Kinetic and Potential Energy Worksheet - Practice Problems
advertisement

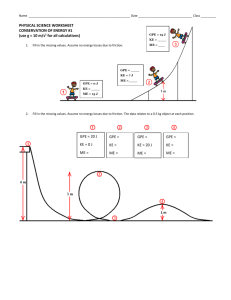
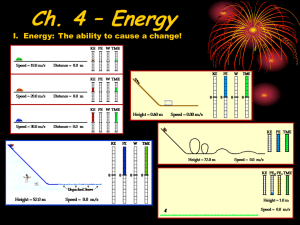
Name:________________________ Period: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 KINETIC AND POTENTIAL ENERGY WORKSHEET Determine whether the objects in the following problems have kinetic or potential energy. Then choose the correct formula to use: KE= 1/2 m v2 GPE = mass x gravitational acceleration (9.8m/s2) x height Energy= Joules (J) Weight= Newton (N) Mass= kilograms (kg) Velocity= meters per second (m/s) Gravitational acceleration= (9.8 m/s2) 1. You serve a volleyball with a mass of 2.1 kg. The ball leaves your hand with a speed of 30 m/s. The ball has Kinetic energy. Calculate it. KE = 1/2mv2 KE = ? J m = 2.1 kg v = 30m/s KE = ½ x 2.1 kg x (30m/s)2 KE = 945 J 2. A baby carriage is sitting at the top of a hill that is 21 m high. The carriage with the baby weighs 12 N. The carriage has potential energy. Calculate it. GPE = mgh w = 12 N h =21 m GPE = 12N x 21 m GPE = 252 J 3. A car is traveling with a velocity of 40 m/s and has a mass of 1120 kg. The car has kinetic energy. Calculate it. KE = 1/2mv2 m = 1120 kg v = 40 m/s KE = ½ x 1120 kg x (40 m/s)2 KE = 896,000 J 4. A cinder block is sitting on a platform 20 m high. It weighs 79 N. The block has potential energy. Calculate it. GPE = mgh GPE = ? J W = 79 N h = 20 m GPE = 79 N x 20 m GPE = 1580 J 5. There is a bell at the top of a tower that is 45 m high. The bell weighs 190 N. The bell has potential energy. Calculate it. GPE = mgh GPE = ? J w = 190 N h = 45 m GPE = 190 N x 45 m GPE = 8550 J 6. A roller coaster is at the top of a 72 m hill and weighs 966 N. The coaster (at this moment) has potential energy. Calculate it. GPE = mgh GPE = ? J w = 966 N h = 72 m GPE = 966 N x 72 m GPE = 69,552 J 7. What is the kinetic energy of a 3-kilogram ball that is rolling at 2 meters per second? KE = 1/2mv2 KE = ? J m = 3 kg v = 2 m/s KE = ½ x 3 kg x (2 m/s)2 KE = 6 J 8. Two objects were lifted by a machine. One object had a mass of 2 kilograms, and was lifted at a speed of 2 m/sec. The other had a mass of 4 kilograms and was lifted at a rate of 3 m/sec. a. Which object had more kinetic energy while it was being lifted? KE = 1/2mv2 Object #1 m = 2 kg v = 2 m/s KE = ? J KE = ½ x 2 kg x (2 m/s) 2 KE = 4 J Object #2 m = 4 kg v = 3 m/s KE = ? J KE = ½ x 4 kg x (3 m/s)2 KE = 18 J b. Which object had more potential energy when it was lifted to a distance of 10 meters? The 4 kg object had more potential energy when it was lifted 10 m. GPE = mgh. A greater mass would make a greater GPE.