File - Groby Bio Page
advertisement

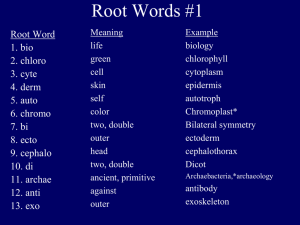
Biology H021 - GCE Test Name: NEW 2015 End of Membranes test Test Duration (minutes): 42 Test Created By: Seran Bradley Number of questions in test: 4 Candidate forename: Candidate surname: INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES Answer all questions Read each question carefully. Make sure you know what you have to do before starting your answer. Write your answers to each question in the space provided. Additional paper may be used if necessary but you must clearly show your candidate number, centre number and question number(s). INFORMATION FOR CANDIDATES The number of marks is given in brackets [ ] at the end of each question or part question. Question: 1 ( a ) Complete the passage below. Membranes have a variety of functions in cells. All membranes are permeable. This means that they allow the passage of certain substances by processes such as active transport or through the membrane. The cell surface membrane, also known as the . membrane, surrounds the cytoplasm. The cell surface membrane consists of a bilayer of and keep it fluid, molecules of . To stabilise the structure of the membrane are also found in this bilayer. [5] ( b ) Membranes contain a variety of proteins. Some of these proteins are combined with carbohydrates to form glycoproteins. Describe the functions of glycoproteins in the cell surface membrane. _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ [5] [Total: 10] Question: 2 ( a ) A student wanted to observe some red blood cells under the microscope. The student placed a small sample of blood onto a microscope slide and added a drop of distilled water. When viewed at high power, the student observed that the red blood cells had burst. In a similar procedure using plant epidermis, the student observed that the plant cells did not burst. ( i ) Explain these observations. _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ [5] (ii) Suggest how the student could modify the procedure to observe red blood cells without them bursting. _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ [1] ( b) Oxygen enters red blood cells as they pass through the capillaries in the lungs. Name the mechanism by which oxygen enters the red blood cells. _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ [1] (c) The cells in the epidermis of a plant root are specialised to absorb minerals from the surrounding soil. State the process by which root epidermal cells absorb minerals from the soil and describe how these cells are specialised to achieve absorption. _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ [3] [Total: 10] Question: 3 (a) (i) Name the process by which water leaves a cell. _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ [1] (ii) Describe the routes that water molecules take through the cell surface membrane. _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ [2] A student carried out an investigation to determine the effects of different sucrose concentrations on cells from pieces of onion epidermis. • Strips of epidermis were taken from an onion. • Separate pieces of epidermis were placed into water and a range of sucrose solutions. • The pieces of epidermis were left for 30 minutes before being removed. • The pieces of epidermis were then viewed at high power under the microscope. The student counted 100 cells from each piece of epidermis. The student noted how many cells had become plasmolysed. The results are shown in Table 6.1. ( b) None of the onion epidermis cells this student observed had burst when left in pure water. Explain why plant cells do not burst when they are left in pure water. _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ [2] (c) (i) The water potential of the onion epidermis cells can be assumed to be the same as the water potential of a solution that causes 50% plasmolysis. Use the information in Table 6.1 to estimate the water potential inside these onion epidermis cells. _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ [1] (ii) Suggest how the student could construct and use a graph to obtain a better estimate of the water potential. _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ [2] ( d ) Suggest how the student could modify the procedure to make the results more reliable and accurate. reliable _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ accurate _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ [4] [Total: 12] Question: 4 The cell surface membrane allows different substances to enter and leave the cell. ( a ) List three components of a cell surface membrane. _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ [3] (b) (i) Explain what is meant by the term active transport. _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ [2] (ii) State two examples of active transport in cells. For each example, you should name the substance that is transported and the cell involved. _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ [2] ( c ) In addition to active transport, substances can pass through cell surface membranes by: • diffusion • facilitated diffusion • osmosis • bulk transport (endocytosis / exocytosis) For each example described in Table 2.1 below, state how the substance crosses the cell surface membrane. The first one has been done for you. Table 2.1 example release of enzymes into the gut mechanism of movement across cell surface membrane bulk transport a plant cell taking up water calcium ions entering a nerve cell down a concentration gradient oxygen entering a red blood cell [3] [Total: 10]