View
advertisement
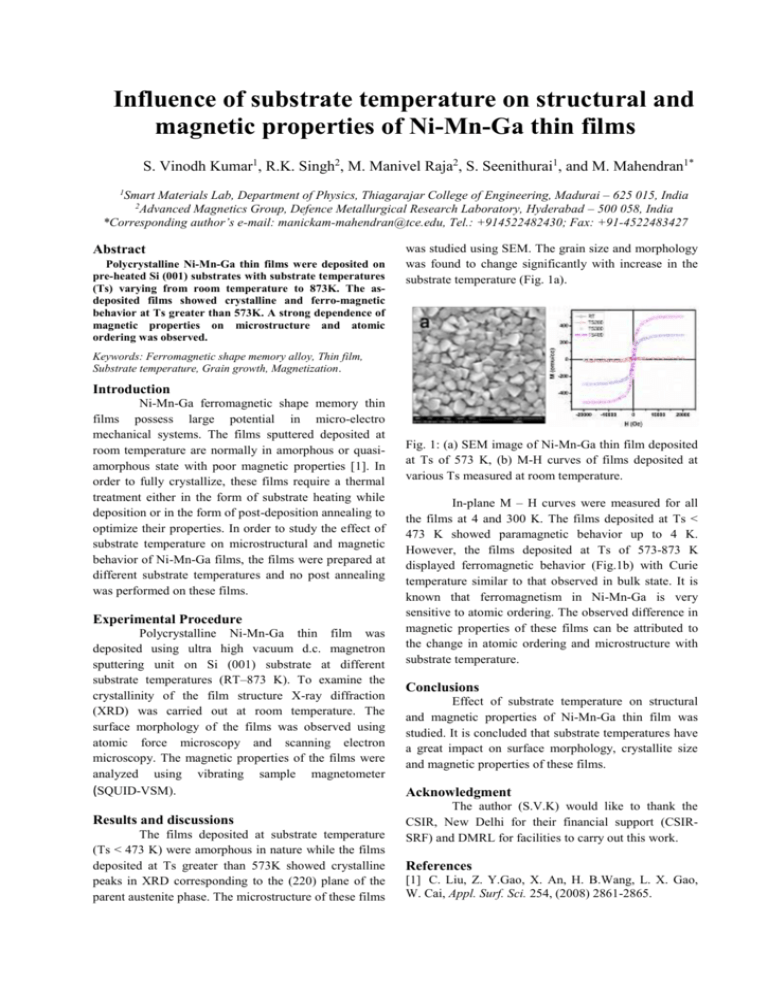
Influence of substrate temperature on structural and magnetic properties of Ni-Mn-Ga thin films S. Vinodh Kumar1, R.K. Singh2, M. Manivel Raja2, S. Seenithurai1, and M. Mahendran1* Smart Materials Lab, Department of Physics, Thiagarajar College of Engineering, Madurai – 625 015, India 2 Advanced Magnetics Group, Defence Metallurgical Research Laboratory, Hyderabad – 500 058, India *Corresponding author’s e-mail: manickam-mahendran@tce.edu, Tel.: +914522482430; Fax: +91-4522483427 1 Abstract Polycrystalline Ni-Mn-Ga thin films were deposited on pre-heated Si (001) substrates with substrate temperatures (Ts) varying from room temperature to 873K. The asdeposited films showed crystalline and ferro-magnetic behavior at Ts greater than 573K. A strong dependence of magnetic properties on microstructure and atomic ordering was observed. was studied using SEM. The grain size and morphology was found to change significantly with increase in the substrate temperature (Fig. 1a). Keywords: Ferromagnetic shape memory alloy, Thin film, Substrate temperature, Grain growth, Magnetization. Introduction Ni-Mn-Ga ferromagnetic shape memory thin films possess large potential in micro-electro mechanical systems. The films sputtered deposited at room temperature are normally in amorphous or quasiamorphous state with poor magnetic properties [1]. In order to fully crystallize, these films require a thermal treatment either in the form of substrate heating while deposition or in the form of post-deposition annealing to optimize their properties. In order to study the effect of substrate temperature on microstructural and magnetic behavior of Ni-Mn-Ga films, the films were prepared at different substrate temperatures and no post annealing was performed on these films. Experimental Procedure Polycrystalline Ni-Mn-Ga thin film was deposited using ultra high vacuum d.c. magnetron sputtering unit on Si (001) substrate at different substrate temperatures (RT–873 K). To examine the crystallinity of the film structure X-ray diffraction (XRD) was carried out at room temperature. The surface morphology of the films was observed using atomic force microscopy and scanning electron microscopy. The magnetic properties of the films were analyzed using vibrating sample magnetometer (SQUID-VSM). Results and discussions The films deposited at substrate temperature (Ts < 473 K) were amorphous in nature while the films deposited at Ts greater than 573K showed crystalline peaks in XRD corresponding to the (220) plane of the parent austenite phase. The microstructure of these films Fig. 1: (a) SEM image of Ni-Mn-Ga thin film deposited at Ts of 573 K, (b) M-H curves of films deposited at various Ts measured at room temperature. In-plane M – H curves were measured for all the films at 4 and 300 K. The films deposited at Ts < 473 K showed paramagnetic behavior up to 4 K. However, the films deposited at Ts of 573-873 K displayed ferromagnetic behavior (Fig.1b) with Curie temperature similar to that observed in bulk state. It is known that ferromagnetism in Ni-Mn-Ga is very sensitive to atomic ordering. The observed difference in magnetic properties of these films can be attributed to the change in atomic ordering and microstructure with substrate temperature. Conclusions Effect of substrate temperature on structural and magnetic properties of Ni-Mn-Ga thin film was studied. It is concluded that substrate temperatures have a great impact on surface morphology, crystallite size and magnetic properties of these films. Acknowledgment The author (S.V.K) would like to thank the CSIR, New Delhi for their financial support (CSIRSRF) and DMRL for facilities to carry out this work. References [1] C. Liu, Z. Y.Gao, X. An, H. B.Wang, L. X. Gao, W. Cai, Appl. Surf. Sci. 254, (2008) 2861-2865.