File
advertisement
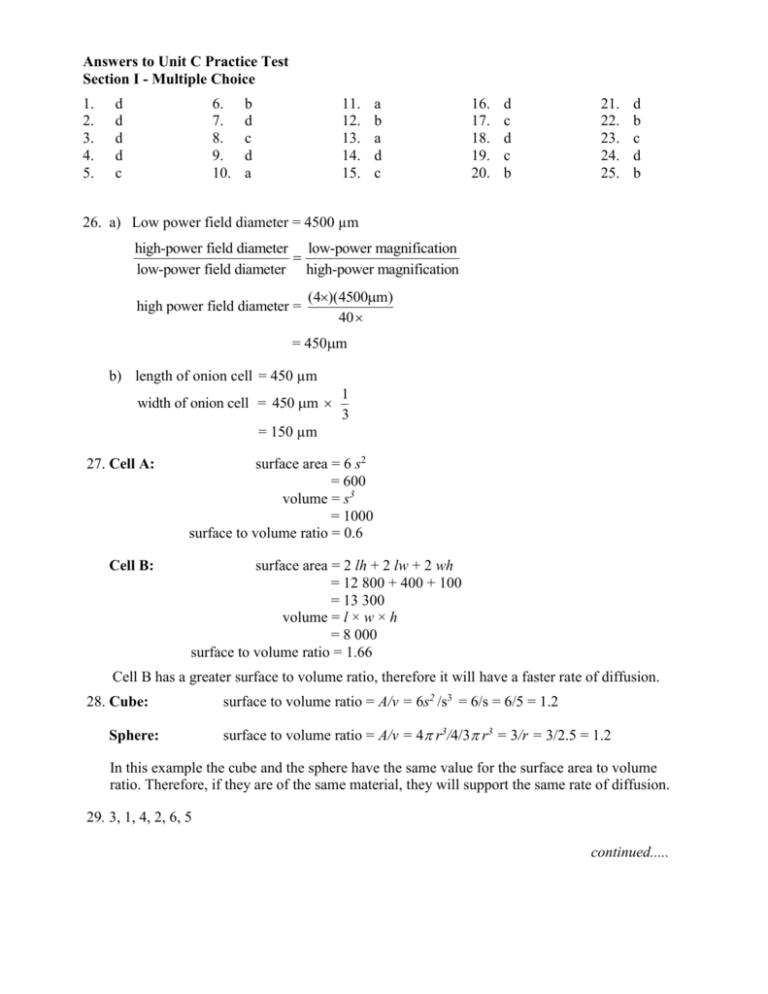
Answers to Unit C Practice Test Section I - Multiple Choice 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. d d d d c 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. b d c d a 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. a b a d c 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. d c d c b 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. d b c d b 26. a) Low power field diameter = 4500 µm high-power field diameter low-power magnification low-power field diameter high-power magnification high power field diameter = (4)(4500m) 40 = 450m b) length of onion cell = 450 µm width of onion cell = 450 m 1 3 = 150 µm 27. Cell A: Cell B: surface area = 6 s2 = 600 volume = s3 = 1000 surface to volume ratio = 0.6 surface area = 2 lh + 2 lw + 2 wh = 12 800 + 400 + 100 = 13 300 volume = l × w × h = 8 000 surface to volume ratio = 1.66 Cell B has a greater surface to volume ratio, therefore it will have a faster rate of diffusion. 28. Cube: Sphere: surface to volume ratio = A/v = 6s2 /s3 = 6/s = 6/5 = 1.2 surface to volume ratio = A/v = 4 r3/4/3 r3 = 3/r = 3/2.5 = 1.2 In this example the cube and the sphere have the same value for the surface area to volume ratio. Therefore, if they are of the same material, they will support the same rate of diffusion. 29. 3, 1, 4, 2, 6, 5 continued..... Unit C—Cycling of Matter in Living Systems Section III Skills 30. Leaf A is probably Elodea, because it grows under water and would not need stomata for carbon dioxide entry. Carbon dioxide will diffuse into the leaf from the water. Thin leaves allow for a large surface to volume ratio for diffusion of carbon dioxide. It also would not need air spaces for carbon dioxide gas and to stay submersed. Leaf B is probably water lily, which will receive sunlight on the upper surface. Chloroplasts here will capture sunlight. Stomata on the upper surface will allow carbon dioxide gas to enter. Air spaces will help it float. A thick cuticle will protect the surface and help keep it flat. Leaf C is probably cattail. The leaf is in the air and stomata allow carbon dioxide entry at both surfaces. The cuticle reduces dehydration from both surfaces. 31. a) The stem will bend away from the auxin site because auxin causes stems to elongate. b) Student answers will vary but should identify the variables to be controlled such as keeping the amount and direction of light the same for all plants. The amount of auxin mixture applied to each stem should be the same. Time between application of auxin and measuring should be constant for all plants. There should be at least two plants used for each concentration (two trials) for greater accuracy. Plants should be kept in the same area so that temperature, humidity, water supplied and light conditions are the same. Control plants should have the same amount of petroleum jelly applied with no auxin added. The method for measuring the degree of bending measurement should be included, and could involve using a protractor to measure the angle from the vertical. Section IV Written Response 32. Answers will include a description of the phospholipid bilayer as the matrix that holds the proteins. Channel proteins create pores to allow small water-soluble particles to cross. Carrier proteins attach to large molecules, change shape, and move the molecule across into the cell. Recognition proteins are embedded at the surface and allow cells to recognize each other and foreign substances. Receptor proteins at the surface may bind to molecules to carry them in by endocytosis or bind and trigger some action within the cell. 33. Spallanzani boiled broth, drew off the air and sealed the flask. This left the possibility of arguing that air was needed for spontaneous generation. Pasteur, however, boiled broth in flasks, which were open to the air, the only difference being in the shape of the neck. No organisms grew in the flask with the bent S-shaped neck. The only explanation was that organisms on dust particles settled out in the neck before reaching the broth. Therefore, organisms must come from other organisms. 34. a) Water moves by osmosis into the root hairs because minerals have been actively transported into the cells. Root pressure builds up. As transpiration draws water from the leaf, water molecules move up the xylem ducts because they are attracted to each other (cohesion). Adhesion also helps water molecules climb up the xylem to the leaf. Water moves into the ground tissue for photosynthesis. b) Sugar is produced in the ground tissue cells of the leaf. Companion cells of the phloem take in sugar by active transport. Water follows by osmosis and then water and sugar move into the sieve cells. The result is increased pressure in the phloem. At the sink, sugar is moved into cells by active transport. These cells may be using the sugar for growth, respiration or storage. Water follows the sugar. This decreased pressure at the sink and the increased pressure at the source results in the movement of sugar from source to sink. continued..... 35. Students may choose to describe one of the following: liposomes used to deliver medications in HIV and cancer therapies, or to deliver DNA into tumor cells; peritoneal dialysis in which toxic substances diffuse into a dialysate in the abdominal cavity; hemodialysis in which blood passes by a dialysate and toxins diffuse across a membrane; or desalination of sea water by reverse osmosis. 36. The slush landing on the trees at the roadside contains salt. This salty solution is hypertonic to the leaf cells. Water moves by osmosis out of the cells and plasmolysis occurs. Over a prolonged time the cells die because they cannot carry on their normal functions.