CSE Referral: Minimum RtI Requirements Checklist
advertisement

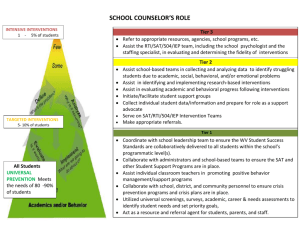
CSE Referral: Minimum RtI Requirements Checklist Student Name:Click here to enter text. Date:Click here to enter a date. Interventions: Evidence-Based & Implemented with Integrity Tier 1: Classroom Interventions. The classroom teacher is the “first responder” for students with academic delays and behavioral difficulties. Classroom efforts to instruct and individually support the student should be documented. Adequately RtI Element If this element is incomplete, Documented? missing, or undocumented… Tier 1: High-Quality Core Instruction - The student has Inadequate or incorrectly received high quality core instruction in the area of concern. focused core instruction may ☐ YES “High quality” is defined as at least 80% of students in the be an explanation for students’ ☐ NO classroom or grade level performing at or above grade level academic and behavioral expectations, through classroom instructional support alone delays. This does not validate a (Christ, 2008). Data sources including AIMSweb, NWEA, referral to special education. referral data and/or student data sheets should be reviewed to determine if classrooms are either at 80% or making progress towards 80% of students meeting grade level expectations. ☐ If no, a tier 1 (core) instructional support plan has been developed for the classroom and a review date of Click here to enter a date. has been set. ☐ YES ☐ NO Tier 1: Classroom/Core Instruction and Support- The classroom teacher has delivered appropriate and consistent academic and behavioral instruction to the student. Differentiation and/or supplemental instruction identified as “evidence-based” has been provided to support learning within the target skill area. [Possible Tier 1, evidence-based reading supports can be found within the Standard Reading Protocol chart.] For students initially identified as at-risk, Tier 1 reading supports have been provided at a minimum of 3xweek, for 30 minutes and supplement core instruction. For initial Tier 1 students academic baseline and goals were calculated, and progress-monitoring data was collected (minimum of 2xmonth for reading) to measure the impact of differentiation and support. Daily behavior data sheets have been maintained through the school day. The classroom reading supports and/or teaching of additional behavioral strategies was provided for a period sufficiently long (e.g., 6-10 instructional weeks for reading; 2 weeks for behavior) to fully assess its effectiveness. The student was in attendance for core instruction 90% of the time. An absence of individualized classroom support or a poorly focused classroom instruction may contribute to the student’s academic and/or behavioral delays and does not validate a referral to special education. CSE Referral: Minimum RtI Requirements Checklist Student Name:Click here to enter text. Date:Click here to enter a date. Tiers 2 & 3: Supplemental Interventions. Interventions at Tiers 2 & 3 supplement core instruction and specifically target the student’s academic and/or behavioral deficits. Adequately RtI Element If this element is incomplete, Documented? missing, or undocumented… A foundation assumption of Tier 2 & 3 Interventions: Minimum Number & Length The student’s cumulative RtI information indicates that an RtI is that a struggling general☐ YES adequate effort in the general-education setting was made to education student is typical ☐ NO provide supplemental interventions at Tiers 2 & 3. The term and simply needs targeted “sufficient effort” includes the expectation that within the instructional support to be student’s general education setting: successful. Therefore, strong A minimum number of two separate, Tier 2 and Tier 3 evidence (i.e., several documented, “good faith” intervention trials have been attempted. Reading intervention attempts) are interventions and changes have been consistently needed before the school can documented in AIMSweb. move beyond the assumption Each intervention trial lasted the minimum period of that the student is typical to time (e.g., 6-10 instructional weeks for reading; 2 weeks for behavior). Reading intervention information consider whether there are possible “within-child” factors, and progress monitoring has been documented in such as a learning disability AIMSweb. that best explain the student’s Interventions and progress monitoring was difficulties. implemented with fidelity and consistency. Fidelity documentation is available upon request (for reading) if the student’s classroom has not shown progress towards 80% on grade level. Any changes in intervention were based on data. Reading guidelines state a change for more intensive tiered support should occur when there are 4 out of 6 consecutive data points below a student’s aimline. Tier 2 & 3 Interventions: Essential Elements - Each Tier