View
advertisement
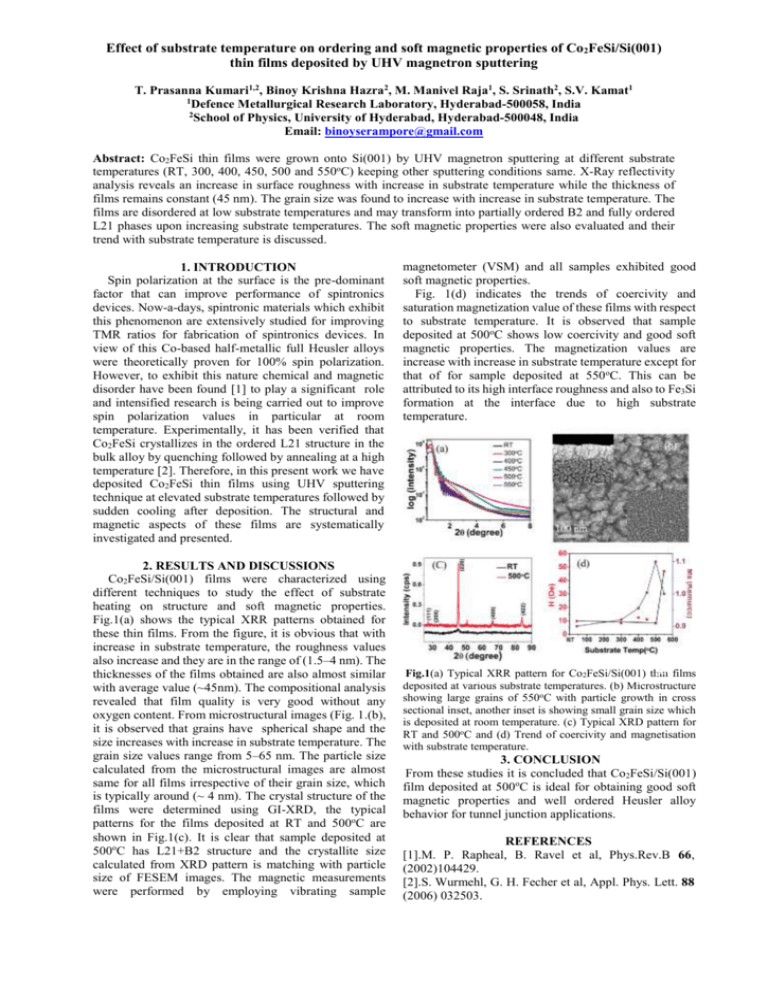
Effect of substrate temperature on ordering and soft magnetic properties of Co2FeSi/Si(001) thin films deposited by UHV magnetron sputtering T. Prasanna Kumari1,2, Binoy Krishna Hazra2, M. Manivel Raja1, S. Srinath2, S.V. Kamat1 1 Defence Metallurgical Research Laboratory, Hyderabad-500058, India 2 School of Physics, University of Hyderabad, Hyderabad-500048, India Email: binoyserampore@gmail.com Abstract: Co2FeSi thin films were grown onto Si(001) by UHV magnetron sputtering at different substrate temperatures (RT, 300, 400, 450, 500 and 550oC) keeping other sputtering conditions same. X-Ray reflectivity analysis reveals an increase in surface roughness with increase in substrate temperature while the thickness of films remains constant (45 nm). The grain size was found to increase with increase in substrate temperature. The films are disordered at low substrate temperatures and may transform into partially ordered B2 and fully ordered L21 phases upon increasing substrate temperatures. The soft magnetic properties were also evaluated and their trend with substrate temperature is discussed. 1. INTRODUCTION Spin polarization at the surface is the pre-dominant factor that can improve performance of spintronics devices. Now-a-days, spintronic materials which exhibit this phenomenon are extensively studied for improving TMR ratios for fabrication of spintronics devices. In view of this Co-based half-metallic full Heusler alloys were theoretically proven for 100% spin polarization. However, to exhibit this nature chemical and magnetic disorder have been found [1] to play a significant role and intensified research is being carried out to improve spin polarization values in particular at room temperature. Experimentally, it has been verified that Co2FeSi crystallizes in the ordered L21 structure in the bulk alloy by quenching followed by annealing at a high temperature [2]. Therefore, in this present work we have deposited Co2FeSi thin films using UHV sputtering technique at elevated substrate temperatures followed by sudden cooling after deposition. The structural and magnetic aspects of these films are systematically investigated and presented. 2. RESULTS AND DISCUSSIONS Co2FeSi/Si(001) films were characterized using different techniques to study the effect of substrate heating on structure and soft magnetic properties. Fig.1(a) shows the typical XRR patterns obtained for these thin films. From the figure, it is obvious that with increase in substrate temperature, the roughness values also increase and they are in the range of (1.5–4 nm). The thicknesses of the films obtained are also almost similar with average value (~45nm). The compositional analysis revealed that film quality is very good without any oxygen content. From microstructural images (Fig. 1.(b), it is observed that grains have spherical shape and the size increases with increase in substrate temperature. The grain size values range from 5–65 nm. The particle size calculated from the microstructural images are almost same for all films irrespective of their grain size, which is typically around (~ 4 nm). The crystal structure of the films were determined using GI-XRD, the typical patterns for the films deposited at RT and 500oC are shown in Fig.1(c). It is clear that sample deposited at 500oC has L21+B2 structure and the crystallite size calculated from XRD pattern is matching with particle size of FESEM images. The magnetic measurements were performed by employing vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM) and all samples exhibited good soft magnetic properties. Fig. 1(d) indicates the trends of coercivity and saturation magnetization value of these films with respect to substrate temperature. It is observed that sample deposited at 500oC shows low coercivity and good soft magnetic properties. The magnetization values are increase with increase in substrate temperature except for that of for sample deposited at 550oC. This can be attributed to its high interface roughness and also to Fe3Si formation at the interface due to high substrate temperature. (b) films Fig.1(a) Typical XRR pattern for Co2FeSi/Si(001) thin deposited at various substrate temperatures. (b) Microstructure showing large grains of 550oC with particle growth in cross sectional inset, another inset is showing small grain size which is deposited at room temperature. (c) Typical XRD pattern for RT and 500oC and (d) Trend of coercivity and magnetisation with substrate temperature. 3. CONCLUSION From these studies it is concluded that Co2FeSi/Si(001) film deposited at 500oC is ideal for obtaining good soft magnetic properties and well ordered Heusler alloy behavior for tunnel junction applications. REFERENCES [1].M. P. Rapheal, B. Ravel et al, Phys.Rev.B 66, (2002)104429. [2].S. Wurmehl, G. H. Fecher et al, Appl. Phys. Lett. 88 (2006) 032503.