Galileo`s Gravitational Experiment
advertisement

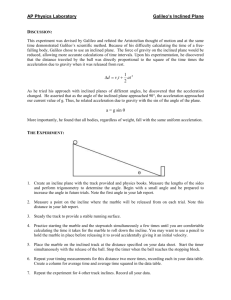
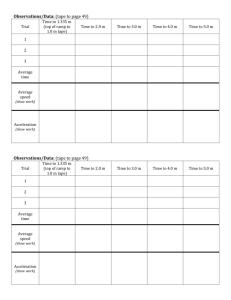
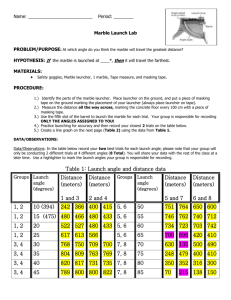
Galileo's Gravitational Experiment Objective Determine the acceleration due to gravity using Galileo’s technique of using an inclined ramp. Materials Stopwatch Marble Meter stick track Procedure Part 1 1. Lay the wooden track ramp on the table. Using the protractor to measure the angle from the table (this has been pre-determined for you). Fasten the track to hole one. Appoint one partner to hold and release the marble, and another to act as a timer. 2. Place the marble in the groove at the top of the board and release. Use the stopwatch to record the time it takes for the marble to reach the bottom (to the 1 m mark, not the curved “catcher” part). Record this in the data table. 3. Raise the track to the second hole. Release the marble from the top, and record the time. 4. Repeat this procedure for all of the angles. Record your results. Do not need to attempt the 90° angle. This will be determined experimentally and graphically using a spreadsheet and linear line equation. Part 2 1. 2. Put data into Microsoft Excel Spreadsheet. Use the equation to find the acceleration of the marble. Algebraically rework the equation to read Make a new column, so the acceleration is calculated for you. 3. 4. 5. 5. Plot acceleration on the y-axis and angle ( of the ramp on the x-axis. Use the best fit line to get the equation of a linear line for your data. Print off the data and plotted line. Plug variables into the equation to find the acceleration of the marble at a 90° angle (freefall). Show your work below. Data Sheet Part I(a): Hole # Angle, 1 7.125° 0 m/s 2 9.462° 0 m/s 3 12.339° 0 m/s 4 15.15° 0 m/s 5 17.40° 0 m/s none 90° Distance, x (m) N/A Time, t (seconds) N/A Initial Acceleration, a (m/s2) Velocity (v0) 0 m/s Part I(b): Hole # Angle, 1 7.125° 0 m/s 2 9.462° 0 m/s 3 12.339° 0 m/s 4 15.15° 0 m/s 5 17.40° 0 m/s none 90° Distance, x (m) N/A Time, t (seconds) N/A Initial Acceleration, a (m/s2) Velocity (v0) 0 m/s Questions 1. What relationship did you find in Part I between the acceleration of the ball and the angle of the wooden board? Explain this in terms of the gravitational force. 2. We know the acceleration due to gravity is 9.8 m/s2. Give some reasons why your experiment may not have given you this value.