10615_Xu-ed_AP
advertisement

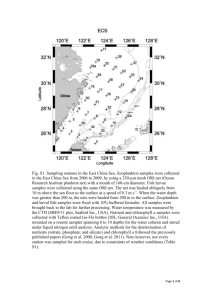
Interannual variation of summer zooplankton size structure and its relation to physical and biological processes in the Yellow Sea and East China Sea Yongjiu Xu1,2, Joji Ishizaka1, Meixun Zhao2 and Jing Zhang3 1 School of Fishery, Zhejiang Ocean University, Zhoushan, Zhejiang, PR China E-mail: xyj-20012318@hotmail.com 2 Hydrospheric Atmospheric Research Center, Nagoya University, Nagoya, Japan 3 Key Laboratory of Marine Chemistry Theory and Technology of the Ministry of Education, Ocean University of China, Qingdao, PR China 4 Graduate School of Science and Engineering, Toyama University, Toyama, Japan Interannual variation of summer zooplankton size community and its relation to physical and biological processes in the Yellow Sea (YS) and East China Sea (ECS) were examined during 2011 to 2013. Zooplankton was size-fractionated with sieves of 2, 1, 0.5, 0.212 and 0.1 mm. The contribution of large size fraction (> 0.5 mm) to total biomass was larger than the small size fraction (<0.5 mm) in the central YS and Kuroshio Water, whereas the smaller size fraction (<0.5 mm) was dominant in the Changjiang Diluted Water (CDW) and its adjacent regions. The geographical distribution of zooplankton size community and its fraction was significantly affected by the physical and biological features of the YS and ECS. The large size fraction in all the stations in the central YS was highly related to the temperature (<10°C) under the thermocline, and these regions corresponded to the Yellow Sea Bottom Cold Water (YSCBW) region. The small size fraction in the majority of the stations in the CDW region was related to low surface salinity (<30). This indicates that the large size zooplankton in the central YS was probably related to the YSBCW, and the small size zooplankton in CDW region was related to Changjiang discharge water. The normalized size spectra of zooplankton community in each region were analyzed, and were compared with other studies to understand the characteristics of the ecosystem in YS and ECS.