Collaborative Common Assessment 1
advertisement

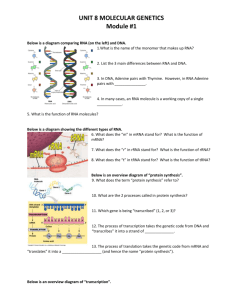
Name: _____________________ Date: _________________ Class Hour: ___________________ Protein Synthesis Test mRNA strand: CUCAAGUGCUUC _____ 1. Use the strand of mRNA above. Which of the following would represent the strand of DNA that the mRNA strand was made from? a) CUCAAGUGCUUC c) GAGTTCACGAAG b) GAGUUCACGAAG d) AGACCTGTAGGA _____ 2. Using the chart above, which of the following is the series of amino acids encoded by the piece of mRNA shown above? a) ser-tyr-arg-gly c) leu-lys-cys-phe b) val-asp-pro-his d) pro-glu-leu-val _____ 3. Use the strand of mRNA above. What sequence of anticodons would complement it? a) GAG-UUC-ACG-AAG c) CUC-GAA-CGU-CUU b) GAG-TTC-ACG-AAG d) CUU-CGU-GAA-CUC ______4. What happens when the ribosome encounters a UGA codon? a) no more RNA is made c) no more protein is made b) no more DNA is made d) tryptophan is added 1 _____ 5. What do codons of mRNA code for? a) stop signals for the ribosomes b) start codon for the ribosomes c) amino acids d) all of these _____ 6. During _____, amino acids are brought to the ribosome by tRNA molecules. a) translation c) replication b) transcription d) synthesis ______ 7. Which of the following is true about a mutation that adds an additional nucleotide? a) They have no effect on the protein b) They are more damaging if they occur at the end of the gene c) They will change every amino acid after the mutation d) They involve the substitution of one base for another _____ 8. What are the nucleotide sequences of tRNA that are complementary to codons? a) amino acids c) protein b) DNA d) anticodon ______9. What are the enzymes responsible for adding nucleotides to the exposed DNA template bases during transcription? a) replicases c) helicases b) RNA polymerases d) DNA polymerases _____10. Which of the types of RNA carries the instructions for making proteins? a) mRNA c) tRNA b) rRNA d) all of them ______11. What are proteins made of? a) nucleotides b) amino acids c) codons d) bases ______12. What are molecules of RNA composed of? a) amino acids b) fatty acids c) monosaccharides d) nucleotides ______13. What does RNA stand for? a) ribonucleic acid b) riboxy nucleic acid c) ribonitrogenous acid d) nucleus 2 _____ 14. Which of the following best describes the function of tRNA? a) synthesize DNA c) make ribosomes b) synthesize mRNA d) transfer amino acids to ribosomes _____ 15. What happens during transcription? a) proteins are synthesized. c) RNA is produced b) DNA is replicated. d) translation occurs. Follow the directions for the following strand of mRNA. mRNA: AUG GCG AAU CGA 16. Translate the strand._________________________________________________ 17. If there was a mutation and the strand was now AUG CCG AAU CGA, what is the new translated strand?______________________________________________ 18. If there was a different mutation from the original strand AUG GGC GAA UCG A, what would be the new translated strand? ______________________________ 19. Which mutation (#17 or #18) is more harmful to the individual? Why? 3 _______20. Which of these drugs would inhibit (prevent) translation in the bacteria? a. Arildone c. Sulfonamides b. Polymyxins d. Aminoglycosides 21. What is another drug that would inhibit (prevent) translation? Explain your answer. 4 22. Match the parts in the diagram with the correct label. _____ RIBOSOME _____ MESSENGER RNA _____ ANTICODON _____ AMINO ACID ______ CODON ______ TRANSFER RNA ______ PROTEIN Explain the diagram and how translation works by using the 7 words listed above in your explanation. UNDERLINE these 7 words. 5 23. Fill in the boxes above with the following terms: Protein, DNA, RNA, transcription, translation 24. Complete the following chart amino acid anticodon codon DNA sequence GGU AAA 6 25. What process does the picture to the right show? Cite one piece of evidence from the image to support your answer. 26. Scientists have found that there are redundant codons that code for amino acids. How does this help protect against harmful mutations? 27. Compare and contrast replication and transcription. 7 28. What are two things that are similar about the structure of the DNA and RNA molecule? 29. What are three things that are different about the structure of the DNA and RNA molecule? 8