Supplemental intervention 2/3 intervention plan shows evidence that: programs are compromised if ☐ YES they are not based on research, Instructional programs or practices used in the ☐ NO are too large, or include intervention met the criteria of an “evidence-based” students with very discrepant intervention and/or are provided within the Standard intervention needs. Schools Reading Protocol chart. cannot have confidence in the The intervention was selected because it logically impact of such potentially addressed the area(s) of academic or behavioral need for the student (e.g., an intervention to address phonics compromised supplemental was chosen for a student whose primary deficit was in intervention programs. this area based on data). The student-teacher ratio in the group-based intervention provided adequate student support. NOTE: For Tier 2, group sizes should be 4-6 students. Tier 3 interventions for reading may be delivered in smaller groups (e.g., 3 students or fewer) or individually. Tier 3 for behavior should be delivered in an individual setting. The intervention provided contact time adequate to the CSE Referral: Minimum RtI Requirements Checklist Student Name:Click here to enter text. ☐ YES ☐ NO Date:Click here to enter a date. student deficit. NOTE: Tier 2 interventions for reading should take place a minimum of 5 times per week in sessions of 30 minutes; Tier 3 interventions for reading should take place daily in sessions of 45 minutes or more (Burns & Gibbons, 2008) Tier 1, 2, & 3 Interventions: Intervention Integrity Data has been collected to verify that the intervention is carried out with integrity and fidelity (Gansle & Noell, 2007; Roach & Elliott, 2008). Relevant fidelity data includes information about at least 3 of the 5 requirements: ☐ Tier 1 core instruction (to be completed by building principal) ☐ Attendance ☐ Tier 2 & 3 interventions (including frequency and length of intervention sessions; rate of improvement; comparisons to peer performance within the classroom or students responding to core instruction). ☐ Progress monitoring ☐ Benchmark assessments for reading Without intervention-integrity and fidelity data, it is impossible to discern whether underperformance is due to the student’s ‘non-response’ to intervention or due to an intervention that was poorly or inconsistently carried out. Academic Screenings: General Outcome Measures and Skill-Based Measures Peer Norms: The school selects efficient measures with good technical adequacy to be used to screen all students at a grade level in targeted academic areas. Adequately RtI Element If this element is Documented? incomplete, missing, or undocumented… Selection of Academic Screening Measures - The school has Academic screening selected appropriate grade-level screening measures for the measures provide a shared ☐ YES academic skill area(s) in which the student struggles (Hosp & standard for assessing ☐ NO Howell, 2007). The selected screening measure(s): student academic risk. If ☐ N/A appropriate grade level Have “technical adequacy” as grade-level screeners and (behavioral screening measure(s) are have been researched and shown to predict future success referral only) not in place, the school in the academic skill(s) targeted (AIMSweb, NWEA) Are general enough to give useful information for at least cannot efficiently identify struggling students who a full school year of the developing academic skill (e.g., need additional General Outcome Measure or Skill-Based Mastery intervention support or Measure such as AIMSweb). calculate the relative Include research norms or benchmarks to guide the probability of academic school in evaluating the risk level for each student success for each student. screened. National Norms are utilized at Least 3 Times Per Year. All In the absence local ☐ YES students at each grade level are administered the relevant screening norms, the ☐ NO academic screenings at least three times per year. The results are school cannot easily judge ☐ N/A compared to national and local norms, which are also referenced whether a student’s skills (behavioral are substantially delayed referral only) when making educational decisions regarding a referral for intensive or restrictive services/supports. from those of peers in the same educational setting. CSE Referral: Minimum RtI Requirements Checklist Student Name:Click here to enter text. Date:Click here to enter a date. Dual Discrepancy Cut-Offs: Academic Skill Level and Student Rate of Improvement Establishment of Guidelines for Determining Student ‘Non-Response’ to Intervention as a Dual Discrepancy: The school has developed definitions for ‘severely discrepant’ academic or behavioral performance and student growth. Adequately RtI Element If this element is Documented? incomplete, missing, or undocumented… The RtI model uses a dual Cut-point Established to Define ‘Severely Discrepant’ Academic