CHEM 161-01
advertisement

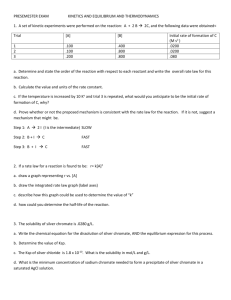
More EXAM III Practice CHEM 162-04 Dr. Overway Instructions: Do not open this test booklet until you are instructed to do so. Show your work in order to receive partial credit. Keep track of units and use the correct significant figures. The following information may be useful during the exam. [A- ] [BH + ] ) [B] 𝑝H = 𝑝𝐾𝑎 + log ([HA]) 𝑝OH = 𝑝𝐾𝑏 + log ( pH = - log [H3O+] pOH = - log [OH-] pH + pOH = 14 Ka ·Kb =Kw Citric Nitrous Hydrofluoric Formic Benzoic Acetic Carbonic Hydrogen sulfite ion Hydrogen sulfide Hypochlorous Dihydrogen phosphate ion Boric Ammonium ion Hydrocyanic Phenol Hydrogen carbonate ion Hydrogen peroide Monohydrogen phosphate ion Chemical Pb2+ (aq) CO32- (aq) PbCO3 (s) pKa = - log Ka Kw=110-14 Acid M1V1=M2V2 R = 8.3145 J/(K mol) −∆𝐺 𝐾𝑒𝑞 = 𝑒 𝑅 𝑇 Formula Conjugate Base H3C6H5O7 H2C6H5O7HNO2 NO2HF FHCOOH HCOOC6H5COOH C6H5COOCH3COOH CH3COOH2CO3 HCO3HSO3SO32H2S HSHClO ClOH2PO4HPO42H3BO3 H2BO3NH4+ NH3 HCN CNC6H5OH C6H5OHCO3CO32H2O2 HO2HPO42PO43- ∆𝐺 = −𝑅𝑇 ln(𝐾𝑒𝑞 ) Ka 7.1 10-4 4.6 10-4 3.5 10-4 1.8 10-4 6.5 10-5 1.8 10-5 4.3 10-7 1.0 10-7 9.1 10-8 3.0 10-8 6.2 10-8 7.3 10-10 5.6 10-10 4.9 10-10 1.3 10-10 5.6 10-11 2.4 10-12 2.2 10-13 Thermodynamic values at 25 C Hfo (kJ/mol) Sfo (J/(K mol)) Gfo (kJ/mol) -1.7 10.5 -24.4 -677.1 -56.90 -527.8 -699.1 131.0 -625.5 CHEM 162-04 More Exam III Practice 1. The equilibrium constant for the following reaction: H2(g) + Br2(g) 2 HBr(g) 6 is 1.9510 at a certain temperature. Find the equilibrium pressure of all of the gases if 5.50 atm of HBr is introduced into a sealed container at this temperature. Equilibrium pressures -3 p(H2) = 3.9410 atm p(Br2) = 3.9410-3 atm p(HBr) = 5.49 atm H2(g) + Br2(g) 2 HBr(g) I (atm) 0 0 5.5 C +x +x -2x E x x 5.5-2x Kp = 1.95106 = (5.5-2x)2/(x2) x = 3.9410-3 assume 2x<< 5.5 0.1% 2. Which of the following solutions will show the properties of a buffer (circle all that apply)? A) 10 mL of 0.10 M NH4Cl + 50 mL of 0.010 M NaOH B) 20 moles of NH4Cl + 10 moles of NaOH in 1.0 L of solution. C) 10 moles of NH4Cl + 20 moles of NaOH in 1.0 L of solution. strong base left over! D) 10 mL of 0.10 M CH3COOH + 10 mL of 0.10 M NaCH3COO E) 10 mL of 0.10 M HCl + 10 mL of 0.10 M NaCl strong acid left over! F) 10 mL of 0.10 M CH3COOH + 5 mL of 0.10 M HCl strong acid left over! 3. (10 pts) In a titration of 75.0 mL of a 0.100 M HCN solution with a 0.200 M NaOH solution, how many mL of the strong base is required to reach the equivalence (stoichiometric) point? (75.0 mL) (0.100 M HCN) = (X mL) (0.200 M NaOH) X mL = 37.5 mL of NaOH 4. What is the equilibrium concentration of [I-] if 12.58 grams of PbI2 (pKsp = 8.10) is added to 500.0 mL of pure water? PbI2 (s) I C E Pb2+ (aq) + 0 +x x 2 I- (aq) 0 +2x 2x 5. Determine the Keq value for the following reaction. Pb2+ (aq) + CrO42- (aq) PbCrO4 (s) Ksp= 10-8.10 = (x)(2x)2 x=1.26×10-3 [I-]=2x=2.51×10-3 M pKsp = 13.74 This is a reverse Ksp ,so Keq = 1/ Ksp = 1/10-13.74 = 5.50×1013 6. Determine the Gibbs Free Energy (G) and Ksp for the following reaction at 88.7 C. Pb2+ (aq) + CO42- (aq) PbCrO4 (s) The temperature is not 25 C, so I must use G = H - TS Hrxn = (1)(-699.1) – (1)(-1.7) –(1)(-677.1) = -20.3 kJ/mol Srxn = (1)(131.0) – (1)(10.5) –(1)(-56.90) = 177.4 J/(K mol) G = H - TS = (-20.3 kJ/mol) – (273.15 + 88.7 K)[ 177.4 J/(K mol) 1000] = -84.49 kJ/mol Keq = e-G/RT = exp(+84.49×1000/(8.3145 × 361.85) = 1.57×1012 7. Given the following reaction, how could you get it to do the following: H2O (l) + CO2 (g) + heat HCO32- (aq) + H+ (aq) A) Two ways to shift the reaction toward the products. Increase temperature OR increase pressure OR increase pressure of CO2 OR decrease the concentrations of HCO32- (aq) or H+ (aq) B) Shift the reaction toward the reactants. Increase the concentration of HCO32- (aq) or H+ (aq) OR decrease the pressure of CO2 or lower the temperature