Unit 1 Test Corrections: Form C Nitrogen cycle: Nitrogen travels from
advertisement

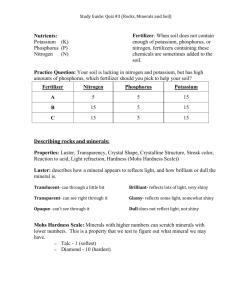
Unit 1 Test Corrections: Form C 1. Nitrogen cycle: Nitrogen travels from air to soil, becomes ammonia. DIAGRAM this process. NAME this process. 2. Phosphorus cycle: How does P cycle through an ecosystem? 3. Nitrogen cycle: decaying organisms releasing nitrogen into soil. DIAGRAM this process. NAME this process. 4. Water cycle – human effects: Graph the amount of run-off over the course of time as humans pave over (parking lots etc.) natural vegetation. Graph the rate of transpiration over the course of time as tropical rainforests are cut/burned down. Write a brief explanation for each. 5. Tropical rainforest soil vs. grassland soil. Contrast these in terms of nutrients and pH. EXPLAIN why they are so different. 6. Make a chart that compares the gases that are released by the following processes: combustion, decomposition, photosynthesis, and cellular respiration (aerobic). 7. Explain energy efficiency and eating at a lower trophic level. 8. Phosphorus cycle: Why is phosphorus a limiting factor in ecosystems? EXPLAIN 9. List all of the anaerobic cellular respiration products. What is anaerobic respiration also known as? 10. Explain why shrimp farming in Mangrove swamps is considered “Tragedy of the Commons”. Choose another free-access resource and explain how it is undergoing Tragedy of the Commons. 11. Soil texture and particle size. Diagram and put in order of either increasing or decreasing size. 12. Diagram: photosynthesis and aerobic respiration in the Carbon cycle. 13. Explain what color has to do with topsoil in terms of a physical, qualitative test. 14. Diagram and label: a soil profile. 15. Diagram and label: how does water cycle through an ecosystem? 16. Contrast: matter cycles vs. energy flow 17. Contrast: abiotic vs. biotic, give two examples of each. 18. Write the equation for the process that is responsible for providing Oxygen to the atmosphere. 19. What is the major sink for Nitrogen? 20. Sulfur cycle – human effects: graph the amount of SO2 in the atmosphere over the course of time. Briefly explain your graph! 21. Define leaching. Explain what leaching has to do with tropical rainforest soil. 22. Contrast clay’s permeability vs. porosity. 23. Use the second law of thermodynamics to explain energy flow through a food chain. 24. Ecological efficiency – energy pyramids: The ecological efficiency of a particular ecosystem is 25%. If the green plants capture 2000 units of energy, about ____ units will be available for SECONDARY consumers and about ____ total units of energy will be “lost”. 25. Make THREE graphs that indicate what is happening to each process with increased urban development: 1) transpiration 2)run-off 3) groundwater recharge 26. Carbon cycle – human effects: describe sources and graph the level of atmospheric CO2 level over the course of time. Write a brief explanation for your graph. 27. Carbon cycle and photosynthesis: describe or diagram/label how abiotic carbon enters the biotic world. 28. Nitrogen cycle: what microscopic organism plays a vital role in the Nitrogen cycle? 29. Using energy pyramids, explain why more people could be fed if they ate at a lower trophic level. 30. What is “loam”??? Why is considered a good type of soil for crops??? 31. Nitrogen cycle: diagram/label the process of creating nitrates – plant food! 32. Explain why polluting the atmosphere is considered “Tragedy of the Commons”. Choose another free-access resource and explain how it is undergoing Tragedy of the Commons. 33. Using the Environmental Impact Model, explain why the developing world’s variable that makes a bigger impact is population while the developed world’s variable that makes a bigger impact is affluence. 34. Phosphorus cycle: Why is phosphorus a limiting factor in ecosystems? EXPLAIN 35. Contrast: GPP vs. NPP, AND calculate the NPP of a field if the GPP is 0.007 g/cm2/day and the plants use 25% of the GPP for their own respiration. 36. Biodiversity: explain what biodiversity has to do with the overall health of an ecosystem. 37. Contrast: population vs. community vs. ecosystem 38 – 40. Draw an energy pyramid with four trophic levels. Include the “source of all energy for life on earth”. Label each trophic level with the appropriate vocabulary. Give an example of a real organism that would occupy each trophic level. Unit 1 Test: diagrams AND explanations!!! Form B 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. Contrast: GPP vs. NPP Soil texture Biodiversity: explain what biodiversity has to do with the overall health of an ecosystem. Matter cycles vs. energy flow Carbon cycle – human effects: describe sources and graph the level of atmospheric CO2 level over the course of time. Write a brief explanation for your graph. Soil texture and particle size Contrast: population vs. community vs. ecosystem Carbon/Oxygen cycle – photosynthesis and aerobic respiration Water cycle – human effects: Graph the amount of run-off over the course of time as humans pave over (parking lots etc.) natural vegetation. Graph the rate of transpiration over the course of time as tropical rainforests are cut/burned down. Write a brief explanation for each. Explain energy efficiency and eating at a lower trophic level Tropical rainforest soil vs. grassland soil Nitrogen cycle: Nitrogen travels from air to soil, becomes ammonia Leaching Humus: definition (put it into your own words – don’t say “decaying organic matter”) Photosynthesis – atmospheric gases absorbed vs. released Anaerobic cellular respiration products Soil particles – chemistry Nitrogen cycle: creating nitrates – plant food! Nitrogen cycle: decaying organisms releasing nitrogen into soil Abiotic vs. biotic Photosynthesis and the carbon cycle Clay: permeability vs. porosity Second law of thermodynamics and the energy pyramid Phosphorus cycle: How does P cycle through an ecosystem? Carbon cycle – photosynthesis Topsoil – color Water cycle: how does water cycle through an ecosystem? Ecological efficiency – energy pyramids: The ecological efficiency of a particular ecosystem is 25%. If the green plants capture 2000 units of energy, about ____ units will be available for SECONDARY consumers and about ____ total units of energy will be “lost”. Energy pyramid – second law of thermodynamics Phosphorus cycle: Why is phosphorus a limiting factor in ecosystems? Soil profile Nitrogen cycle: atmospheric portion 33. Energy problem: One gram of grass provides 25 kJ of energy. If a mouse eats 15 grams of grass and uses 60% of the energy for its own cellular respiration, how much energy would be available for the next trophic level? 34. Nutrients and limiting factor 35. Nitrogen cycle: Nitrogen travels from air to soil, becomes ammonia 36. Sulfur cycle – human effects: graph the amount of SO2 in the atmosphere over the course of time. Briefly explain your graph! 37 – 40. Draw and energy pyramid with four trophic levels. Include the “source of all energy for life on earth”. Label each trophic level with the appropriate vocabulary. Give an example of a real organism that would occupy each trophic level.