or Behavioral Performance - Using local or discrepancy approach to ☐ YES national norms, the school sets “cut-points” below which a identify a student as a ☐ NO student’s academic performance is defined as “severely “nonresponder” to academic discrepant” from that of peers in the enrolled grade. and behavioral intervention (Fuchs, 2003) to include: (1) Students referred to the Committee on Special Education are a severe discrepancy in th performing below the 10 percentile as compared to same academic or behavioral aged peers AND often two or more years below their enrolled performance and (2) a grade level. AIMSweb progress monitoring data should be discrepancy in rate of student consistent with benchmark data, within a standard error of growth during intervention measurement. Additional data used by the district (NWEA, (e.g. rate of improvement or Fountas & Pinnell) should also indicate consistent deficits and ROI). Demonstration that the validate student achievement levels. student continues to lag severely behind peers in Progress monitoring data for behavior has an individually academic or behavioral established goal, developed using baseline data. Progress skills, despite intensive monitoring data indicates behavior which is significantly intervention, is a key discrepant from same aged peers and below that expected as requirement in certifying RtI compared to building and classroom behavioral expectations. “nonresponder” status. ☐ YES ☐ NO ☐ N/A (behavioral referral only) Cut-Off Criterion Selected to Define Discrepant Slope The school has selected a formula for determining when a student’s rate of improvement (ROI) is severely discrepant from that of peers. AIMSweb benchmark data indicates that a student’s rate of improvement is less than that of 50% of students in a national sample who started at a similar level. This ROI can be obtained from AIMSweb once at least 2 benchmarks have been obtained on a student. AIMSweb progress monitoring data indicates that the student’s individual ROI is significantly below their goal ROI, which was calculated for their goal or instructional level. A clear formula is needed for determining whether a student slope reaches the threshold of “discrepancy” to ensure consistency across all student cases. Data Collection Intervention Outcome Data: Student baseline level and goals are calculated for each intervention, and a sufficient number of data points are collected during progress-monitoring to judge accurately whether the intervention is successful. CSE Referral: Minimum RtI Requirements Checklist Student Name:Click here to enter text. Date:Click here to enter a date. Adequately RtI Element Documented? ☐ YES ☐ NO ☐ YES ☐ NO If this element is incomplete, missing, or undocumented… If an off-level student is Use of Both “Off-Level” and Enrolled Grade-Level tracked using only Benchmarks & Progress-Monitoring Measures to Assess Student Skills and Growth - For students with substantial unrealistically difficult skill deficits (e.g., a 2-year delay in reading) or behavioral progress monitoring difficulties, any Tier 2/3 intervention is likely to be off level measures from his or her or differentiated to match the student’s actual skills. Here are enrolled-grade level, any data-collection guidelines for off-level interventions (Shapiro, actual evidence of student 2008): progress may be masked by the challenging nature of the Reading: Survey level assessments (SLAs) were completed when the student was initially identified as assessment materials. This below the 10th percentile on grade level text. SLAs are intervention assessment mismatch could lead the used to determine the student’s progress monitoring school to erroneously judge level. Reading: Progress-monitoring should generally match the student as a nonresponder to an off-level intervention, the intervention level. So, if a 5th-grade student when in fact the student is receives a supplemental reading fluency intervention actually making substantial using grade 2 texts, the school would use grade 2 reading fluency progress-monitoring measures to track academic or behavioral student growth and to determine when the student has progress. reached mastery at this off-level intervention point. Behavior: Interventions and progress monitoring for behavior should take into account general student ability (i.e. cognitive, academic). For example a 6th grade student with impaired cognitive ability should have a visual schedule instead of a written schedule and progress monitoring data should reflect this differentiation. Student Baseline Calculated - For each Tier 2/3 intervention being reviewed, the school calculates the student’s baseline level, or starting point, in the academic or behavioral skill before starting the intervention (Witt, VanDerHeyden, & Gilbertson, 2004). Baseline is calculated in one of the following ways: Reading: Using benchmark data, which