narrative que cards for close reading
advertisement

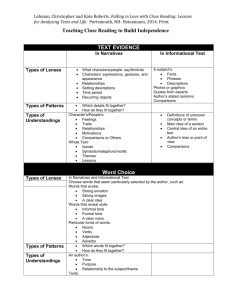
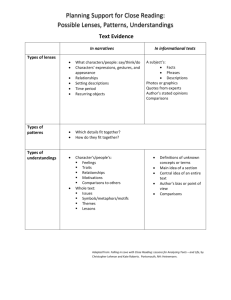
1. Narrative Text: Evidence Types of lenses Possible Questions/Noticings: What does the author want me to understand? What role does the character(s) play in the text? In narratives… What characters/people: say/think/do Characters' expressions, gestures, and appearance Relationships Setting Time period Recurring objects Why did the character act that way? Types of patterns Types of understanding Which details fit together? How they fit together? Character’s/people’s: Feelings Traits Relationships Motivations Comparisons to other Whole text: Issues Symbols/metaphors/motifs Themes Lessons (central message; lessons learned) 2. Narrative Text: Word Choice Types of lenses In narratives… Choose words that seem particularly selected by the author such as: Words that evoke: Possible strong emotions Questions/Noticings: strong images Are there any hard or a clear idea important words? Words that reveal style: informal tone Why did the author use formal tone that particular word? a clear voice Particular kinds of words: What words jump out nouns right away? verbs adjectives adverbs Types of patterns Which details fit together How they fit together Types of An author’s understanding Tone Purpose Relationship/theme Text’s: Central ideas Issues and Lessons Symbols/metaphors/motifs Themes Planning Support for Close Reading 2.Narrative Text: Word Choice Anchor Standards Standard 1: Read closely to determine what the text says explicitly and to make logical inferences from it; cite specific textual evidence when writing or speaking to support conclusions drawn from the text. Standard 4: Interpret words and phrases as they are used in a text, including determining technical, connotative, and figurative meanings, and analyze how specific word choices shape meaning or tone. Adapted from Falling in Love with Close Reading, Lehman & Roberts, 2014 Planning Support for Close Reading 1. Narrative Text: Evidence Anchor Standards for Reading Standard 1: Read closely to determine what the text says explicitly and to make logical inferences from it; cite specific textual evidence when writing or speaking to support conclusions drawn from the text. Standard 4: Interpret words and phrases as they are used in a text, including determining technical, connotative, and figurative meanings, and analyze how specific word choices shape meaning or tone. Standard 6: Assess how point of view or purpose shapes the content and style of a text. Adapted from Falling in Love with Close Reading, Lehman & Roberts, 2014 3.Narrative Text: Structure In narratives… Types of lenses Lens #1: Describe the organization of the text: Genre as structure chosen for a purpose: Fantasy, to explore good and evil Historical fiction, to reflect on current ideas in a historical context Location of parts within the whole: Plot mountain: -Exposition: introducing character, setting , and backstory -Rising Action: pressures and obstacles -Climax: dramatic point, characters or problems come together -Falling Action: characters or communities change, lessons learned -Resolution: ending, some things wrap up, others might not Techniques the author uses: Descriptions Dialogue between characters Action Setting Inner thinking Scene endings and beginning Flashbacks Definitions of a term Comparisons Lens #2: Purpose of that organization: To set the stage To reveal To create suspense To foreshadow How are the parts similar? How are the parts different? What purpose do the parts serve? Character: Development Changes Critical movements Whole text: Themes Central ideas Issues and Lessons Symbols/ metaphors/ motifs Author’s purpose Possible questions/Noticings: Why might this memory be important (for flashbacks) What is being compared? (comparisons) Why does this keep happening again & again? Where is the narrator talking? Where are the parts of the story where the characters are talking? Types of patterns Types of understanding 4.Narrative Text: Point of View and Argument Types of lenses Possible questions/Noticings: What stands out in the text? How does the dialogue reflect the character’s/author’s perspective or thinking? In narratives… Lens #1: What is the author’s and/or character’s point of view here? What are they thinking What they believe What they feel or want Lens #2: What makes the author and/or character’s point of view persuasive? Text evidence Why does this character/author Word choice have this point of view? Structure What characters say/think/do Character expressions, gestures, and appearance Relationships Setting descriptions Time period Recurring objects Types of patterns Which points of view/ideas are repeated What technique does the author use to make his or her point of view/argument What sticks out as different unusual in the text? Types of understanding What is the purpose or effect of these points of view? What is revealed about a theme? The author’s purpose? The effect on the reader? Which point of view is rewarded in the text? Comparison of pints of view Planning Support for Close Reading 4.Narrative Text: Point of View and Argument Anchor Standards Standard 1: Read closely to determine what the text says explicitly and to make logical inferences from it; cite specific textual evidence when writing or speaking to support conclusions drawn from the text. Standard 4: Interpret words and phrases as they are used in a text, including determining technical, connotative, and figurative meanings, and analyze how specific word choices shape meaning or tone. Standard 6: Assess how point of view or purpose shapes the content and style of a text. Adapted from Falling in Love with Close Reading, Lehman & Roberts, 2014 Planning Support for Close Reading 3.Narrative Text: Structure Anchor Standards Standard 1: Read closely to determine what the text says explicitly and to make logical inferences from it; cite specific textual evidence when writing or speaking to support conclusions drawn from the text. Standard 5: Analyze the structure of texts, including how specific sentences, paragraphs, and larger portions of the text (e.g., a section, chapter, scene, or stanza) relate to each other and the whole. Adapted from Falling in Love with Close Reading, Lehman & Roberts, 2014 5.Narrative Texts: Reading Across Texts Types of lenses Possible Questions/Noticings: What similarities do you notice in these texts? Do they share a point of view, theme, or idea? Are there similarities in the characters? How does that help me form my own understanding? Types of patterns Types of understanding In narratives… Lens #1: Choose a comparison: Characters or subjects Themes or central ideas Settings Authors (texts by the same author or different author) Genres Styles Other ways (awards won, time period, social issues, etc.) Lens #2: Then choose your texts: What other text fits with this chosen comparison? - Some students may find it helpful to flip these steps. Decide how to compare: Text evidence Word choice Structure Point of view Have new ideas about: The lens you looked through The authors’ choices The messages these texts send See characters or subjects as more complex Analyze kinds of relationships between characters or ideas in texts Theme or central idea When considering author’s purpose: Analyze each author’s point of view Understand more of an author’s style See how genre choices affect story, topic, or readers Examine what it takes to be an “award-winning” book Analyze what texts from a time period show us about that period in history Blank Blank Planning Support for Close Reading 5.Narrative Text: Reading Across Texts Anchor Standards Standard 1: Read closely to determine what the text says explicitly and to make logical inferences from it; cite specific textual evidence when writing or speaking to support conclusions drawn from the text. Standard 9: Analyze how two or more texts address similar themes or topics in order to build knowledge or to compare the approaches the authors take. Adapted from Falling in Love with Close Reading, Lehman & Roberts, 2014