procedure - Columbus Technical College
advertisement

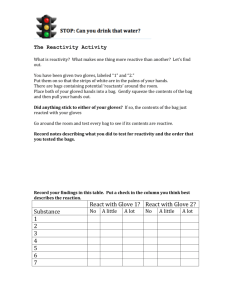
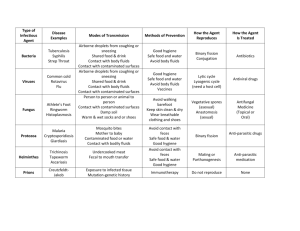
II. D. 3. a. Occupational Exposure to Blood Borne Pathogens OPR: Vice President of Operations STATEMENT: The Technical College System of Georgia has developed plans and established procedures to control exposure to blood borne pathogens to minimize or eliminate potential exposure by certain categories of faculty members and students in high-risk occupational training programs. Columbus Technical College shall have in place a state-approved Blood Borne Pathogen Exposure Control Plan designed to minimize or eliminate faculty and student occupational exposure to blood and other potentially infectious body materials in certain high-risk occupational training programs. PROCEDURE: Columbus Technical College maintains a state-approved Blood Borne Pathogens Exposure Control Plan and operates in compliance with State Board policy “Occupational Exposure to Blood Borne Pathogens” (II. D. 3. a.) adopted August 5, 1993 and last revised March 30, 2001. EXPOSURE CONTROL PLAN BODY FLUIDS AND BLOOD BORNE PATHOGENS General Information The body fluids of all persons should be considered to contain potentially infectious agents (germs). The term “body fluids” includes: blood, semen, drainage from scrapes and cuts, feces, urine, vomitus, respiratory secretions (e.g. nasal discharge) and saliva. Contact with body fluids presents a risk of infection with a variety of germs. In general, however, the risk is very low and dependent on a variety of factors including the type of fluid with which contact is made and the type of contact made with it. AVOID CONTACT WITH BODY FLUIDS Make sure that you assess the situation and use universal precautions. When possible, direct skin contact with body fluids should be avoided. Disposable gloves should be available for custodians, nurses, faculty/staff, and others who come in contact with body fluids. Gloves are recommended when direct hand contact with body fluids is anticipated. Hands should be washed after gloves are removed and gloves discarded in a biohazard bag. IF DIRECT SKIN CONTACT OCCURS Hands and other affected skin areas should be washed with soap and water immediately or as soon as possible after removal of gloves and after hand contact with blood.. Clothing and other non-disposable items that are soaked with body fluids should be placed in biohazard bags. Contaminated laundry items shall be handled with gloves. Disposable items should be handled with disposable gloves. REMOVAL FROM THE ENVIRONMENT The College should stock EPA registered absorbent agents specifically intended for disinfection of contaminated objects containing blood or body fluid spills. Disposable gloves should be worn when using these agents. The dry material is applied to the area, left for a few minutes to absorb the fluid, and then vacuumed or swept up. The vacuum bag or the material swept should be disposed of in a biohazard bag. Broom and dustpan should be washed in warm soapy water and rinsed and then disinfected by soaking in the EPA registered approved disinfectant that kills HIV/HBV. APPROVED DISINFECTANT Following the initial cleanup, one of the following shall be used for cleaning blood or O.P.I.M. Chemical germicides that are approved as hospital disinfectants and are tuberculocidal when used in recommended dilutions. Products registered by the U.S.E.P.A. as being effective against HIV with an accepted “HIV label” A solution of 5.25% sodium hypochlorite (household bleach) diluted with water between 1:10 to 1:100 strength. This solution should be mixed fresh on a daily basis. HAND WASHING PROCEDURES Proper hand washing requires the use of anti-microbial skin cleaner or soap and water. Wet the hands first, then apply the anti-microbial skin cleaner/soap. Scrub the hands for ten seconds to a minute. Then rinse hands and dry thoroughly. Use towel to turn off water. Do not touch faucet with hands. Clean contaminated surfaces with warm soap and water and rinse thoroughly. Apply disinfectant solution of Clorox 1:10 or an EPA registered hospital level disinfectant to surfaces contaminated with body fluids. Let the area air dry for 24 hours. DISINFECTION OF HARD SURFACES AND CARE OF EQUIPMENT After removing the soil, sanitize the area with warm soap water and rinse. Apply the approved disinfectant. Mops should be washed thorough with warm soap and water and rinse thoroughly and then soaked in the approved disinfectant and rinsed thoroughly or washed in a hot water cycle with bleach before rinse and then disinfected in approved disinfectant. Non-disposable cleaning equipment should be thoroughly washed in warm soapy water and rinsed and the disinfected in the approved disinfectant. The disinfectant solution should be disposed of down a drainpipe and sink thoroughly cleaned. 