elps5609-sup-0001-figureS1-S4
advertisement

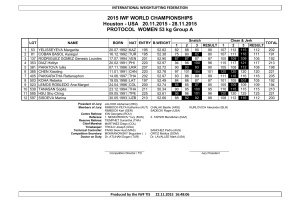
SUPPLEMANTARY DATA and FIGURES 3.1 Preparation of Trietazine Imprinted Monolithic Column The column performance of the MIP column was estimated using alkyl benzenes with the unretained marker THA. Fig S.1 Column performance estimation with the separation of alkyl benzenes. Conditions: buffer 50% pH 7.0, 10 mM PB; 50% ACN; sample: 0.5 mg mL–1 for THA, 0.2 μL mL–1 for alkyl benzenes; sample injection: 5 kV, 0.25 min; UV wavelength: 200 nm; applied voltage: 20 kV; 1THA; 2-eb; 3-pb; 4-bb; 5-peb; 6-hb”. 3.2.1 Effect of pH and the Electric Field Fig S.2 Separation of trietazine selectively from aqueous media containing the competitor reagent, cyanazine, by a MIP column at different pH. Conditions: buffer 50%, 10.0 mM PB; 50% ACN; sample: 1.0 mg mL–1 THA, cyanazine and trietazine; sampleninjection: 5 kV, 0.50 min; UV wavelength: 214 nm; applied electrical field: 10 kV; order of peaks: (1) THA, (2) cyanazine, (3) trietazine. Fig S.3 Separation of trietazine selectively from aqueous media containing the competitor reagent, cyanazine, by a MIP column. Conditions: buffer 50%, pH 11.0, 10.0 mM PB; 50% ACN; sample: 1.0 mg mL–1 THA, cyanazine and trietazine; sample injection: 5 kV, 0.50 min; UV wavelength: 214 nm; applied electrical field: 5 kV, 10 kV, 15 kV and 20 kV; order of peaks: (1) THA, (2) cyanazine, (3) trietazine. 3.2.2 Effect of the Organic Solvent Content (explanations) Fig S.4 Separation of trietazine selectively from aqueous media containing the competitor reagent, cyanazine, by a MIP column. Conditions: pH 11.0, 10.0 mM PB/ACN; sample: 1.0 mg mL–1 THA, cyanazine and trietazine; sample injection: 5 kV, 0.50 min; UV wavelength: 214 nm; applied electrical field: 10 kV; order of peaks: (1) THA, (2) cyanazine, (3) trietazine. In this study, the optimized mobile phase adjusted to pH 11.0 is used for the separation of the trietazine from competitor agent cyanazine with different ACN content. With the increase of ACN content in mobile phase, EOF decreases. The surface of the monolithic column is also totally negatively charged at pH 11.0. Thus, the column exhibited cathodic EOF, which results in the direction of EOF from anode to cathode. Decreased elution time is expected at PB ratio 65% but in our study increment of PB ratio resulted in longer retention times. Due to interactions between nonpolar groups of capillary column and hydrophobic triazine rings of trietazine and cyanazine strong hydrophobic interaction is observed which result in longer elution time. When buffer ratio (pH 11.0) is decreased from 65% to 35%, increased elution time was obtained so dominant separation mechanism is based on EOF. So separation of the solutes at lower ACN ratio is governed mainly by hydrophobic interaction chromatography.