Course: Foundations & Pre-Calculus 10 Stage 1 – Desired Results
advertisement

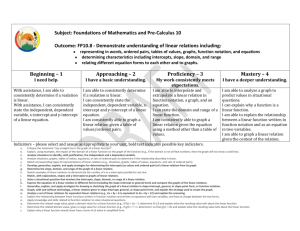
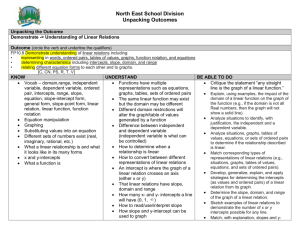
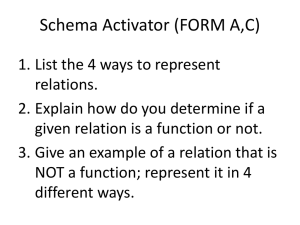
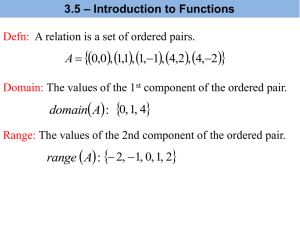
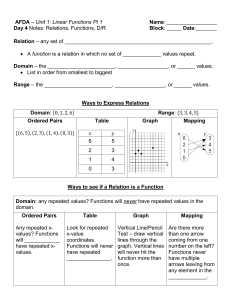
Course: Foundations & Pre-Calculus 10 Stage 1 – Desired Results Outcome FP10.8: Students will demonstrate understanding of linear relations including: Representing in words, ordered pairs, tables of values, graphs, function notation and equations Determining characteristics including intercepts, slope, domain, and range relating different equation forms to each other and to graphs [C,CN,PS,R,T,V] Enduring Understandings: Essential Questions: Identifying patterns is useful in determining relationships A relationship which exhibits a constant rate of change is a linear relationship. Visually, a linear function is represented by a straight, non-vertical line. What patterns can be identified in a linear relationship? How is the constant rate of change of a linear relationship useful in real life? Explain and illustrate at least three strategies which can be used to graph a linear relationship. How can properties of linear functions be used to solve real life problems? Many real life relationships are modelled by linear functions. Students will know: Students will be able to: identify, with justification, independent and dependent variables in situations identify situations, graphs, tables of values, equations or sets of ordered pairs as linear or non-linear relationships match corresponding types of representations of linear relations identify domain and range of the graph of a linear function determine slope of a graph of a linear function develop, generalize, explain and apply strategies for determining intercepts of a graph of a linear relation independent and dependent variables linear relation equation of a linear relation ordered pair tables of values graph of a linear function slope y-intercept domain and range slope-intercept form general form point-slope form function notation draw, with and without technology, the graph of a linear relation given in slopeintercept, general, slope-point form, or function notation (continued) explain strategies used in graphing linear functions determine the related range or domain values of a linear function given in function notation write a linear function as an equation in two variables in slope-intercept form, slope-point form, general form or in function notation and explain the relationship between the forms. apply knowledge and skills related to linear relations to real life situations Stage 2 – Assessment Evidence Performance Tasks: Formative: Participation in class discussion and collaborative problem solving Completion of daily assignments - self assess solutions, get clarification where necessary and revise work Entry question – “journalize” concept from last day’s lesson Exit question – skills inventory question on concept in today’s lesson (or skills previously learned) Getting it Straight! (mini quizzes) - reflect on and revise errors after assessed Unit Reflections – students reflect on unit targets they understood well and those that need more study, and consider what they need to do to be more successful in the future. Summative: Unit Test