Multigenre Research Project
advertisement

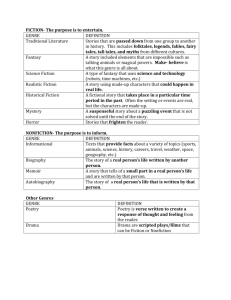
Multigenre Research Project Title: Multigenre Research Project Author: Rene Ribant-Amthor Grade Level: 9–10 Subject/Content: English/Multigenre Research Project Summary of Lesson: Students research someone who has influenced the development of African American literature and create a multigenre research project. Focus Question: Who do you think has had a great influence on African American literature and why? Databases(s): Student Resources in Context, Biography in Context Procedures: Steps/Activities by the teacher: Ask students to think about someone who has influenced African American literature. Encourage students to think about how this person has help shape the genre. Approve all subjects before students start their research. Allow students time to access the Student Resources in Context and Biography in Context databases to locate more information on their subject. As students complete their research, they should pay special attention to how their subject contributed to African America literature. Students should try to find both primary and secondary sources for their project. Primary sources might include excerpts from the subject's writings or interviews with the subject. Secondary sources might explain how or why the subject has influenced African American literature. After students have collected their sources they will complete a multigenre research project using their chosen person as the focal point. Each section of the project will focus on a different genre or style of writing. Students may also choose to use styles or themes that their subject incorporated into his or her work in their projects. The following is an outline of the genres for each section of the paper: o Genre 1—Students may complete a poem or short story about their subject. Although this allows students to be creative they should include facts about the subject in their poems or stories. o Genre 2—Students may complete a newspaper article about their subject or a review of one of their subject's works. o Genre 3—Students may complete a diary entry or letter written from the perspective of their subject. Remind students to include facts in their diary entries or letters. They may, however, use their creativity to imagine how the subject may have felt about certain events. Genre 4—Students may create an advertisement for one of their subject's works or write a persuasive essay that explains why people should study the subject's work. Explain to the students that each section must rely on research from credible sources. Students should include a works cited page at the end of their project. o Steps/Activities by student(s): Think about someone who has contributed to African American literature. You will research this person and use the information you find to complete a multigenre research project. Get your teacher to approve the subject you have chosen before you start your research. Access the Student Resources in Context and Biography in Context databases to find resources about your subject. Look for primary and secondary sources that provide information about your subject's life and works. Primary sources might include excerpts from the subject's writings or interviews with the subject. Secondary sources might explain how or why the subject has influenced African American literature. Take careful notes of all the sources you use. You will need to cite them in a works cited page at the end of your project. Complete a multigenre research project using your chosen person as the focal point. The following is an outline of the genres for each section of the paper: o Genre 1—You may complete a poem or short story about your subject. Although this allows you to be creative, you should include facts about the subject in your poem or story. o Genre 2—You may complete a newspaper article about your subject or a review of one of your subject's works. o Genre 3—You may complete a diary entry or letter written from the perspective of your subject. You must include facts in your diary entry or letter. You may, however, use your creativity to imagine how the subject may have felt about certain events. o Genre 4—You may create an advertisement for one of your subject's works or write a persuasive essay that explains why people should study the subject's work. Each section must rely on research from credible sources. You must include a works cited page at the end of your project. Outcome: Students will research someone who has had an influence on the development of African American literature. They will use their research to create a multigenre research project about the person they chose. Related Activities: This activity can be easily integrated with the activities suggested. English Students work in groups to compile a class booklet of influences on African American literature. Learning Expectation: Students will use their research skills to locate information on a prominent figure in African American literature. They will then use their research to write about their subject using a variety of styles and techniques. Standards for the English Language Arts 2. Students read a wide range of literature from many periods in many genres to build an understanding of the many dimensions (e.g., philosophical, ethical, aesthetic) of human experience. 4. Students adjust their use of spoken, written, and visual language (e.g., conventions, style, vocabulary) to communicate effectively with a variety of audiences and for different purposes. 5. Students employ a wide range of strategies as they write and use different writing process elements appropriately to communicate with different audiences for a variety of purposes. 6. Students apply knowledge of language structure, language conventions (e.g., spelling and punctuation), media techniques, figurative language, and genre to create, critique, and discuss print and nonprint texts. 7. Students conduct research on issues and interests by generating ideas and questions and by posing problems. They gather, evaluate, and synthesize data from a variety of sources (e.g., print and nonprint texts, artifacts, people) to communicate their discoveries in ways that suit their purpose and audience. Standard Source: IRA and NCTE 1996 ISTE NETS for Students 1. Creativity and Innovation Students demonstrate creative thinking, construct knowledge, and develop innovative products and processes using technology. Students: B. create original works as a means of personal or group expression. 3. Research and Information Fluency Students apply digital tools to gather, evaluate, and use information. Students: B. locate, organize, analyze, evaluate, synthesize, and ethically use information from a variety of sources and media. Standard Source: ISTE NETS for Students, 2007 Information Power; Information Literacy Standards: Standard 1: The student who is information literate accesses information efficiently and effectively. Standard 2: The student who is information literate evaluates information critically and competently. Standard 3: The student who is information literate uses information accurately and creatively. Standard 4: The student who is an independent learner is information literate and pursues information related to personal interests. Standard 6: The student who is an independent learner is information literate and strives for excellence in information seeking and knowledge generation. Standard 8: The student who contributes positively to the learning community and to society is information literate and practices ethical behavior in regard to information and information technology. Standard Source: American Library Association, 1998