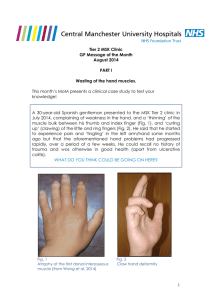
Peripheral Nerves of Upper Limb: Ulnar, Median, Radial
advertisement

We have 3 principal nerves of the upper limb (UL) Ulnar nerve Median nerve Radial nerve C7,8,T1 Medial cord C5678T1 Medial and lateral cord C5-T1 Posterior cord Motor supply Forearm Motor supply Forearm Motor supply Triceps , brachialis (small part), brachioradialis. Extensors of the forearm; by the posterior interosseus nerve - ED - EDM - ECU - ABPL - EPL - EPB - EIN Ulnar ½ of the FDP,FCU Intrinsic hand muscles All intrinsic muscles of the hand except 4 muscles; LOAF are supplied by the median nerve. Flexors of the forearm; pronator teres, FCR, palmaris longus, FDS. Anterior interosseus nerve supplies FPL and ½ of the FDP. Intrinsic hand muscles LOAF; - Lateral 2 lumbricals - Opponens pollicis - Abductor pollicis brevis - Flexor pollicis brevis Sensory supply Medial one and ½ fingers and medial third of the palm of the hand Sensory supply Lateral 3 and ½ fingers and lateral 2/3 of the palm of the hand. The palmar cutaneous branch supplies the lateral palmar skin Partial claw hand Finger spreading test Card test Froment’s test Sensory distribution Ape hand Abductor pollicis brevis test Tinel’s test Phalen’s test Sensory supply Radial 1 ½ fingers dorsally by the superficial branch. Skin on the back of the forearm by the posterior cutaneous nerve of the forearm. Wrist drop Wrist extension test As before; 1. Greet the patient and introduce your self 2. Expose both hands, forearms and elbows 3. Don’t shake hand with the patient Map; Inspect; Sensory Skin Soft tissue Bone & Joint Motor Don’t forget: I would like to examine the neck i.e. cervical rib I would like to examine other peripheral nerves. Four quick tests of the motor and sensory innervation of the hand Autonomous Motor innervation; Median nerve……abduct the thumb Radial nerve……extend the wrist at the level of the MCP joint Ulnar nerve……abduct the fingers Autonomous sensory innervation; Median nerve……index finger Radial nerve……..lateral aspect of the base of the thumb Ulnar nerve……….little finger Ulnar nerve injury Inspect; Scar of injury Claw hand ( ring & little finger) Wasting of the hypothenar muscles Guttering of the dorsum of the hand obvious on the 1st web space. Sensory; Loss of sensation on the little finger (middle & distal phalanges) N.B; compare both sides Motor; Palmar interossei Dorsal interossei Adductor polices card test finger spreading test froment’s test N.B; compare both sides How to identify level of injury? 1. Scar site 2. Flexion of both PIP.J and DIP.J indicate lower lesion but if PIP.J only indicate proximal lesion (Ulnar Paradox) 3. Wasted medial forearm proximal lesion 4. Inability to flex ring & little finger proximal lesion 5. Loss of sensations at the ulnar side of the dorsum of the hand proximal lesion. DDX; Partial claw hand 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Ulnar nerve injury Volkmann’s ischemic contracture Dupuytren’s contracture Post-burn skin contracture Congenital contracture of the PIP.J of the little finger. Complete claw hand 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Combined ulnar & median nerve injury Volkmann’s ischemic contracture Advanced rheumatoid arthritis Lesions of the medial cord of the B.P Lesions of the spinal cord e.g. poliomyelitis Radial nerve injury (spiral groove) Saturday night paralysis Inspect; Wrist drop & finger drop ( ask the patient to keep his hands out in front of him, palms downwards) No wasting of the hand muscles. Sensory; Loss of sensation over the 1st dorsal interosseus space ( between the thumb and the index finger) Loss of sensation over the dorsal aspect of the forearm. Motor; Loss of extension at the level of the MCP.J and wrist. N.B: Triceps weakness only in higher lesion (axilla) Posterior interosseus lesion only finger drop & no sensory loss IPJ extension is preserved in radial n. injury as lumbricals & interossei are supplied by the ulnar and median ns. Median nerve injury Inspect; Thenar muscle wasting Sensory; Loss of sensation over the distal phalanges of the index and middle fingers Motor; Test of abductor polices brevis & Opponens polices Tests; Tinel’s test Phalen’s test Tapping Maximum flexion for one minute will induce pain Qs; What is the finger that receives sensory fibers from all 3 nerves of the hand? Middle finger How to assess the motor power of the 3 nerves of the hand? “ OK ” sign What are the causes of ulnar nerve lesions? How do you treat ulnar nerve palsies? What are the causes of radial n. lesions? What are the causes of carpal tunnel syndrome?