1. Cleaning—All instruments should be rinsed and scrubbed prior to disinfections and/or sterilization to remove fluids, tissue or other materials that may have become embedded in the instrument. 2. Disinfection-After they have been cleaned, instruments may be disinfected by soaking in an approved disinfectant. They should soak for at least the minimum time specified by the manufacturer of the solution. The solution should be changed at the frequency recommended by the manufacturer to assure the effectiveness of the disinfection process. 3. Sterilization- After they have been cleaned, instruments may also be soaked in a disinfecting solution prior to sterilizing solution or in an autoclaving instrument. 4. Equipment disinfection summary-Equipment that may have become contaminated with blood or other potentially infectious materials shall be examined and decontaminate with an appropriate disinfectant. DISINFECTION OF RUGS Apply sanitary EPA approved disinfectant for blood borne pathogens absorbent agent, let dry, and vacuum. If necessary, mechanically remove with dustpan and broom, then apply a rug shampoo (a tuberculocidal disinfectant) with a brush and re-vacuum. Wash dustpan and broom in soap and water and then rinse dustpan and broom thoroughly before immersing in approved disinfectant. Leave for time recommended by manufacture. DISPOSAL OF BIOHAZARD MATERIALS 1. Handling of blood and other potentially infected body fluids: Please use Universal Precautions at all times when dealing with blood or body fluids. Any material (e.g., cloth, gauze, paper product) that is contaminated with visible blood shall be placed in a small red bag labeled Biohazardous and tied securely. Place the small biohazard bag in the larger red bag that lines the corrugated box provided by the company authorized by Columbus Technical College to pick up and dispose of Biohazardous waste. This box should be placed in an area that has limited access. The specific directions for placing contaminated items in the box will be posted near the box that contains the biohazard red bag that meets federal, state, and local regulations. When the box is full or there is a concern about contents that might cause an unpleasant odor, contact the Director of Plant Services. If the box needs to be picked up, it will be necessary to follow the directions for taping or sealing the box before it is picked up. Tracking labels will be used for liability purposes in the event that a pick up is necessary. Excluded material includes sanitary products. 2. Sharps must be placed in special puncture resistant containers provided by the Company authorized by Columbus Technical College. Sharps include needles, broken glass contaminated with blood, scalpel blades, pins, and any other objects, which could potentially pierce a plastic bag. The sharps container should be kept in a secure location in the office and/or area where sharps are used on a regular basis. Sharps containers will be made available through COLUMBUS TECHNICAL COLLEGE. When the container is full, it should be placed in the biohazard bag that lines the corrugated box (see item 1) provided by the company authorized by Columbus Technical College to pick up and dispose of Biohazardous waste. 3. Latex gloves should be made available to all employees. Each building should implement a plan for making sure all Faculty/Staff know where the gloves are located. If gloves are used and thus contaminated with body fluid, they should be placed in the biohazard red bag discussed in item 1. 4. Small red bags labeled "Biohazardous" should be available in areas considered by The College to be most logical for regular use. However, all category I and II occupational programs will have PPE kits located in respective classrooms and additional bags will be place in convenient locations on campus. Each College car or van should be equipped with appropriate PPE kits. Note: For more information, refer to the College’s Occupational Exposure to Bloodborne & Airborne Pathogens Standards. Cross Ref: 03-17.html Adopted: Revised: Revised: SBTAE POLICY II. D. 3. a. August 1993 March 30, 2001 October 2002 https://tcsg.edu/tcsgpolicy/docs/04-