UNIT 2_Study Guide Chapters 4
advertisement

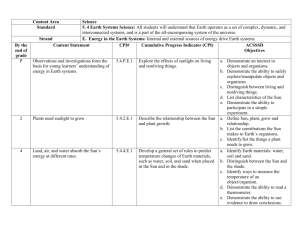
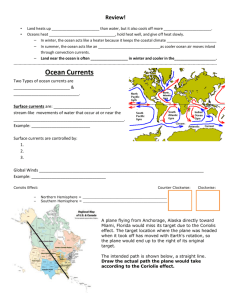
APES Study Guide - Unit 2: THE LIVING WORLD APES Study Guide - Unit 2: THE LIVING WORLD The second unit of APES is an introduction to ecology - the study of how living organisms interact with one another and with their surroundings. The second unit of APES is an introduction to ecology - the study of how living organisms interact with one another and with their surroundings. Reference: Chapter 4 – Global Climates Handouts: – Albedo, – Wind, – Layers of Atmosphere – Ocean Currents, – Climate Vocabulary: • Adiabatic Cooling • Adiabatic Heating • Albedo • Coriolis Effect • El Nino-Southern Oscillation (Enso) • Gyres • Convection Cells • Intertropical Convergence Zone • Latent Heat Release • Trade Winds • Positive Feedback Loop • Negative Feedback Loop • Rain Shadow • Westerlies • Stratosphere • Thermohaline Circulation • Troposphere • Upwelling • Mesosphere • Deep Ocean Currents • Thermosphere • Ozone Layer Reference: Chapter 4 – Global Climates Handouts: – Albedo, – Wind, – Layers of Atmosphere – Ocean Currents, – Climate Vocabulary: • Adiabatic Cooling • Adiabatic Heating • Albedo • Coriolis Effect • El Nino-Southern Oscillation (Enso) • Gyres • Convection Cells • Intertropical Convergence Zone • Latent Heat Release • Trade Winds • Positive Feedback Loop • Negative Feedback Loop • Rain Shadow • Westerlies • Stratosphere • Thermohaline Circulation • Troposphere • Upwelling • Mesosphere • Deep Ocean Currents • Thermosphere • Ozone Layer Study Guide Questions (SGQ): Chapter 4 1. Describe the forces that drive global circulation patterns and how those patterns determine weather and climate 2. What effect does Earth’s rotation have on atmospheric circulation and ocean currents? 3. In what ways are atmospheric and oceanic circulation patterns similar? How are they different? 4. Explain how certain factors can affect an areas climate. 5. Distinguish between weather and climate. 6. Define types of ocean currents and explain how they, along with global air circulation, support the formation of humid, temperate, and arid regions. 7. What is the rain shadow effect and how can it lead to the formation of deserts? 8. Why do cities tend to have more haze and smog, higher temperatures, and lower wind speeds than the surrounding countryside? 9. Describe how climate and vegetation vary with latitude and elevation. 10. Be familiar with El Nino and La Nina 11. Understand the Gulf of the Farallones and the type of current that influence its ecosystem. 12. Be familiar with the diagram of the layers of the atmosphere, albedo, global winds and convection diagram. 13. Be prepared to describe an areas climate. Study Guide Questions (SGQ): Chapter 4 1. Describe the forces that drive global circulation patterns and how those patterns determine weather and climate 2. What effect does Earth’s rotation have on atmospheric circulation and ocean currents? 3. In what ways are atmospheric and oceanic circulation patterns similar? How are they different? 4. Explain how certain factors can affect an areas climate. 5. Distinguish between weather and climate. 6. Define types of ocean currents and explain how they, along with global air circulation, support the formation of humid, temperate, and arid regions. 7. What is the rain shadow effect and how can it lead to the formation of deserts? 8. Why do cities tend to have more haze and smog, higher temperatures, and lower wind speeds than the surrounding countryside? 9. Describe how climate and vegetation vary with latitude and elevation. 10. Be familiar with El Nino and La Nina 11. Understand the Gulf of the Farallones and the type of current that influence its ecosystem. 12. Be familiar with the diagram of the layers of the atmosphere, albedo, global winds and convection diagram. 13. Be prepared to describe an areas climate.