File
advertisement

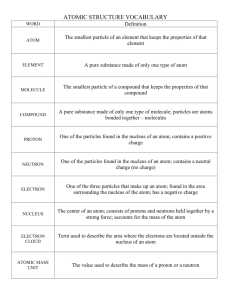
Science 9 Section 1.3 Handout 1 Section 1.3 Notes Atomic Theory (Text Pages 24 – 33) Key Terms: Atom Neutron Subatomic particle Conjecture (notes) Atomic Theory Proton Scientific Theory (notes) Inference Electron Nucleus Scientific Law (notes) Learning Objectives: Distinguish between a theory and a law in terms of science Be able to describe the structure and parts of an atom. Know the charge, location and relative mass of the following subatomic particles: (i) protons (ii) electrons (iii) neutrons Describe the contributions of the following to the development of our current atomic theory: (i) Early Greeks (Empedocles, Democritus, Aristotle) (ii) Dalton (iii) Thompson (iv) Rutherford (v) Bohr Be able to describe how Rutherford’s experiment as an example of how improved technology allows scientists to develop and refine theories. _____________________________________________________________________________________ Portfolio Items: Worksheet #5 – Bill Nye Video - Text Questions: Page 33 #’s 1, 3-5, 7-11, 14, 15, 16 Worksheet #6 – “Black Box” Activity Atom foldable _____________________________________________________________________________________ Scientific Theory vs Scientific Law List any theories or laws you may have heard of in the space below! Add examples from the board! What is the difference between theory and law? - The amount of _____________________________ that scientists have in the _______________ ___________________________________________. - More ______________________________ leads to a higher level of confidence. - Evidence comes from _________________________ and careful _________________________. Science 9 Section 1.3 Handout 2 Scientific Laws - Very high _____________________________________________. - Supported by a ________________________________________________________________. o - (Observation is not enough to form a law.) ____________________________________________________________. Ex: Law of Gravity, Law of Reflection Scientific Theories - ______________________________________________________________________________. - ___________________________________ needed for __________ scientists to accept the idea. - ______________________________________________________________________________. Ex: Big Bang Theory, Atomic theory Conjecture - When scientists propose ideas based on ______________________________________. - Conjecture must be _________________________________ Atomic Theory Scientists that first tried to describe the properties of atoms faced a significant challenge: How do you study what you cannot see? They developed their ideas and models without every touching or seeing an individual atom. How is this possible? - They made inferences based on what they COULD observe. Inference: ____________________________________________________________. Analogy: Science 9 Section 1.3 Handout 3 In the next activity you will make inferences about the contents of several mystery boxes. You will use these inferences to develop a theory about what is inside of each box! - Some things that could be inferred include size, shape, weight, density, number of items, etc. **Complete the Mystery Box Activity attached at the end of this handout.** Structure of an Atom - All matter is composed of incredibly small particles called atoms. o - For example, you can fit about one million atoms on the tip of a pin! The word atom comes from the Greek word atomos which means “cannot be cut” Atom: __________ _____. Atom Diagram: (note that this is a simplified diagram! It is actually much more complex) Science 9 Section 1.3 Handout 4 Main Parts of an Atom: Nucleus: the dense, relatively heavy central part of an atom. It contains protons and neutrons. Energy Levels: areas surrounding the nucleus. They contain electrons. Subatomic particles: smaller particles including protons, neutrons and electrons. (foldable) Subatomic Particle Charge Location in Atom Relative Mass Important Points about Atoms - Different types of matter are made of __________________________________________________. o One atom is different from another atom based on the . - Atoms are mostly _______________________ _! are very far away from the nucleus. o If an atom was the size of a football field, the nucleus would be the size of a in the centre. Science 9 Section 1.3 Handout Mystery Box Activity - Arrange in groups of 4. Each group will make observations on as many boxes as time allows. Each group is given a “mystery box” You will have 8 minutes to make as many observations and inferences as you can. Each observation must have an accompanying inference. State your theory about the contents for your boxy based on the observations and inferences you made. **There will be prizes for the group with the most observations/inferences** **There will be prizes for the most accurately described theory for each box!** Black Box # __________ Observations Inferences Theory: (can be a diagram or description) Black Box # __________ Observations Inferences 5 Science 9 Section 1.3 Handout Theory: Black Box # __________ Observations Theory: Inferences 6