1.2 Basics of Functions and Graphs
advertisement

Section 1.2
Basics of Functions
Math 112
Section 1.2
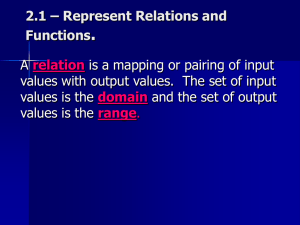
Definition of a Relation
A relation can be expressed as a set of ordered pairs.
The domain of a relation is the set of first elements
in the ordered pairs, and the range is the set of
second elements.
Relation: {(0 , 5), (2 , 1), (2 , 1), (3 , 8)}
Domain: {0, 2, 3}
Range: {5, 1, 1, 8}
Example
Find the domain and the range.
98.6, Felicia , 98.3,Gabriella , 99.1, Lakeshia
Math 112
Section 1.2
Definition of a Function
A function is a relation for which each element of the
domain corresponds to exactly one element of the range.
Relation: {(0 , 5), (2 , 1), (2 , 1), (3 , 8)}
Function: {(0 , 2), (1 , 8), (5 , 2), (1 , 3)}
0
2
3
5
1
1
8
0
1
5
1
2
8
3
In other words, no x coordinate can be paired with
more than one y coordinate.
Example
Determine whether each relation is a function?
1,8 , 2,9 , 3,10
2,3 , 2, 4 , 2,5
3, 6 , 4, 6 , 5, 6
Function Notation
Math 112
Section 1.2
Function Notation
A function can also be expressed as an equation.
f(x) = x2 + 5x 2
“f of x”
f(3) = 32 + 5(3) 2 = 22
f(1) = (1)2 + 5(1) 2 = 6
f(z+2) = (z+2)2 + 5(z+2) 2
= z2 + 4z + 4 + 5z + 10 2
= z2 + 9z + 12
Example
Evaluate each of the following.
Find f(3) for f(x)=2x 4
2
Find f(-2) for f(x)=9-x
2
Example
Evaluate each of the following.
Find f(x+2) for f(x)=x 2 2 x 4 ?
Is this is same as f(x) + f(2) for f(x)=x 2 x 4
2
Example
Evaluate each of the following.
Find f(-x) for f(x)=x 2 2 x 4
Is this is same as -f(x) for f(x)=x 2 x 4?
2
Graphs of Functions
The graph of a function is the graph of its ordered pairs.
First find the ordered pairs, then graph the functions.
Graph the functions f(x)=-2x; g(x)=-2x+3
x
f(x)=-2x (x,y)
g(x)=-2x+3
(x,y)
-2
f(-2)=4 (-2,4)
g(-2)=7
(-2,7)
-1
f(-1)=2 (-1,2)
g(-1)=5
(-1,5)
0
f(0)=0
(0,0)
g(0)=3
(0,3)
1
f(1)=-2 (1,-2)
g(1)=1
(1,1)
2
f(2)=-4 (2,-4)
g(2)=-1
(2,-1)
See the next slide.
g(x)
y
f(x)
x
Example
Graph the following functions f(x)=3x-1
and g(x)=3x
y
x
The Vertical Line Test
y
y
x
The first graph is a function, the second
is not.
Example
Use the vertical line test to identify graphs in
which y is a function of x.
y
y
x
x
Example
Use the vertical line test to identify graphs in
which y is a function of x.
y
y
x
Obtaining Information
from Graphs
Example
Analyze the graph.
y
f ( x) x 2 3x 4
a. Is this a function?
b. Find f(4)
c. Find f(1)
d. For what value of x is f(x)=-4
Identifying Domain and Range
from a Function’s Graph
Math 112
Section 1.2
The domain of a function is the set of all x values for
which the function is defined.
x2
f(x) 2
x 4
Domain
x2 4 0
x 2, 2
( , 2) (2 , 2) (2 , )
f(x) 2x 6
Domain
2x + 6 0
2x 6
x 3
[3 , )
Math 112
Section 1.2
Finding the Domain & Range of a Function
The domain of a function is the set of all x values from the graph.
The range of a function is the set of all y values from the graph.
Domain: ( , )
Range: [1 , )
Identify the function's domain and range from the graph
y
y
Domain (-1,4]
Range [1,3)
x
Domain [3,)
Range [0,)
Example
y
Identify the Domain and Range from the graph.
Example
y
Identify the Domain and Range from the graph.
x
Example
y
Identify the Domain and Range from the graph.
x
Identifying Intercepts
from a Function’s Graph
y
Example
Find the x intercept(s). Find f(-4)
x
Example
y
Find the y intercept. Find f(2)
x
Example
y
Find the x and y intercepts. Find f(5).
x
y
Find f(7).
x
Find the Domain and Range.
y
x
2 x2 3
f ( x)
Find f(-1)
7
Example
Determine whether each equation defines y
as a function of x.
x 4y 8
x 2 2 y 10
x 2 y 2 16