Nucleus of a Eukaryotic Cells - British School Quito Blogs Sites
advertisement

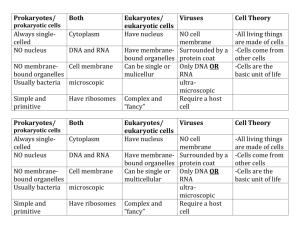
Nucleus of a Eukaryotic Cells: The Nucleus of a Eukaryotic cell contains the DNA, which is the genetic material of a cell. The DNA has a big importance when it comes to the construction of a cell. The DNA contains the information needed for constructing a cell and directing the multitude of synthesis tasks a cell must carry during the process of life and reproduction. The nucleus has as a function being the brain of the cell, it directs cell activities and contains the genetic material also called chromosomes which are made of DNA. Nuclear Envelope: A nucleus contains a nuclear envelope or also called nuclear membrane. This membrane is divided into outer nuclear membrane and inner nuclear membrane, it surrounds the nucleus with multiple pores. Nuclear Pores: This pores are used to regulate the passage of macromolecules such as proteins and RNA, however these pores allow the free passage of water, ions, ATP as well as other small molecules. Through this way the membrane is able to exert control over the flow of information in the cell due to the fact that information is carried by the macromolecules. These pores have a geat impact as well on how the cell ends up looking and doing as they control what comes in adn out. Chromatin: Inside the nucleoplasm, between the nucleolus and the membrane, chromatin can be found wrapped around histone proteins. A histone protein can be defined as “any of various simple water-soluble proteins that are rich in the basic amino acids lysine and arginine and are complexed with DNA in the nucleosomes of eukaryotic chromatin” Chromatin contains the organism`s genome, which is the collection of all the genes. This chromatin is composed of a compound names deoxyribonucleic acid, or DNA which is associated with proteins which allows the formation of long strands also called chromosomes. The DNA of the cell remains in the nucleus, therefore it controls most of the processes that occur in the cytoplasm of the cell. The information from the DNA may be transcribed to mRNA and then be transmitted into other cellular synthesis processes. The information generated in the cytoplasm can provide feedback again to the nucleus. Nucleolus: The nucleolus is located in the central part of the cell nucleus, this is the one composed of ribosomal RNA, proteins and DNA. The nucleolus produces ribosomes, which move out of the nucleus in order to take positions on the rough endoplasmic reticulum where they accomplish the process of protein synthesis. In various stages of synthesis ribosomes may also be contained. The nucleolus completes the function of accomplishing the manufacture of ribosomal RNA which are then transmitted to the chromatin as DNA. The nucleolus is the place where ribosome synthesis occurs. Ribosomes, RNA (large complexes of protein and ribonucleic acid) are in charge of the protein synthesis. The process followed in order to complete the protein synthesis is the following: the DNA inside the nucleus is being copied into small strands of RNA which then form the chromatin, these mRNA molecules are then transported about of the nucleus through the nuclear pores in the membrane and go into the cell`s cytoplasm where they eventually are translated into proteins thanks to ribosomes. In other words: DNA---RNA---finally=PROTEIN The scale of the model compared to the real one is: 0.1mm is the actual size 300mm model size 300mmx1000/100micrometres=30000xmagnification http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/biology/celnuc.html tp://www.windows2universe.org/earth/Life/cell_organelles.html http://www.cellsalive.com/cells/cell_model.htm https://www.boundless.com/physiology/textbooks/299/cellular-structure-andfunction-3/nucleus-and-ribosomes-44/structure-and-function-of-the-nucleus-andribosome-340-11449/