3D Modeling For Complex Hip Replacement
advertisement

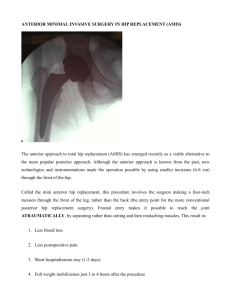
SP15 3D Modeling For Complex Hip Replacement Professor Dr Azhar M. Merican Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, University of Malaya Medical Centre 3D modelling of the hip for complex THR is an extension of templating. In its basic form, the preoperative 3D image of the hip is studied and virtual implantation of the acetabular component and femur can be performed. This allows the surgeon to anticipate if a different choice of implant or strategies for bony defect is preferred, give good estimates of the size of components and identify the most optimal location for the acetabular component. In cases where the local anatomic landmarks have been lost or distorted by previous surgery, trauma or dysplasia, the orientation of the acetabular component can be determined referenced to anatomic planes such as the anterior pelvic plane. The identification of the location of the true hip centre can be inferred by mirroring the opposite normal acetabulum. With this templating, the operating surgeon has better appreciation of the 3D anatomy and is familiar with local bony features seen in the template to be used as landmarks during surgery. The use of sterilisable patient specific jigs is a simple intraoperative method to help the surgeon in the execution of surgery according to the preoperative plan. These jigs are printed by rapid prototyping and is widely available commercially in total knee replacement. A similar concept applied in the complex primary hip uses patient specific jigs to localise the pre planed acetabulum and guide the direction and depth of acetabular reaming for optimal component placement especially when local landmarks are unreliable. Cases will be presented to illustrate this concept. Lastly, printing 3D models of the hip is useful in rehearsing surgery in specific cases. The surgeon can perform surgery on the 3D models of these cases before the actual case. This allows for anticipation of problems, surgeon familiarity, experimenting with alternative plans and a 3D aide memoir for the surgery. The design files for the case can be kept for future use in workshops to educate other surgeons in performing, for example, modular hip implantation in more realistic disease specific sawbones. 3D modelling of the hip preoperatively for the complex primary THR is a useful adjunct to preoperative templating and intraoperative execution of the surgery.