Thermal Energy & Heat Worksheet: Vocabulary & Questions
advertisement

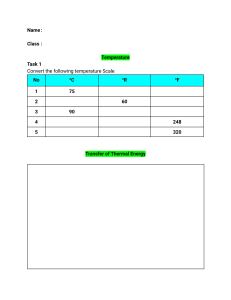
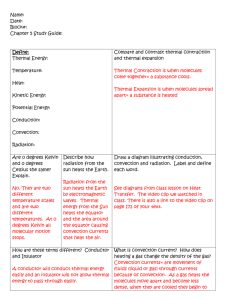
Chapter 6 Thermal Energy and Heat Section 6.1 Vocabulary 1. Temperature-measure of the average kinetic energy of the individual particles in matter 2. Fahrenheit scale-most common temperature scale, freezing point 32, boiling 212. 3. Celsius scale 4. Kelvin scale 5. Absolute zero 6. Heat 7. Specific heat Assessment Questions 1. How do thermometers measure temperature? 2. How are the three temperature scales different? 3. What is the relationship between thermal energy and temperature? 4. What happens to the motion of an object’s particles as the object’s thermal energy increase? What happens to the temperature of the object? 5. Why do some materials get hot more quickly than others? 6. Use the figure on page 181 to answer the following question. You stir your hot cocoa with a silver spoon that has a mass of 0.032 kg. The spoon’s temperature increases from 20K to 60K. What is the change in the spoon’s thermal energy? 1 Section 6.2 Vocabulary 1. Conduction 2. Convection 3. Convection current 4. Radiation 5. Conductor 6. Insulator Assessment Questions 1. Identify each example of heat transfer as conduction, convection, or radiation: opening windows in a hot room; a lizard basking in the sun; putting ice on a sprained ankle. 2. How can heat be transferred across empty space? 3. In what direction will heat flow between two objects with different temperatures? 4. How does a glass of lemonade become cold when you put ice in it? 5. What kind of substance conducts thermal energy well? 6. Would a copper pipe work better as a conductor or an insulator? Why? 7. Why are two panes of glass used in windows? Section 6.3 Vocabulary 1. Change of state 2. Melting 3. Freezing 2 4. Evaporation 5. Boiling 6. Condensation 7. Thermal expansion Assessment Questions 1. Name the three states of matter. 2. How are the states of matter different from each other? 3. What causes a change in state? 4. Why does the temperature of matter remain the same while the matter changes state? 5. How can a liquid expand without changing state? 6. Why should you poke holes in a potato before baking it? 7. How does a thermostat make use of thermal expansion? Section 6.4 Vocabulary 1. Heat engine 2. External combustion engine 3. Internal combustion engine 4. Refrigerant 3 Assessment Questions 1. How are internal combustion engines different from external combustion engines? How are they similar? 2. What changes of state occur in the refrigerant of a refrigerator? Where do these changes of state occur? 3. If the compressor in a refrigerator stopped working, how would its failure affect the heat transfer cycle? 4