Acute Renal Failure
advertisement

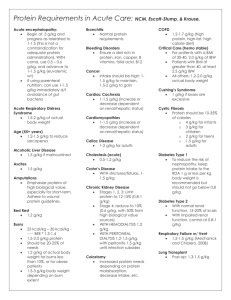
Taryn Berry Medical Nutrition Therapy Diet-Acute Renal Failure 1. Purpose a. Nutrition Indicators-screening the individuals should be the first step of nutrition assessment, both subjective and objective components. This includes anthropometric measures and physical examination (height, weight, presence of edema), biochemical data (serum, BUN, GFR, cholesterol, calcium, phosphorus, intake/output), and nutrition (usual intake, 24 hour recall, chewing/swallowing ability) and medical history (disease state, treatment, nutrition implications, medication interactions). b. Criteria to Assign the Diet-weight indicators (percent IBW, unintentional weigh change, edema/fluid loss), alimentation indicators (decrease P.O. intake, TPN/PPN/TF, nausea/vomiting/anorexia/ileus), biochemical indicators (hypoalbuminemia, trend of electrolytes), clinical indicators (etiology of renal failure, comorbid conditions, recent surgery, ventilator support, renal replacement therapy, medication) c. Rationale for Diet-nutrition consultation is indicated if enteral or parenteral nutrition is prescribed. Risk factors for protein-energy malnutrition in acute renal failure increase in certain states and should be monitored. 2. Population a. Overview-Acute renal failure occurs in approximately 20% of the patients admitted into the intensive care unit because of complications following sepsis, trauma, or multiple organ failure. For acute renal failure, Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy (CRRT) is used in some cases. This form of dialysis is used to slowly remove fluids and solutes, as well as, correct electrolyte and metabolic abnormalities. There are two different kinds of CRRT, arteriovenous renal replacement therapies and venovenous renal replacement therapies based on the patients blood pressure. b. Disease Process- Acute renal failure, or acute renal injury, is often a response to sepsis, trauma, or multiple organ failure. There are three stages of acute renal failure, prerenal, intrarenal, and postrenal. The prerenal stage is when something decreases blood flow to the kidney, decreasing the glomerular filtration rate. The intrarenal stage is when part of the kidney is damaged. The postrenal stage is when a crystal or other structure is obstructing urine flow. The dialytic method depends on the situation. In any stage, the kidneys lose the ability to create urine and filter the body’s waste. This can cause dangerous levels of waste to accumulate and affect the chemical makeup of the blood. c. Biochemical and Nutrient Needs-Protein intake should be adjusted according to the following, clinical condition, degree of catabolism, extent of impairment of renal function, and whether renal replacement has been started. Electrolytes should be monitored to avoid refeeding syndrome and vitamin/mineral should also be monitored to maintain within the acceptable range. 3. General Guidelines a. Nutrition Rx Protein: 0.8-1.2 g/kg of bodyweight without dialysis; 1.2-1.5 g/kg bodyweight catabolic. Energy: 25-35 kcal/kg of bodyweight depending on stress/status of nutrition. Sodium: 2-3 g/day based on blood pressure, edema-replace in diuretic phase. Potassium: 2-3 g/day- replace in diuretic phase. Phosphorous: 8-15mg/kg Calcium: maintain serum value with normal limits Fluid: 500 cc + urine output. Vitamins/Minerals: use DRIs and adjust to catabolic amounts. b. Adequacy of Nutrition Rx- nutrition support might improve prognosis, but has not been confirmed. Negative nitrogen balance indicates that the patient should be provided with optimal nutrients. c. Goals-Include eliminating the cause of kidney failure, prevent further damage, support kidneys and other affected organs, provide adequate protein and energy, preserve lean body mass, prevent deficiencies, maintain/improve electrolyte and fluid imbalance, manage anemia, reassess drugs, promote recovery. d. Does it Meet DRI-if given the correct amount of nutrients, as stated above, the DRI values should be met. Based on dialysis losses, inadequate intake, drugnutrient interaction, and increased needs, supplements should be given. 4. Education Material a. Nutrition Therapy-it has not been proven that nutrition support helps in the recovery of renal function or survival but its has supporting evidence to suggest it is beneficial in those with acute renal failure. Preventing and minimizing malnutrition by providing adequate amounts of protein, calories, and other nutrients is necessary. b. Ideas for Compliance-focusing on one nutrient at a time, providing daily meal plans, providing lists of foods that are low or high in a specific nutrient of interest, be positive, be accessible to patient, and explain the benefits of following the new diet. 5. Sample Menu a. Foods Recommended Low potassium: apples, blackberries, grapes, pineapple, celery, corn, onions, pasta, bread, rice. b. Foods to Avoid Limit phosphorous: phosphorous containing food include seeds, nuts, cheese, pork, shellfish, soy foods, beans, and salmon Avoid added salt: tv dinners, bagged foods (ex. chips, pretzels), canned soup, and fast food. c. Example of a meal plan Breakfast-toast with butter, 1egg, apple juice. Snack-Mixed berry smoothie. Lunch-Grilled chicken sandwich, celery and peanut butter. Snack- Grapes. Dinner-Mixed green salad (lettuce, cucumber, onion, low sodium dressing), quesadilla with peppers, eggplant, and corn. Snack-Dairy free ice cream 6. Websites a. Organizations with Websites American Kidney Fund- http://www.kidneyfund.org/ DaVita- http://www.davita.com/ The National Kidney Foundation- https://www.kidney.org/ b. Government Websites MedlinePlushttp://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/000501.htm National Kidney Disease Education Programhttp://nkdep.nih.gov/resources/eating-right-508.pdf 7. References a. Journal articles references Nutrition Care Manual. “Acute Renal Failure.” https://www.nutritioncaremanual.org/topic.cfm?ncm_category_id=1&lv1=5537&lv2=25 5347&ncm_toc_id=23011&ncm_heading=Nutrition%20Care “Acute Kidney Failure: Lifestyle and Home Remedies.” Mayo Clinic. http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/kidney-failure/basics/lifestyle-homeremedies/con-20024029