Extinct, Endangered, Existing
advertisement

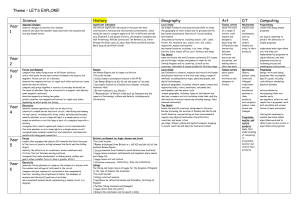
Theme – EXTINCT, ENDANGERED, EXISTING! Science History Geography Art DT Computing Year 1 Animals identify and name a variety of common animals including fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds and mammals identify and name a variety of common animals that are carnivores, herbivores and omnivores describe and compare the structure of a variety of common animals (fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds and mammals, and including pets) Beyond living memory events beyond living memory that are significant nationally or globally (e.g. the Great Fire of London, the first aeroplane flight or events commemorated through festivals or anniversaries) Weather identify seasonal and daily weather patterns in the United Kingdom and the location of hot and cold areas of the world in relation to the Equator and the North and South Poles Sculpture to use sculpture to develop and share their ideas, experiences and imagination Mechanisms explore and use mechanisms, such as levers, sliders, wheels and axles, in their products. Year 2 Animals notice that animals, including humans, have offspring which grow into adults find out about and describe the basic needs of animals, including humans, for survival (water, food and air) Safety use technology safely and respectfully, keeping personal information private; know where to go for help and support when they have concerns about material on the internet Year 3 Animals identify that humans and some other animals have skeletons and muscles for support, protection and movement. Animals construct and interpret a variety of food chains, identifying producers, predators and prey recognise that environments can change and that this can sometimes pose dangers to living things. Earliest Civilizations the achievements of the earliest civilizations – an overview of where and when the first civilizations appeared and a depth study of one of the following: Ancient Sumer; The Indus Valley; Ancient Egypt; The Shang Dynasty of Ancient China Weather and Time identify the position and significance of latitude, longitude, Equator, Northern Hemisphere, Southern Hemisphere, the Tropics of Cancer and Capricorn, Arctic and Antarctic Circle, the Prime/Greenwich Meridian and time zones (including day and night) Sculpture to improve their mastery of art and design techniques, including sculpture with a range of materials (e.g. pencil, charcoal, paint, clay) Mechanisms (Gears, pulleys, cams, levels and linkages) understand and use mechanical systems in their products, such as gears, pulleys, cams, levers and linkages Safety use technology safely, respectfully and responsibly; know a range of ways to report concerns and inappropriate behaviour Year 4 Year 5 Year 6 Evolution and inheritance recognise that living things have changed over time and that fossils provide information about living things that inhabited the Earth millions of years ago recognise that living things produce offspring of the same kind, but normally offspring vary and are not identical to their parents identify how animals and plants are adapted to suit their environment in different ways and that adaptation may lead to evolution. Non-European a non-European society that provides contrasts with British history - one study chosen from: early Islamic civilization, including a study of Baghdad c. AD 900; Mayan civilization c. AD 900; Benin (West Africa) c. AD 900-1300. Comparative Study understand geographical similarities and differences through the study of human and physical geography of a region of the United Kingdom, a region in a European country, and a region within North or South America physical geography, including: climate zones, biomes and vegetation belts, rivers, mountains, volcanoes and earthquakes, and the water cycle human geography, including: types of settlement and land use, economic activity including trade links, and the distribution of natural resources including energy, food, minerals and water