Landforms / Earth Science Study Guide Answer Key
advertisement

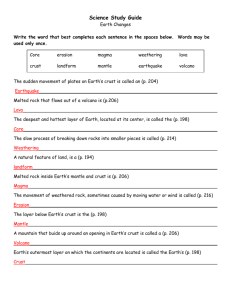
Name _______________________________ Class _______ Date ___________________ Earth’s Landforms Study Guide Fill in the blank. Vocabulary: Surface features 1. A delta is sediment that is deposited at the mouth of a river. 2. Magma is molten rock under Earth’s crust. 3. A hill of sand, made and shaped by the wind is called sand dune. 4. All the kinds of landforms in a certain place are considered a topography. 5. A volcano is a mountain made of lava, ash, or other materials. 6. Jetty is a wall-like structure that traps sand and small rocks. 7. A movement of the ground caused by a sudden release of energy in Earth’s crust is identified as a/an earthquake. 8. A fault is a break in Earth’s crust and runs through the Blue Ridge and Valley & Ridge regions of Georgia. 9. A natural land shape or feature is described as a landform. 10. The collapse of an underground cave, created by water erosion can produce a sink hole. Constructive Processes 11. A constructive process is the building-up of Earth’s surface Landforms created are: a.) A sand_dune created by build-up of blowing sand b.) Barrier islands are formed by water waves and currents moving sand along beaches. c.) Mountain and volcano caused by magma and lava d.) Delta produced by deposition of sediment at the mouth of a river. Destructive Processes 12. A _________________ process is the wearing away of Earth’s surface. Landforms created are: a.) Canyons and valleys produced by running water eroding both sides of a rock formation. b.) Sink hole formed by a collapsed cave due to erosion. Some causes that change Earth’s landforms 13. Erosion the movement of sediment from one place to another. 14. Weathering is the breakdown of rock into smaller pieces called sediment. Technology and Human Intervention used to control landform changes 15. A seismograph and richter scale are tools used to help scientist measure the movement of Earth’s crust. 16. A seismologist studies earthquakes. Short Answer. 17. What is a wall of earth or concrete called and used for? Levee; holds back water to prevent flooding. 18. What is a wall that sticks out into the ocean used to help protect beaches called? Jetty; it traps sand and helps a beach erode more slowly. 19. What can be used to stop the flow of water in a river or stream and can be let out slowly to prevent what? A dam. 20. How can contour plowing prevent soil erosion? The curved plowing allows water to settle in the burrows created by the contour plowing. This helps the soil to stay in place longer and wash away more slowly. Multiple Choice. 21. Which landform change is most easily controlled by humans? a. b. c. d. volcanic deposition coastal erosion surface movement in earthquakes erosion of desert sand by wind 22. Which is NOT a way that plants affect landforms? a. by weathering rock with chemicals b. by adding new nutrients to the soil c. by weathering rock with their roots d. by holding soil in place with their roots 23. Which of the following is NOT a means of flood control? a. dam b. jetty c. levee d. flood plains 24. Which is a cause of earthquakes and volcanic eruptions? a. weathering b. plate movement c. the outer core d. cinder cone 25. Which part of Earth is divided into plates? a. inner core b. outer core c. mantle d. crust 26. How do plants growing on sand dunes prevent wind erosion? a. the dune will move toward the land. b. the dune will move toward the ocean. c. the dune will erode more slowly and may even grow. d. the dune will erode more quickly. 27. How do volcanoes change Earth’s landforms? a. They release pressure that has built up under Earth’s crust. b. They blow ash and lava high into Earth’s atmosphere. c. They form over hot spots. d. They form mountains of ash and lava. Fill in the blank. 28. When two tectonic plates move away from each other it is called divergent. 29. When two tectonic plates push into or collide with each other it is called convergent. 30. When two tectonic plates slide past each other this is considered transform.