is consistent with progress monitoring. Benchmark assessments should be periodically assessed for fidelity. Reading: If benchmark data was obtained more than 4 weeks prior AND a tiered intervention has been recently attempted, baseline can be assessed by taking the three final (that is, most recent) data points from that progress monitoring data series and selecting the median value from the three points as a calculation of baseline. This is also used for students who are being Without information about baseline student performance prior to an intervention, it is difficult to estimate the actual progress that the student made during the intervention. Lack of baseline data therefore comprises a “fatal flaw” (Witt, VanDerHeyden, & Gilbertson, 2004) that invalidates any RTI intervention. CSE Referral: Minimum RtI Requirements Checklist Student Name:Click here to enter text. ☐ YES ☐ NO ☐ YES ☐ NO Date:Click here to enter a date. progress monitored below their current enrolled grade level, where SLAs were completed following a prior benchmark period. Behavioral: a preliminary decision by the RtI team should be made regarding length of time for baseline data collection and may be dependent on target behavior. For example: a high frequency behavior such as yelling-out might result in data collection over a few days; whereas a low frequency behavior might be collected over a 2-week period. Student Goal Calculated - For each intervention being reviewed, the school calculates a predicted goal for student progress to be attained by the end of the intervention period. The goal: Is based on acceptable norms for student growth (i.e., research-based growth norms). Reading only. Is periodically reviewed and updated when a student meets or exceeds their goal for three consecutive data points. Represents a realistic prediction of student growth that is sufficiently ambitious - assuming that the intervention is successful - to eventually close the gap between the student and grade-level peers. If no clear goal for student progress is established prior to the start of a tiered intervention, the school cannot know at the conclusion whether the intervention was successful. Lack of a specific criterion or goal for student improvement, therefore comprises a “fatal flaw” (Witt, VanDerHeyden, & Gilbertson, 2004) that invalidates any RTI intervention. Regular Progress-Monitoring Conducted - Each tiered A student’s rate of intervention is monitored on a regular basis. improvement, or slope, Reading: during an intervention is If Tier 1 (at-risk), the intervention is monitored at least calculated from the total progress monitoring data 2xmonth. points collected. The greater If Tier 2, the intervention is monitored at least the number of data points, 1xweek. the greater the confidence If Tier 3, the intervention is monitored following rd that the slope is a good every 3 intervention session. Students who are of relative concern (e.g. average but approximation of actual progress. If, however, the performing below their grade level target score) can data is too sparse, the school also be monitored 1xmonth. cannot have confidence that Behavior: the data points collected are Frequency of progress monitoring will be based on baseline data, as well as frequency and severity of the an accurate representation of actual student progress. behavior. CSE Referral: Minimum RtI Requirements Checklist Student Name:Click here to enter text. Date:Click here to enter a date. Application of RTI Decision Rules to a Particular Student Case RTI Data Analysis. The student’s individual RtI data is analyzed to determine if that student is a “nonresponder” despite the best efforts to provide evidence-based interventions in the general-education setting. Adequately RtI Element If this element is Documented? incomplete, missing, or undocumented… A discrepant student Despite the Tier 2/3 Interventions Attempted, the performance level is the first Student’s Skills Continue to Fall Below the Boundary of ☐ YES Severely Discrepant Academic Performance Using the element of a dual ☐ NO school’s definition for calculating “severely discrepant discrepancy needed under performance”, it is determined that the student’s current RtI to define a student as a academic or behavioral performance is discrepant from that of non-responder to general peers. education interventions. A discrepant student slope is Despite the Tier 2/3 Interventions Attempted, the the second element of a dual Student’s Rate of Improvement (Slope) Continues to Be ☐ YES Discrepant - Applying the school’s methods for calculating discrepancy needed under ☐ NO discrepant slope (above), it is determined that the student’s RtI to define a student as a slope (growth during the intervention) is discrepant from that non-responder to generalof peers. education interventions. Adapted from Jim Wright’s RtI Toolkit: A Practical Guide for Schools