Unit 2: Rocks & Minerals Test Study Guide
advertisement
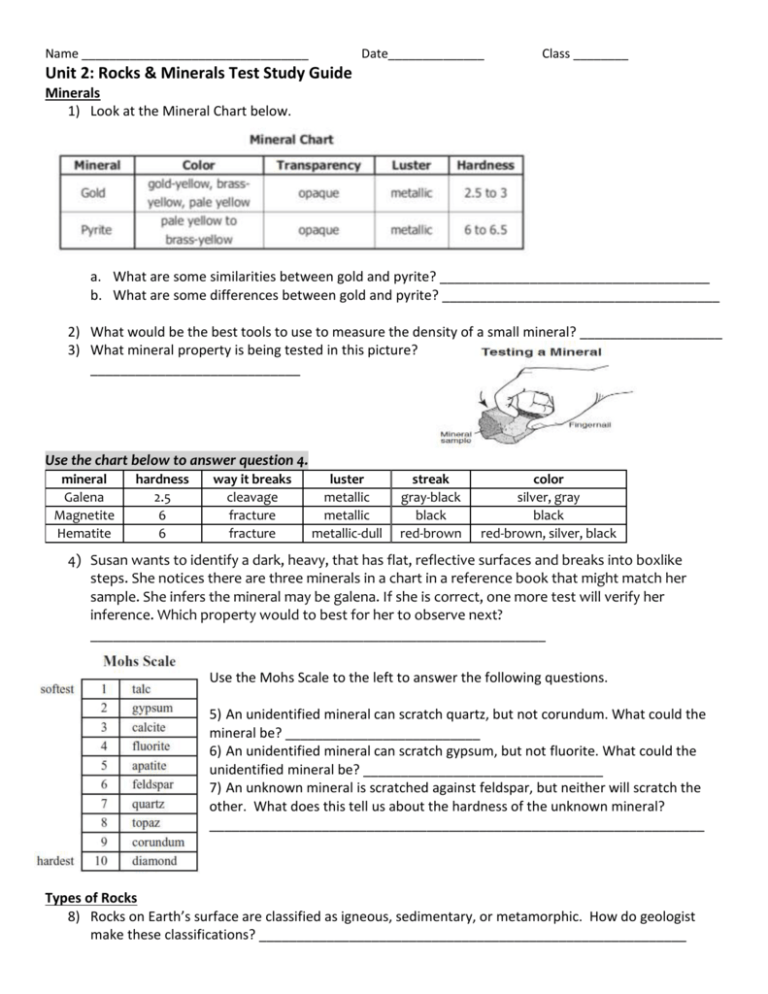
Name _________________________________ Date______________ Class ________ Unit 2: Rocks & Minerals Test Study Guide Minerals 1) Look at the Mineral Chart below. a. What are some similarities between gold and pyrite? ____________________________________ b. What are some differences between gold and pyrite? _____________________________________ 2) What would be the best tools to use to measure the density of a small mineral? ___________________ 3) What mineral property is being tested in this picture? ____________________________ Use the chart below to answer question 4. mineral Galena Magnetite Hematite hardness 2.5 6 6 way it breaks cleavage fracture fracture luster metallic metallic metallic-dull streak gray-black black red-brown color silver, gray black red-brown, silver, black 4) Susan wants to identify a dark, heavy, that has flat, reflective surfaces and breaks into boxlike steps. She notices there are three minerals in a chart in a reference book that might match her sample. She infers the mineral may be galena. If she is correct, one more test will verify her inference. Which property would to best for her to observe next? ____________________________________________________________ Use the Mohs Scale to the left to answer the following questions. 5) An unidentified mineral can scratch quartz, but not corundum. What could the mineral be? __________________________ 6) An unidentified mineral can scratch gypsum, but not fluorite. What could the unidentified mineral be? ________________________________ 7) An unknown mineral is scratched against feldspar, but neither will scratch the other. What does this tell us about the hardness of the unknown mineral? __________________________________________________________________ Types of Rocks 8) Rocks on Earth’s surface are classified as igneous, sedimentary, or metamorphic. How do geologist make these classifications? _________________________________________________________ Igneous Rocks 9) Pumice is an igneous rock. What process created it? _________________________________________ 10) Fine-grained rocks are ________________, formed when lava erupts to the surface and cools ____________. 11) Rocks that cooled VERY RAPIDLY have what texture? _____________________ Name an igneous rock that has this texture? ______________ Describe how it looks. _______________________________ Sedimentary Rocks 12) Rocks and minerals that are broken down into smaller particles (without changing in composition) is called __________________. 13) Sandstone is a ______________________ rock. What process formed it? ________________________ 14) What processes turn sediment into sedimentary rock? _______________________________________ 15) Which process involved in making a sedimentary rock is when sediment piles up in layers, and exerts pressure on the sediments below, squeezing them together? __________________________ 16) True or False: If we measure the rate at which similar layers of sediment are laid down currently, it will give us an estimate of how long it took for a layer of sedimentary rock to form. 17) __________________ are often found in sedimentary rock, organisms can easily be preserved in the layers of sediment. because The picture below shows sedimentary rock layers. 