File
advertisement

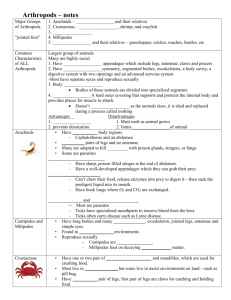
Arthropods A) List the classes within the phylum? The classes within the Phylum Arthropoda include Crustacea, Arachnida, Chilopoda, Diplopoda and Insecta. B) Describe each class in words and pictures? Crustacea Also known as Crustaceans this class is very diverse. Its members display much variation in tagmata and appendages. There is up to 30,000 species of crustaceans. Most are aquatic meaning they live in water, the majority of these are marine which means not just any water the ocean. This class includes lobsters, crabs, crayfish, shrimp, barnacles and several other less familiar forms including the Isopoda, Sowbugs and Pillbugs or Roly-polys. The two most common orders of Crustaceans are Decapoda and Isopoda. Arachnida This class belongs to a subphylum of the Arthropods known as Chelicerata. This means the organisms only have two distinct body regions, a cephlothorax and an abdomen. They six pairs of appendages the first two pairs belong to the mouth part and the other four pairs are the legs and they have no antennae. The first pair of mouth parts are the chelicerae they are three-segmented and pincer-like. For spiders the third segment is the fang. The second pair of mouth parts are the six segmented pedipalps. They may appear leg like for spiders or claw like for scorpions. The four pair of legs are identical all having seven segments. Common orders of Arachnids include Araneae (Spiders), Acari (Mites and Ticks) and Scorpiones (Scorpions). Chilopoda The Centipedes, they long elongated and flattened. They are usually found hidden and one species is even commonly found in houses and buildings. Centipedes are predatory and feed on insects and small animals. Larger centipedes can bite humans but it will usually hurt no then the sting from a bee or wasp. The centipede is made up of a pair of mandibles and two pairs of maxillae. Appendages on the first trunk segment are two curved hollow fangs which contains venom that quickly paralyzes its prey. Diplopoda Millipedes, eyes are usually present, they have one pair of antennae usually containing seven segments, two pairs of legs on each segment (30 or more pairs in total), one pair of mandibles and one pair of maxillae. Millipedes are usually cylindrical which means slightly flattened. Except for the first three segments, each segment has two pairs of short legs. Millipedes are found in damp places like soil leaf litter and so on, most millipedes are beneficial scavengers of decaying plant material. Millipedes do not bite but they give off a foul smelling odour that is strong enough to kill an insect confined with a millipede. Insecta The insects may have wings, either one or two pairs, they have three pairs of legs and one pair of antennae. Insects are the most abundant life for now known to science there are around 1,000,000 species that have been described and named. That is more than all the other known animals put together. C) Identify the characteristics used by scientists to separate the classes? Scientists would use characteristics such as the number of antennae or whether the number of legs vary depending on the organism. The will look at how many distinct body regions they have where the legs are located how many legs. If it has wings and if it has trunk sections on its body how many pairs of legs per segment. D) Create a dichotomous key for the Phylum? 1a. Two pairs of antennae (one pair may be reduced, difficult to see) Number of legs variable. Class Crustacea, go to 2. 1b. One pair of antennae or none. Go to 3. 2a. Two distinct body regions (cephlothorax and abdomen) Five pairs of thoracic legs crayfish, lobsters, shrimp; Order Decapoda. 2b. Three distinct body regions (head, thorax, abdomen) Seven pairs of thoracic legs sowbugs, pillbugs, roly-polys) Order Isopoda. 3a. No antennae; Two distinct body regions (cephlothorax and abdomen) Four pairs of legs spiders, ticks, scorpions, etc. Class Arachnida. 3b. One pair of antennae go to 4. 4a. Three distinct body regions (head, thorax, abdomen) Three pairs of thoracic legs. Wings present or absent Class Insecta. 4b. Two distinct body regions (head and trunk) go to 5. 5a. One pair of legs per trunk segment centipedes Class Chilopoda. 5b. Two pairs of legs per trunk segment millipedes Class Diplopoda.