Ch 13.1 Streams & Rivers pg 280 – 282
advertisement

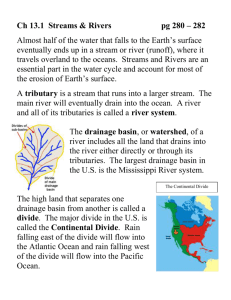
pg 280 – 282 Ch 13.1 Streams & Rivers Almost half of the water that falls to the Earth’s surface eventually ends up in a stream or river (_______), where it travels overland to the oceans. Streams and Rivers are an essential part in the water cycle and account for most of the _________________________. A __________ is a stream that runs into a larger stream. The main river will eventually drain into the ocean. A river and all of its tributaries is called a _____________. The _____________, or _________, of a river includes all the land that drains into the river either directly or through its tributaries. The largest drainage basin in the U.S. is the ____________________. The high land that separates one drainage basin from another is called a _______. The Continental Divide The major divide in the U.S. is called the ______________________. Rain falling east of the divide will flow into the Atlantic Ocean and rain falling west of the divide will flow into the Pacific Ocean. Parts of a River System The beginning of a river is known as the ______________. When the _________ of a river finally reaches its destination, the water slows down & deposits its sediment, forming a _______________. An _________________ is similar to a delta, but forms on land where a river emerges from a mountainous area and flows out onto a more gently sloping plain. Label Me! River Development The three stages in the development of a river are described as _________, __________ & _________. Most rivers begin in the highlands or mountains. There, water sources such as melting snow and ice feed ____________ young rivers. As the young rivers feed into larger rivers over _________ they may take on characteristics of mature rivers. As the river approaches the ocean it __________ and becomes ___________________taking on the characteristics of an old river. 1. A ____________ river has a steep slope, fast-moving water, V-shaped valleys, and many rapids and waterfalls. Rapids & Waterfalls – caused by _________________________________ 2. A _______________ river has a shallower slope, is slow moving, and winds back and forth in broad curves called ______________. 3. An ________ river moves very slowly, has a nearly flat slope, and has oxbow lakes. Elevated ridges along stream banks are called __________ ________________. Meander Formation: Inside curve:___________ Outside curve: __________ Meanders Oxbow Lakes A river wants to find the shortest, straightest way to the ocean, so it will change paths along the floodplain cutting off wide loops leaving behind a curved body of water called an __________________. 3.4 Floods pg 290 – 292 Rivers may overflow its banks as a _________________. The floodwater may cover part or the entire valley floor where the river runs eroding and depositing sediments. This part of the valley floor is called the ___________________. Floods can _________________ or ___________________. Coarse-grained sediments are deposited by ____________ ____________ water. Fine-grained sediments are deposited by ________ ________ or standing water. Characteristics of Streams & Rivers pg 281-282 _________________ – the distance water travels in a certain amount of time; fast moving rivers erode material more quickly and can carry larger particles. _________________ – the slope or incline of a stream; sources of rivers tend to have large gradient whereas deltas of rivers have small gradients. _________________ – the volume of water a river or stream passes in a certain amount of time; becomes larger as tributaries add water; seasonal changes. _________________ – the path through which water flows; size and shape effect velocity. Basic Drainage Patterns by streams/rivers: