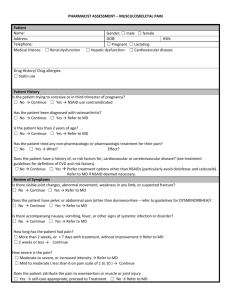
Supplementary Table 1. Overview of observational studies on
advertisement

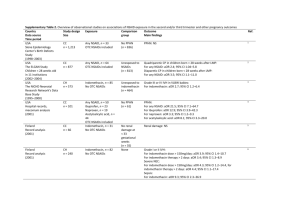
Supplementary Table 1. Overview of observational studies on associations of NSAID exposure in the first trimester and miscarriage and congenital malformations Country Data source Time period Israel OB–GYN database, hospitalisation database, medication dispensing database (2003–2009) Study design Size Exposure Comparison group Outcome Main findings CH n = 65,457 Unexposed to NSAIDs (n = 60,962) Miscarriage: NS For indomethacin: adjusted HR 2.8, 95% CI 1.70–4.69; no dose–response effect 1 Norway Norwegian Mother and Child Cohort Study database, medical birth registry (1999–2008) Israel Maternal and infant hospitalisation database, medication dispensing database (1998–2009) USA Right from the Start Study – community based study (2004–2010) USA National Birth Defects Prevention Study (1997–2004) CH n = 90,417 Unexposed to NSAIDs (n = 83,906) Congenital malformations: NS Cardiac malformations detected 18 months postpartum: NS 2 Unexposed to NSAIDs (n = 105,537) Congenital malformations: NS Musculoskeletal malformations: For selective COX-2 inhibitors: aOR 3.39; 95% CI 1.37–8.34 3 CH n = 2,780 Any NSAID, n = 4,495 Non-selective COX-2 inhibitors, n = 4,424 Selective COX-2 inhibitors, n = 71 OTC NSAIDs included Any NSAID, n = 3,529 Ibuprofen, n = 3,034 Diclofenac, n = 192 Naproxen, n = 168 OTC NSAIDs included Any NSAID, n = 5,267 Conventional NSAIDs, n = 5,153 Selective COX-2 inhibitors, n = 114 Any NSAID, n = 1,185 OTC NSAIDs included Unexposed to NSAIDs (n = 1,595) Miscarriage: NS 4 CC n = 19,741 Any NSAID, n = 4,625 OTC NSAIDs included No congenital malformations (n = 5,546) 5 Norway Norwegian Mother and Child Cohort Study database, medical birth registry (1999–2006) CH n = 67,891 Any NSAID, n = 3,023 OTC NSAIDs included Unexposed to NSAIDs (n = 64,074) Anophthalmia/micropthalmia: For any NSAID: aOR 2.1; 95% CI 1.3–3.5 Cleft lip +/- palate: For ibuprofen: aOR 1.3; 95% CI 1.1–1.6 For naproxen: aOR 1.7; 95% CI 1.1–2.5 Amniotic bands: For ibuprofen: aOR 2.2; 95% CI 1.4–3.5 For acetylsalicylic acid: aOR 2.5; 95% CI 1.1–5.6 Pulmonary valve stenosis in term infants: For naproxen: aOR 2.4; 95% CI 1.3–4.5 Selected congenital malformations (neural tube, cardiac, oesophageal, anorectal, abdominal wall malformations, diaphragmatic hernia, and amniotic bands): NS CH n = 110,783 Ref. 6 1 Canada Quebec Pregnancy Registry (1997 onwards) Italy TIS database (1988–2008) Canada Quebec Pregnancy Registry (1997 to 2003) CC n = 51,755 Any NSAID, n = 352 No OTC NSAIDs No miscarriage (n = 47,050) Miscarriage: For any NSAID: aOR 2.4; 95% CI 2.1–2.8 7 CH n = 917 Diclofenac, n = 145 OTC NSAIDs included Congenital malformations: NS Miscarriage: NS 8 CH n = 36,387 Any NSAID, n = 1,056 No OTC NSAIDs Exposed to nonteratogens (n = 501) Unexposed to NSAIDs (n = 35,331) 9 Denmark Hospital discharge registry, medical birth registry, prescription database (1998–2002) USA National Birth Defects Prevention Study (1997–1998) USA Prenatal interview (1996–1998) CC n = 17,589 Any NSAID, n = 1,554 No OTC NSAIDs Children of corresponding gestational age (n = 15,990) Congenital malformations: For any NSAID: aOR 2.2; 95% CI 1.7–2.8 Cardiac septal malformations: For any NSAID: aOR 3.3; 95% CI 1.9–6.0 Respiratory system malformations: For any NSAID: aOR 9.5; 95% CI 3.1–29.6 Miscarriage: NS CC n = 858 Any NSAID, n = 30 OTC NSAIDs included No congenital malformations (n = 690) VSD: NS 11 CH n = 1,055 Any NSAID, n = 53 OTC NSAIDs included Unexposed to NSAIDs (n = 980) 12 Sweden Medical birth registry, Swedish Register of Congenital Malformations, Swedish Child Cardiology Register (1995–1998) Denmark Hospital discharge registry, medical birth registry, prescription database (1991–1998) CH