(pre-questions) West Coast 2015
advertisement

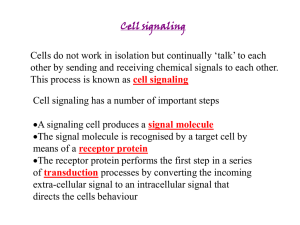
Suggested pre-class questions: 1. Define the following terms from your reading: Signaling molecule Receptor G protein-coupled receptor 2nd messenger Target cell Agonist Antagonist 2. a) Must a signaling molecule enter a target cell in order to trigger a response? b) Explain your answer in part a. 3. Circle the true statements below: One type of signaling molecule triggers one and only one response. One type of signaling molecule can trigger a response from many different types of cells. A single signaling cell can produce only one type of signaling molecule. A cell signaling pathway can be turned on, but not off. Cellular responses can be triggered by molecules made by the body, molecules ingested, or molecules injected. Suggested pre-class questions With answers: 1. Define the following terms from your reading: Signaling molecule A molecule that causes a response in target cells. Receptor The molecule on a target cell that a signaling molecule must interact with in order to cause a response. G protein-coupled receptor A receptor on the surface of a cell that passes a signal into the cell by activating a G protein. 2nd messenger When a G protein-coupled receptor is activated, the G protein activates a 2nd messenger. The second messenger is a molecule within the target cell that amplifies the signal from the receptor. Target cell A cell that responds to a particular signaling molecule. Agonist A molecule that binds the receptor and activates a response. Antagonist A molecule that partially binds the receptor and prevents the signaling molecule from binding. 2. a) Must a signaling molecule enter a target cell in order to trigger a response? No. (Not always.) b) Explain your answer in part a. A few do, but most interact with a receptor on the surface of the target cell. 3. Circle the true statements below: F One type of signaling molecule triggers one and only one response. T One type of signaling molecule can trigger a response from many different types of cells. F A single signaling cell can produce only one type of signaling molecule. F A cell signaling pathway can be turned on, but not off. T Cellular responses can be triggered by molecules made by the body, molecules ingested, or molecules injected.