fig. 17.10: The (test) model under Properties folder displayed in a 3 D window 11 Chapter 17 – Petrophysical Modeling 3D Geological Modeling Histogram and Filter Functionality Histogram shows the distribution of values for the selected well logs or for a selected individual property. The histograms are used for checking and comparing input- and model-data. The histogram panels are found under Settings for individual properties as well as for well logs, for individual wells or for all wells. The histogram displays original log values, blocked well values and property values. The histograms are filter-sensitive. To create histogram and filter functionality, follow the steps: 1. Under the Models tab open the Settings window for an individual property (e.g. Porosity) by double-clicking on it. Within the Settings window, open the Histogram tab. 2. Select the zone you want to study. 3. Toggle on/off the boxes for displaying property and well logs (original and up- scaled). 4. Play around with the option to change the number of columns and check the interval values in the Legend. 5. Toggle on the Use filter option and open the Settings window for the Properties folder and choose the Filter tab. The Filter gives the option to show only parts of a property model. 6. Choose a filter option, e.g. the Value filter. Observe the changes. See Fig. 17.11. 12 Chapter 17 – Petrophysical Modeling 3D Geological Modeling Fig. 17.11: Histogram for the "Porosity" in property folder Calculation of Sw The water saturation in the hydrocarbon zone is a function of height above the fluid contact, permeability and porosity. The calculator can be used to make a water saturation property that takes these parameters into account. In this case, we have water saturation in the oil zone that can be expressed by the following equation: K Sw a h Where: h = height above the OWC K = permeability φ = porosity a = 0.5 b = 0.2 13 b Chapter 17 – Petrophysical Modeling 3D Geological Modeling The contact is given by: OWC = -2010 meters for all zones and all segments. A permeability property is needed to generate the Sw property. A linear expression has been found between porosity and log permeability which can be expressed by: LogPerm = 10.9*Porosity - 0.48 A macro has been written to simplify this calculation and for easy reproduction in case of an update. The macro has been written in a text editor program and saved as a text file with the extension (.mac). All the functions in the macro are listed below each other, just as they would be written as separate functions using the Property Calculator. 14 Chapter 17 – Petrophysical Modeling 3D Geological Modeling To create a water saturation (Sw) property, follow the steps: 1. Activate and expand the 3D Grid model in the Models Pane 2. Right click the Properties item as shown in Fig. 17.12. Fig. 17.12: The Properties item under the 3D Grid model 3. Click the Calculator option. The Calculator for Properties 'Properties' dialog box appears as shown in Fig. 17.13. Fig. 17.13: The Calculator for Properties 15 Chapter 17 – Petrophysical Modeling 3D Geological Modeling 4. Check the "From file:" check box. 5. Click the browse button (…) and select the macro file to be used. The macro file is called 'sw_formula.mac' and it is stored under the directory called 'Other Data', which is found together with the other demo data. See Fig. 17.14. This macro file contains the formulas to be used for calculating properties. These formulas are given as macros written in text format. You may change the formulas to suit your needs. For example, the formulas in the 'sw_formula.mac' macro file are written as: LogPerm=10.9*Porosity-0.48 Perm=Pow(10,LogPerm) Temp=(Above_Contact)*SQRT(Perm/Porosity) Sw=0.5*Pow(Temp,-0.2) Sw=IF(Sw>1,1,Sw Fig. 17.14: The file sw_formula.mac under the 'Other Data' folder 16 Chapter 17 – Petrophysical Modeling 3D Geological Modeling 6. Make sure to select "Seismic (default)" from the "Attach new to template" drop down box. 7. Press the Run button. Notice that all formulas will appear in the history window at the top. See Fig. 17.15. Fig. 17.15: The Calculator for Properties after running the calculations 17 Chapter 17 – Petrophysical Modeling 3D Geological Modeling 8. Four new properties will be created, called LogPerm, Perm, Temp and Sw. They will all be attached to the template that was selected next to ‘Type’ in the property calculator "Seismic (default)". Fig. 17.16: The Sw property displayed in a 3D window 9. Familiarize yourself to using this functionality in Petrel by using different templates. For example, change the templates for the Sw and Perm properties by opening the Settings window for each of them, go to the Info tab, and change to another template from the pull down list and watch the results. See Fig. 17.17. 18 Chapter 17 – Petrophysical Modeling 3D Geological Modeling Fig. 17.17: Settings for Sw 19