18) 19) Which layer was deposited first? ___________________ Which layer was deposited last? ____________________ Metamorphic Rocks 20) What is the source of the heat & pressure that creates metamorphic rocks? ____________________________________________________________________________________ 21) Limestone goes through heat & pressure, and changes into a different kind of rock called marble. What kind of rock is marble? ______________________________ The Rock Cycle 22) What process would change a sedimentary rock into an igneous rock? __________________________ 23) When an igneous rock, such as granite, undergoes heat & pressure, what type of rock does it change into? ______________________________________ 24) Large amounts of rainfall, or water, in an area can speed up which process in the rock cycle? ____________________________________ Use the rock cycle diagram to determine if the following statements are true or false. True or False: 25) _____ Weathering & erosion can turn igneous rock into sediment. 26) _____ Heat & pressure turn metamorphic rock into igneous rock. 27) _____Heat & pressure convert igneous rock into metamorphic rock. 28) _____ Each type of rock gets melted & the magma turns into igneous, metamorphic & sedimentary rock. 29) _____ All three rock types weather to create sediments. All three types of rocks can become metamorphic by going through heat & pressure. All three types of rocks melt to make magma. Magma creates igneous rocks. 30) _____ Igneous rock is weathered to create sedimentary rock. Sedimentary rock is melted to form igneous rock. Metamorphic rock is weathered to form igneous rock. 31) _____ Heat & pressure creates igneous rocks. 32) _____Only sedimentary rocks get weathered & eroded. 33) _____ Sedimentary rocks are made from the sediments of igneous, metamorphic or other sedimentary rocks. My child studied this study guide this week in preparation for their test on October 14th. Please sign each night you study with your child. Parent Signature _______________________________________ Date_________________ Parent Signature _______________________________________ Date_________________ Parent Signature _______________________________________ Date_________________ Answer Key 1) a. color, transparency & luster b. hardness 2) graduated cylinder and a balance 3) hardness 4) hardness 5) topaz 6) calcite 7) the unknown mineral WILL scratch apatite (or anything with a lower number on the scale). 8) How the rocks were formed 9) Cooling & hardening (solidification) of magma or lava 10) Extrusive; quickly/rapidly 11) No visible grain or glassy; obsidian; black, shiny, glass-like surfaces 12) Sediments 13) Sedimentary rock; lithification 14) Compaction & cementation 15) Compaction 16) True 17) Fossils 18) M 19) L 20) From the weight of the overlying rock layers, deep inside the earth 21) Metamorphic 22) Melting, cooling & solidification (hardening) 23) Metamorphic 24) Weather & erosion 25) True 26) False 27) True 28) False 29) True 30) False 31) False 32) False 33) True








