File - Mrs. McNair`s Math Page

Box-and-Whisker Plot- NOTES
Preparation
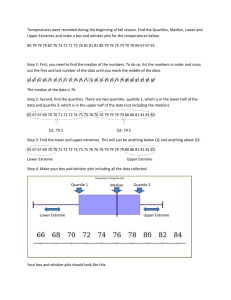
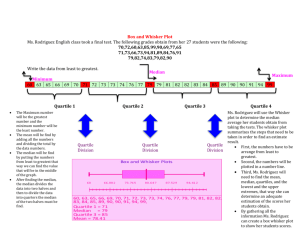
1. The numbers you are working with need to be in order from lowest to highest.
2. Make a number line that can include the highest and lowest numbers in your ordered set.
Making a Box and Whiskers
1. Find the median.
2. Find the median of the lower half of your numbers. This is the lower quartile.
3. Find the median of the upper half of your numbers. This is your upper quartile.
4. Now draw a small box above or below the number line. One end of the box corresponds with the upper quartile, the other with the lower quartile. Draw a vertical line in the box which corresponds to the median.
5 .Find your highest number and your lowest number. These are the upper and lower extremes.
6. Draw a line (whisker) from the upper end of your box to a point corresponding with the upper extreme. Do the same for the lower extreme.
Checking for Outliers
1. Subtract the lower quartile from the upper quartile. This is the interquartile range.
2. Multiply the interquartile range by 1.5. This is your "outlier checker."
3. ADD the outlier checker to your upper quartile. See if your upper extreme is beyond this point. If not everything is O.K. on this end. If the upper extreme is beyond your outlier checker, erase your whisker. Have it end at the highest score NOT beyond the outlier checker. Mark outliers with a *.
4. SUBTRACT the outlier checker from your lower quartile. See if your lower extreme is beyond this point. If not, everything is O.K on this end. If the lower extreme is beyond this point, erase your whisker. Have it end at the lowest score NOT beyond the outlier checker. Mark all outliers with a *.
Congratulations. You are finished!!
Fun Facts: The box-and-whisker plot was invented in the 1970's by John Tukey.
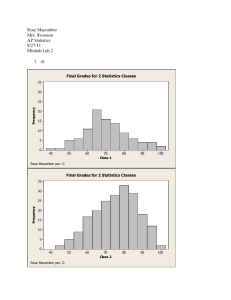
In the 1960's John Tukey also invented the stem-and-leaf plot. This type of graph is useful when comparing one variable for several different groups. A box-andwhisker plot of that variable can be drawn for each group on one page, giving you a visual representation of the differences of that variable according to group. For example, the poverty rate of different countries might be compared by looking at the box-and-whisker for that country in relation to the box-and-whisker graph of the poverty rates of the other countries.