Kinetic and potential energy
advertisement
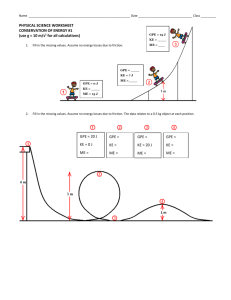
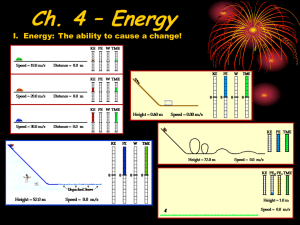
Energy • Every observable change requires energy. • Energy comes in several different forms (food, electrical, solar, chemical), and can be converted from one form to another. Kinetic energy • Energy associated with motion • KE = ½ mv2 • units are Joules • mass MUST be in kg • velocity MUST be in m/s Example: What is the kinetic energy of a baseball moving at a speed of 40 m/s if the baseball has a mass of 0.15 kg? KE = ½ mv2 KE = ½ (0.15 kg)(40 m/s)2 KE = 120 J Potential Energy: The energy stored in motionless objects Four types: 1. Elastic potential energy • Stored by something that can stretch or compress • Energy is released when the object is allowed to return to its normal state 2. Chemical Potential Energy • Chemical bonds store energy. • Breaking the bonds releases the energy 3. Electrical and Nuclear Potential Energy • Electrical-stored energy due to the position of electrical charges. • Nuclear-energy stored in the nucleus of an atom 4. Gravitational Potential Energy • Anything that can fall has stored GPE • GPE = mgh • m = mass in kg • g = gravitational acceleration (9.8 m/s2) • h = height above the ground • The higher above the ground something is, the greater the GPE EX: Find the height of a baseball with a mass of 0.15 kg that has a GPE of 73.5 J. GPE = mgh 73.5 J = (0.15 kg)(9.8 m/s2)h h = 50 m Conservation of Energy: Energy is neither created nor destroyed as is changes from one form to another GPE = mgh= (2 kg)(9.8 m/s2)(10 m) = 196 J 2 kg KE = 0 J While the energy has changed form, the amount of energy has not changed. Energy has been conserved. h = 10 m 2 kg KE = ½ mv2 = 196 J GPE = 0 J 8m 6m 4m 2m 3 kg GPE = (3 kg)(9.8 m/s2)(8 m) = 235 J KE = 0 3 kg GPE = (3 kg)(9.8 m/s2)(6 m) = 176 J 3 kg GPE = (3 kg)(9.8 m/s2)(4 m) = 118 J KE = 235 J - 118 J = 118 J 3 kg GPE = (3 kg)(9.8 m/s2)(2 m) = 59 J KE = 235 J - 59 J = 176 J 3 kg GPE = 0 J KE = 235 J KE = 235 J - 176 J = 59 J 8m 6m 4m 2m 3 kg KE = 0 v=0 3 kg KE = 59 J = ½(3 kg)v2 v = (2*59/3) = 6.3 m/s 3 kg KE = 118 J v = (2*118/3) = 8.9 m/s 3 kg KE = 176 J v = (2*176/3) = 10.8 m/s 3 kg KE = 235 J v = (2*235/3) = 12.5 m/s Mechanical Energy = KE + GPE GPE = max KE = 0 GPE = max KE = 0 GPE = 0 KE = max Q: Why does a real pendulum stop swinging? A: Because friction converts some of the mechanical energy into thermal energy. E = mc2 During nuclear fusion, some of the mass of the fusing nucleii is transformed into energy. 4 He 2 + 2 H 1 + Energy 3 H 1 neutron