Reptiles of Utah
advertisement
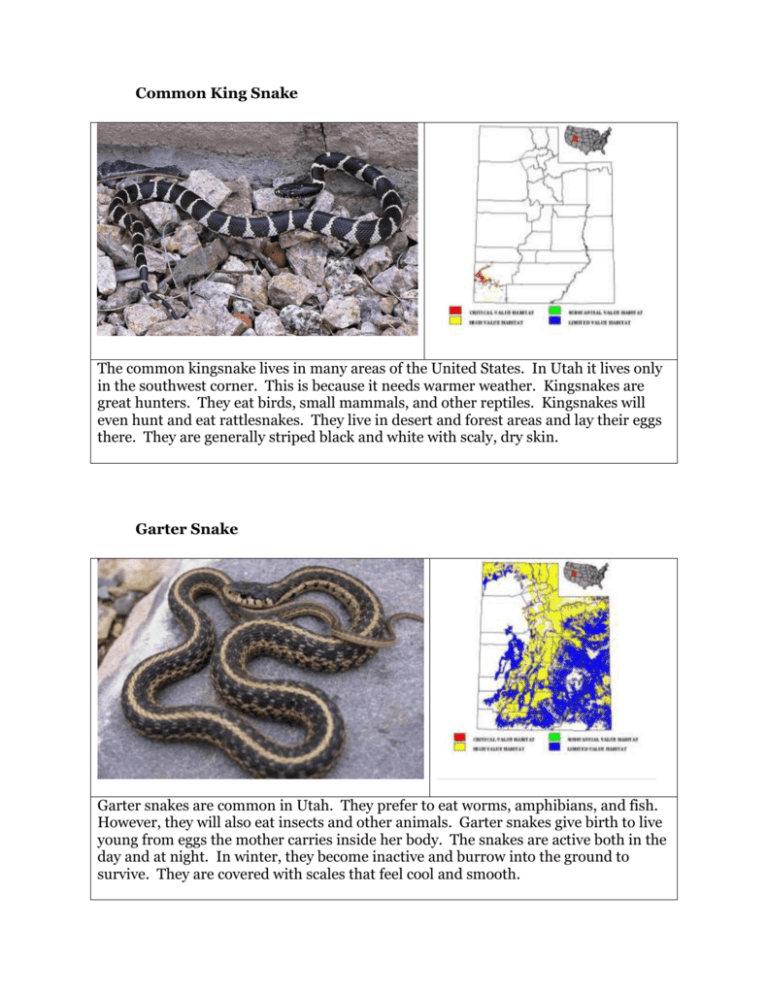
Common King Snake The common kingsnake lives in many areas of the United States. In Utah it lives only in the southwest corner. This is because it needs warmer weather. Kingsnakes are great hunters. They eat birds, small mammals, and other reptiles. Kingsnakes will even hunt and eat rattlesnakes. They live in desert and forest areas and lay their eggs there. They are generally striped black and white with scaly, dry skin. Garter Snake Garter snakes are common in Utah. They prefer to eat worms, amphibians, and fish. However, they will also eat insects and other animals. Garter snakes give birth to live young from eggs the mother carries inside her body. The snakes are active both in the day and at night. In winter, they become inactive and burrow into the ground to survive. They are covered with scales that feel cool and smooth. Western Rattlesnake The Western rattlesnake lives in much of Utah. It can live in either forest or desert areas. Rattlesnakes eat small mammals, birds, and lizards. Females give birth to live young from eggs stored in their bodies. Rattlesnakes are covered with scales that feel smooth and cool. They are active during warmer months of the year. In the winter they hide and become inactive. They have hollow fangs with poison for catching prey. The rattle at the end of their tail warns larger animals away from them. Sagebrush Lizard The Sagebrush lizard is usually found living near sagebrush. Lizards are active during the warmer months. In winter, they hibernate under rocks or in abandoned animal dens. Sagebrush lizards lay around 12 eggs that take 2 months to hatch. Both adult and young lizards eat insects and spiders. Sagebrush lizards are covered with scales and have long, strong legs and feet. Gila Monster Gila Monsters are venomous lizards that live in the southwest part of Utah. They are covered with scales and have bright orange and black markings. They eat mostly eggs, small mammals, lizards, and insects. They lay about 10 eggs in the middle of summer. Gila monsters use their venom to capture prey. They are inactive about 95% of the time. These slow-moving lizards are becoming endangered because of habitat loss. Desert Horned Lizard The Desert horned lizard is sometimes called a “horned toad” though it isn’t a toad. It is covered with scales and is a sandy brown color with black and white spots. The lizard lives in desert areas of Utah and can occasionally be found in city backyards. They eat ants and beetles along with plant material. The female lays around 7 eggs in summer. The lizards become inactive in the winter and also when it becomes very hot in summer. Desert Tortoise Desert tortoises live in southern Utah. They are a threatened species. Tortoises are covered with a hard, scaly shell. Their skin is also scale covered. Females lay a few eggs each summer that hatch in the fall. Desert tortoises eat plant material such as cacti, grasses, and shrubs. They live in desert areas as well as in low forests and grasslands. The tortoises hibernate in the winter in burrows that may have house many tortoises. Snapping Turtle Snapping Turtles live in wetlands in southwestern Utah. They are covered with a strong scaly shell. Their skin is also covered in scales. Snapping turtles will eat nearly anything including plants, fish, small mammals, insects and amphibians. They lay eggs in the spring that take 3 months to hatch. Snapping turtles are not native. They threaten endangered fish that live in the rivers of southwest Utah.