n = 72,142 Any NSAID, n = 2,557 OTC NSAIDs included Rest of population Miscarriage: For any NSAID: adjusted HR 1.8; 95% CI 1.0–3.2 For NSAIDs used around conception: adjusted HR 5.6; 95% CI 2.3–13.7 For NSAIDs used > 1 week: adjusted HR 8.1; 95% CI 2.8–23.4 Congenital malformations: NS Cardiac malformations: For any NSAID: aOR 1.86; 95% CI 1.32–2.62 Orofacial clefts: For any NSAID aOR 2.61, 95% CI 1.01–6.78 CH* and CC** n* = 18,721 n** = 34,018 Any NSAID, n* = 1,257 Any NSAID, n** = 63 No OTC NSAIDs Unexposed to any drugs* (n = 17,259) No miscarriage** (n = 29 750) Congenital malformations*: NS Miscarriage**: For NSAID exposure in gestational weeks 0 to 1: aOR 7.0; 95% CI 2.7–17.7, weeks 2 to 3: aOR 3.0; 95% CI 1.2–7.4, weeks 4 to 6: aOR 4.4; 95% CI 2.7–7.2, weeks 7 to 9: aOR 2.7; 95% CI 1.8–4.0 14 10 13 Abbreviations: aOR, adjusted OR; CH, cohort; CC, case–control; NS, no excess risk (statistically not significant); OB–GYN, obstetrics and gynaecology; OTC, over-the-counter; TIS, Teratology Information Services database; VSD, ventricular septal defects. 2 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. Daniel, S. et al. Fetal exposure to nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and spontaneous abortions. CMAJ 186, E177-E182 (2014). Nezvalová-Henriksen, K., Spigset, O. & Nordeng, H. Effects of ibuprofen, diclofenac, naproxen, and piroxicam on the course of pregnancy and pregnancy outcome: a prospective cohort study. BJOG (2013). Daniel, S. et al. Major malformations following exposure to nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs during the first trimester of pregnancy. J. Rheum. 39, 2163-2169 (2012). Edwards, D.R. et al. Periconceptional over-the-counter nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug exposure and risk for spontaneous abortion. Obstet. Gynecol. 120, 113-122 (2012). Hernandez, R.K., Werler, M.M., Romitti, P., Sun, L. & Anderka, M. Nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drug use among women and the risk of birth defects. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 206, 228 e1-8 (2012). van Gelder, M.M.H.J., Roeleveld, N. & Nordeng, H. Exposure to non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs during pregnancy and the risk of selected birth defects: a pospective cohort study. PLoS ONE 6, e22174 (2011). Nakhai-Pour, H.R., Broy, P., Sheehy, O. & Berard, A. Use of nonaspirin nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs during pregnancy and the risk of spontaneous abortion. CMAJ 183, 17131720 (2011). Cassina, M. et al. First trimester diclofenac exposure and pregnancy outcome. Reprod. Toxicol. 30, 401-404 (2010). Ofori, B., Oraichi, D., Blais, L., Rey, E. & Berard, A. Risk of congenital anomalies in pregnant users of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: A nested case-control study. Birth Defects Res. B Dev. Reprod. Toxicol. 77, 268-279 (2006). Nielsen, G.L., Skriver, M.V., Pedersen, L. & Sørensen, H.T. Danish group reanalyses miscarriage in NSAID users. BMJ 328, 109 (2004). Cleves, M.A. et al. Maternal use of acetaminophen and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and muscular ventricular septal defects. Birth Defects Res. A Clin. Mol. Teratol. 70, 107-113 (2004). Li, D.K., Liu, L. & Odouli, R. Exposure to non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs during pregnancy and risk of miscarriage: population based cohort study. BMJ 327, 368 (2003). Ericson, A. & Kallen, B.A. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in early pregnancy. Reprod. Toxicol. 15, 371-375 (2001). Nielsen, G.L., Sørensen, H.T., Larsen, H. & Pedersen, L. Risk of adverse birth outcome and miscarriage in pregnant users of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: population based observational study and case-control study. BMJ 322, 266-270 (2001). 3